Outlook maintains a local cache of your mailbox items in an Offline Storage Table (OST) file, also referred to as an Offline Outlook Data file, at a default location on the local storage. This helps improve Outlook performance and allows you to quickly access the mail items, even if the system is offline, not connected to the main server, or on a poor network connection.
With usage, your local cache may grow larger to an extent where it may become harder for Outlook clients to store more or process information to or from the cache. This occurs due to resource crunch (RAM, storage, and processor) and inconsistencies, leading to common Outlook performance issues, such as:
- Outdated mailbox
- Delay in sending or receiving emails
- Slow or no search results for your queries
- Outlook takes time to start
- Sync issues between Outlook client and webmail
These are some early signs of local cache problems that may further lead to inaccessible cache and loss of mail items. In addition, the following events can also cause damage to your local cache leading to Outlook errors.
- Unexpected shutdown, Outlook freeze, or system crash
- Forced Outlook app termination
- Incompatible or faulty add-ins
- Storage drive issues or file system errors
- Corrupt mail item
- A large number of folders/subfolders in the mailbox or mail items per folder
- Low mailbox or local storage
However, you can prevent such a situation and fix these issues by resetting the local cache of your Exchange, Outlook.com, Office/Microsoft 365, or IMAP email account configured in Outlook 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, or 2021.
Why Reset Local Outlook Cache?
Resetting the local Outlook cache is required to resolve common Outlook performance issues and errors, such as:
Steps to Reset Local Cache of Exchange, Outlook.com, or IMAP Account
There are two types of cache stored by Outlook at the default location, i.e., %localappdata%\Microsoft\Outlook.
- Offline Folders (OST)
- RoamCache Folder
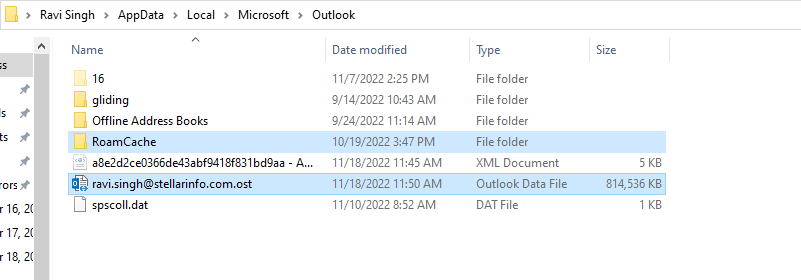
The file with .ost extension is the offline local cache that stores all mail items, such as emails, contacts, attachments, notes, tasks, calendar items, etc. On the other hand, the RoamCache folder stores extracted properties of your mailbox, such as addresses that you have sent an email to previously, to improve Outlook performance and reduce disk and resource usage.
You can reset both caches of your Exchange, Outlook.com, Office/Microsoft 365, or IMAP email account to troubleshoot and fix errors or Outlook performance issues.
Reset RoamCache
To reset the Outlook RoamCache, follow these steps:
- Close Outlook.
- Press Windows + R and type %localappdata%\Microsoft\Outlook\RoamCache.
- Press the Enter key or click OK. This opens the RoamCache folder stored in the default directory where Outlook stores all caches.
- Select all the files in the RoamCache folder and delete them. You don’t need to back up RoamCache before deletion.
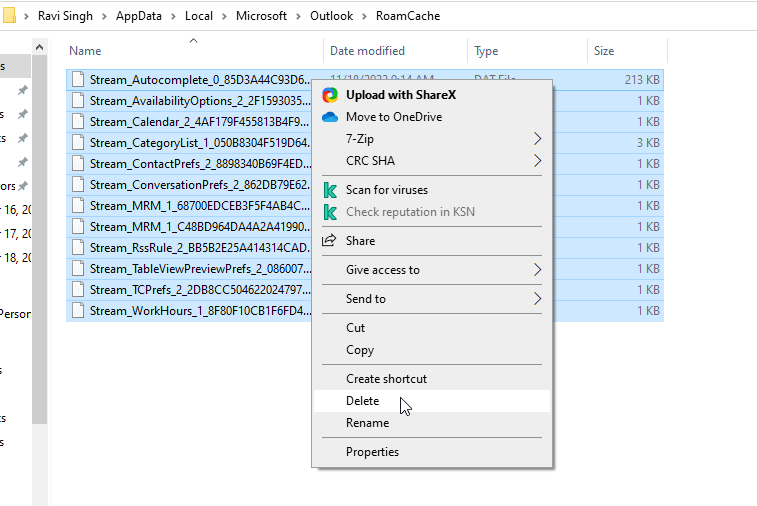
- Start Outlook. This will recreate and reset the RoamCache, which may help fix issues and improve Outlook performance.
