In SQL Server, you can use the DELETE statement with WHERE clause to delete specific records in a table. Sometimes, while executing the command, you fail to mention the WHERE clause. This can result in the deletion of all the records in the table. It might also happen that you’ve specified the incorrect WHERE clause, resulting in the deletion of some important records from the table, which you don’t want to delete. However, you can easily recover such deleted table records in SQL Server. In this post, we will discuss different methods to recover deleted records from table.
Methods to Recover Deleted Table Records in SQL Server
You can follow the given methods to recover the deleted records in MS SQL Server.
Method 1 – Use Log Sequence Number (LSN)
If you know the time when the record is deleted, then you can use the Log Sequence Number (LSN) to recover the deleted rows and their records from a SQL database table. LSN is a unique identifier given to each record in a transaction log. You can construct restore sequences by using the LSN of a log record.
Note: This method will only work if you’ve a healthy Transaction Log backup.
To understand how to use the LSN to recover deleted table records, we’ll create a test database and a table, insert rows into the table, delete some rows using the DELETE operation, get information about the deleted data, and then recover the data using LSN.
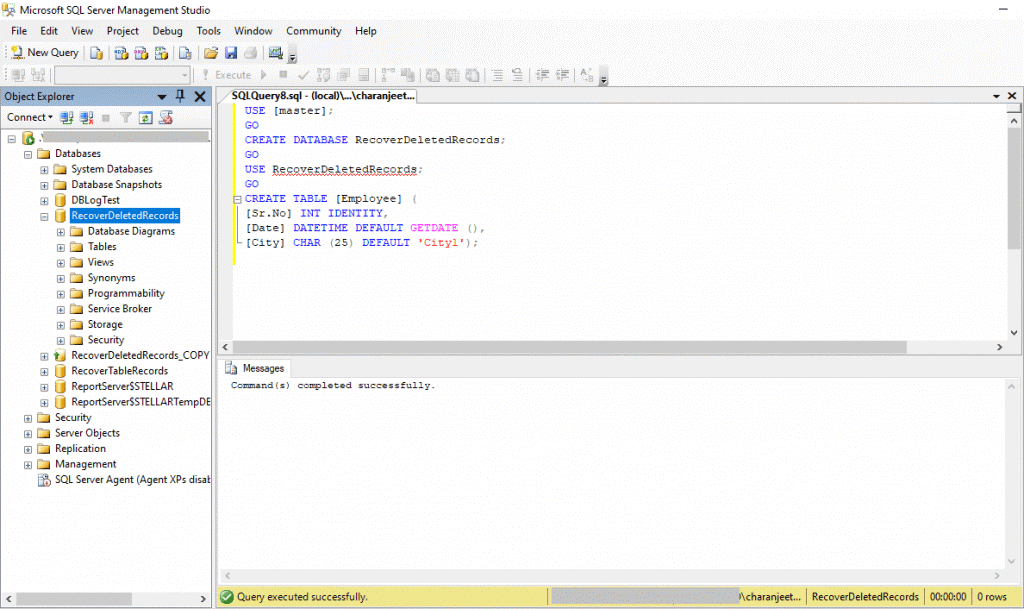
Step 1: Create a Database
By executing the following query, we will create a database named ‘RecoverDeletedRecords’ and a table named ‘Employee’ with three columns:
USE [master];
GO
CREATE DATABASE RecoverDeletedRecords;
GO
USE RecoverDeletedRecords;
GO
CREATE TABLE [Employee] (
[Sr.No] INT IDENTITY,
[Date] DATETIME DEFAULT GETDATE (),
[City] CHAR (25) DEFAULT 'City1');
Step 2: Insert Data into the Table
Now, we’ll insert rows into the table by running the following query:
USE RecoverDeletedRecords;
GO
INSERT INTO Employee DEFAULT VALUES;
GO 100
Step 3: Delete Rows from the Table
