The indexes in the SQL Server database may get corrupted due to different reasons. When the indexes are corrupt, you may see any of the following error messages:
Error: 823, Severity: 24, State: 2.
The operating system returned error 38 to SQL Server during a read at offset 0x016I64x in file ‘c:\data\stellar.mdf’. Additional messages in the SQL Server error log and system event log may provide more detail. This is a severe system-level error condition that threatens database integrity and must be corrected immediately. Complete a full database consistency check (DBCC CHECKDB). This error can be caused by many factors; for more information, see SQL Server Books Online.
Error 824, Severity: 24, State: 2.
SQL Server detected a logical consistency-based I/O error: incorrect pageid (expected 12345; actual 67890) in database ‘stellardb’, file ‘YourFileName.mdf’, page 1234. It occurred during a read of page 1234 in database ID 5 at offset 67890 in file ‘stellardb.mdf’. Additional messages in the SQL Server error log or system event log may provide more detail.
Error 832:
“A page that should have been constant has changed (expected checksum: 0xABCDEF, actual checksum: 0x123456) in database ‘stellardb’, file ‘stellardb.mdf’, page 5678. This usually indicates a memory or disk problem. Please contact technical support.”
Below, we will see how to detect index corruption in SQL Server database and how to fix the index corruption.
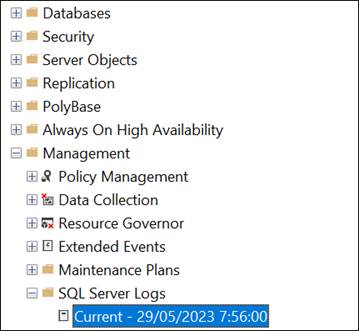
You can see the above error messages in the SQL Server Log. In SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), go to the Object Explorer and then go to Management > SQL Server Logs. Open the logs and you will see the error messages, including the 823, 824, and 832.
Alternatively, you can use the xp_readerrorlog command in T-SQL. This system stored procedure reads the SQL Server error log.
The following example illustrates how to use this command:
EXEC xp_readerrorlog 0, 1, N’disk problem’
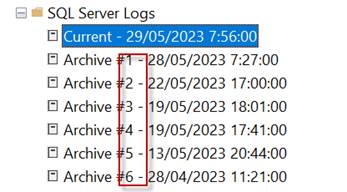
The command will look for disk error messages in the error log. In SQL Server, there are several error logs. The ‘0’ indicates the current one and others from 1 to 6 by default.
The number 1 means that you want to read the SQL Server log file.
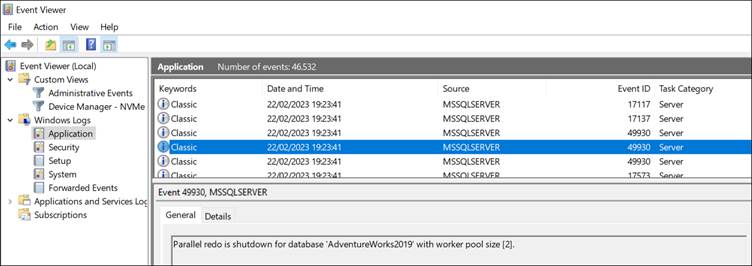
In Windows, the Event Viewer is used to check errors in the Windows operating system, the application, and security events. SQL Server is not the exception.
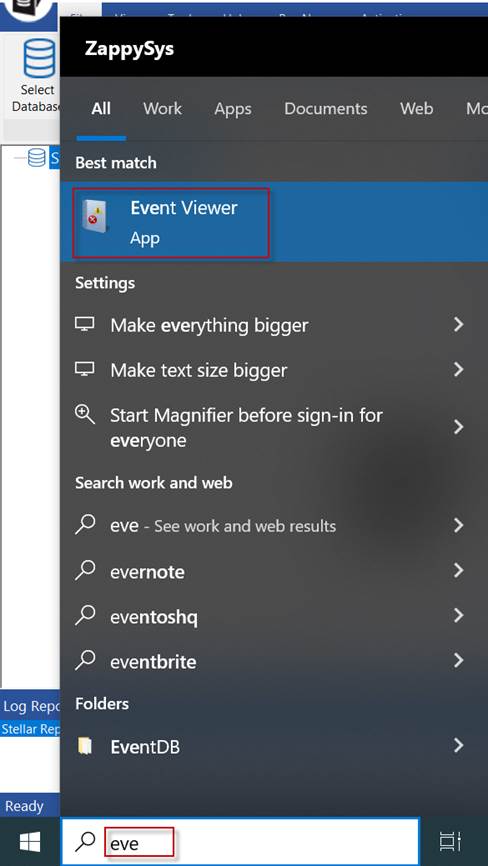
You can open the Event Viewer in Windows, write the word event, and click on the Event Viewer.
Then, go to Windows Logs > Applications.
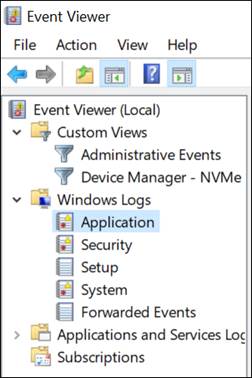
Here, you can look for the error messages.
The DBCC CHECKDB command can detect not only general error messages in the database but also errors in the indexes.
The following DBCC CHECKDB command will detect errors in the database including the index errors.
DBCC CHECKDB(‘stellardb’)
If you want to exclude informational messages, you can use the following command.