Reset Offline Folders Cache (OST)
Follow these steps to reset Offline Folders (OST) or cache of your mailbox from your local storage to fix the issues and errors you are encountering with Outlook.
- Close Outlook.
- Press Windows + R, type %localappdata%\Microsoft\Outlook, and press the Enter key or click OK.
- Look for the OST file that belongs to your Exchange, Outlook.com, Microsoft/Office 365, or IMAP email account.
- Copy the .OST file to a different folder, volume, or external media for backup.
- After the backup, right-click on the .OST file and choose Delete.
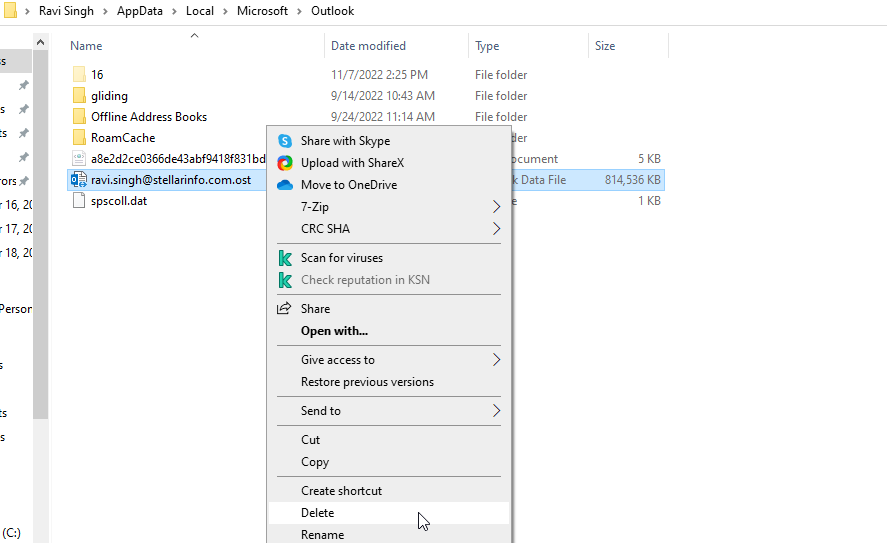
- Once the .OST cache file is deleted, start Outlook.
- Outlook will create a new .OST cache at the same location, download (synchronize) all mail items from the mailbox server and update all mail folders.
- This can take a while to complete based on your mailbox size and network speed.
After resetting the local cache and synchronization, check your mail folders and mail items. If you could not find some mail items, subfolders, or folders, they were not synced to the mailbox server. However, you can use an OST to PST converter tool, such as Stellar Converter for OST, to extract the missing mail items from the backup OST file and save them in Outlook importable PST format. You can then import this PST into your Outlook via Import/Export wizard and restore the missing folders, subfolders, and mail items.
Conclusion
A partially damaged or inconsistent Outlook local cache can lead to Outlook performance issues. Damage to the local cache can lead to various issues, such as sending or receiving errors, missing mail items, outdated mailbox, slow Outlook performance, synchronization-related issues, etc. If you encounter such issues or a slowdown in Outlook performance, you can try to reset the local cache (Offline Outlook data file) by following the steps discussed in this article. But before you reset the local cache (.OST) of your Exchange, Microsoft 365, Outlook.com, or IMAP account, backup your mail items to PST via Outlook Import/Export wizard to avoid data loss. However, if you can’t access the Outlook account or find missing folders, subfolders, or mail items, use an OST to PST converter to extract mail items from your backup or inaccessible/orphaned OST file.
Was this article helpful?