DBCC CHECKDB(‘stellardb’) WITH NO_INFOMSGS;
There is another option to see the errors in table format. The following example shows how to do it:
DBCC CHECKDB(‘stellardb’) with TABLERESULTS;
Methods to Repair Index Corruption in SQL Server Database
Here are some methods you can follow to fix index corruption in SQL database.
The DBCC CHECKTABLE is useful to repair index corruption if just a single index is damaged and you do not want to repair the entire database. The following command will check for errors in a table, named Person.PersonPhone:
DBCC CHECKTABLE(‘[Person].[PersonPhone]’);
To repair the table, you need to set it in single-user mode first. The following code shows how to do it:
ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorks2019]
SET SINGLE_USER WITH ROLLBACK IMMEDIATE;
Once it is in single-user mode, run this code to repair the table and the index:
DBCC CHECKTABLE(‘[Person].[PersonPhone]’, REPAIR_REBUILD);
If you want to repair the table fast, you can use the following command:
DBCC CHECKTABLE(‘[Person].[PersonPhone]’, REPAIR_FAST);
If the above commands fail, you can use the following command:
DBCC CHECKTABLE(‘[Person].[PersonPhone]’, REPAIR_ALLOW_DATA_LOSS);
You can also use a third-party SQL database repair tool, such as Stellar Repair for MS SQL to repair the corrupt SQL Server database indexes. To repair the database using the software, follow these steps:
- Install the software.
- Take the database offline.
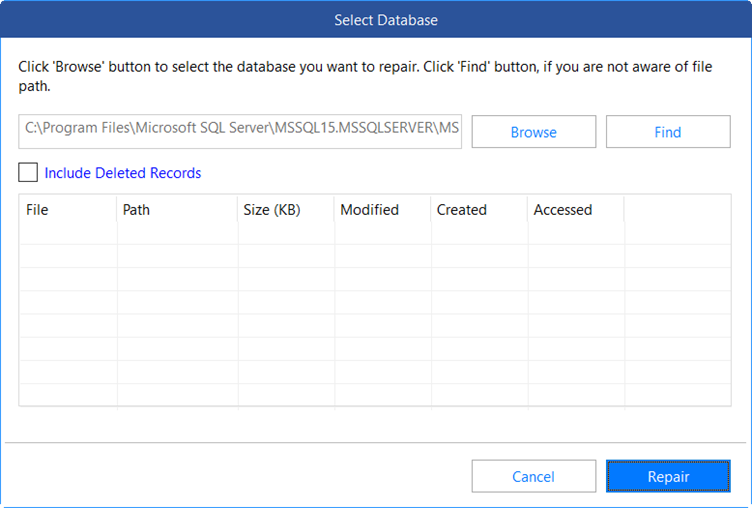
- Select the database file you want to repair (you can use the Find button if you do not know where the file is stored).
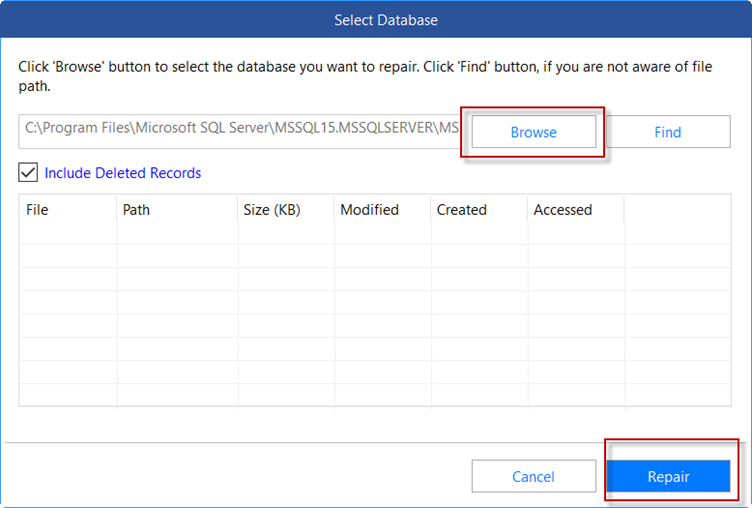
- Once selected, press the Repair button.
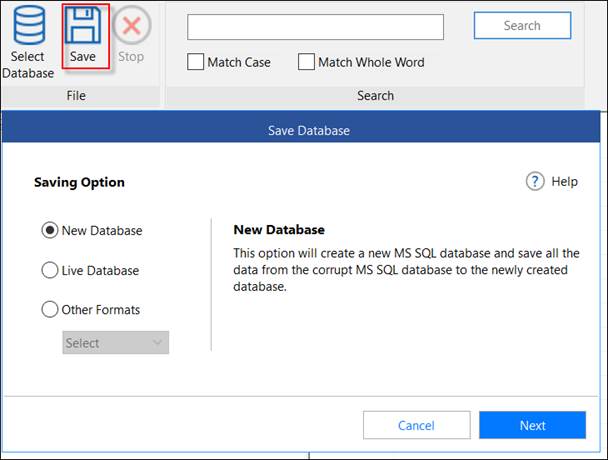
- After repair, you can save the data in a new/live database or in other formats like CSV, HTML, and Excel.
In this article, we have mentioned different ways to detect index corruption in SQL Server databases. You can detect the problem using the SQL Server Log, the Event Viewer, and the DBCC commands. We have also mentioned how to repair index corruption in SQL databases using the DBCC CHECKDB and DBCC CHECKTABLE commands. In case these options fail, then you can repair the corrupt database using Stellar Repair for MS SQL and recover all the data.
Was this article helpful?