Now, we will delete some rows from the table (named Employee) by executing the following:
USE RecoverDeletedRecords
Go
DELETE Employee
WHERE [Sr.No] < 10
GO
Select * from Employee
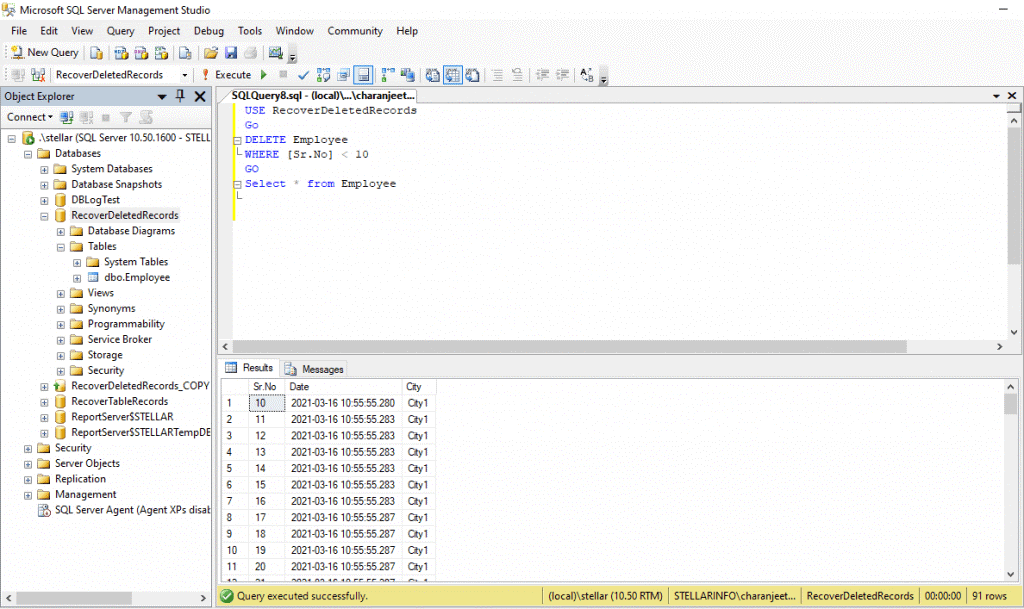
All the rows having Sr. No less than 10 will be deleted from the table ‘Employee’ (see the above image).
Step 4: Get Information about Deleted Rows
Next, we will get information about the deleted rows by searching the transaction log by executing the below query:
USE RecoverDeletedRecords
GO
SELECT
[Current LSN],
[Transaction ID],
Operation,
Context,
AllocUnitName
FROM
fn_dblog(NULL, NULL)
WHERE
Operation = 'LOP_DELETE_ROWS'
After getting the Transaction IDs of the deleted rows, we’ll have to find the time when the rows were deleted.
Step 5: Get Log Sequence Number of the LOP_BEGIN_XACT Log Record
To find the exact time when the rows were deleted, we will use the transaction ID to get the LSN of the LOP_BEGIN_XACT log record of a transaction:
USE RecoverDeletedRecords
GO
SELECT
[Current LSN],
Operation,
[Transaction ID],
[Begin Time],
[Transaction Name],
[Transaction SID]
FROM
fn_dblog(NULL, NULL)
WHERE
[Transaction ID] = '0000:0000020e'
AND
[Operation] = 'LOP_BEGIN_XACT'
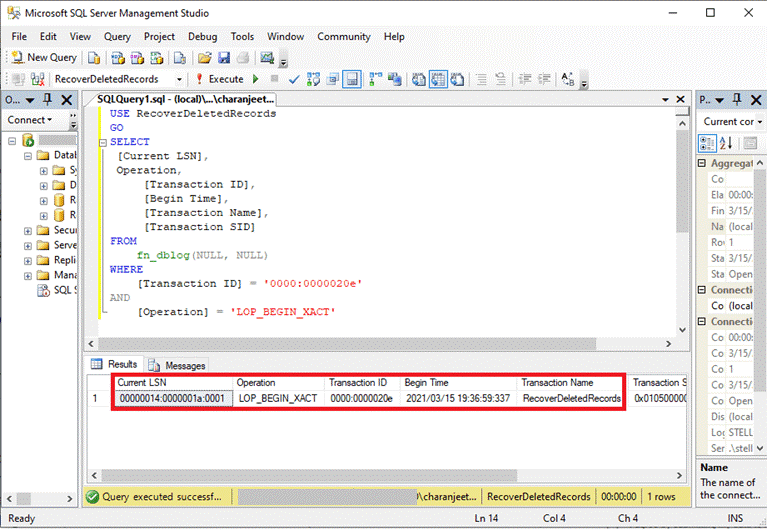
The above command will show the current LSN of the transaction, the time (2021/03/15 19:36:59:337) when the DELETE statement was executed, LSN (00000014:0000001a:0001), and Transaction ID (0000:0000020e).
Step 6: Recover Deleted Records
To recover the deleted SQL table records, we need to convert the LSN values from hexadecimal to decimal form. To do so, we need to add ‘0x’ before the log sequence number (see the below code).
--Restoring Full backup with norecovery.
RESTORE DATABASE RecoverDeletedRecords_COPY
FROM DISK = 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10_50.STELLAR\MSSQL\Backup\RecoverDeletedRecords.bak'
WITH
MOVE 'RecoverDeletedRecords' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10_50.STELLAR\MSSQL\Backup\RecoverDeletedRecords.mdf',
MOVE 'RecoverDeletedRecords_log' TO 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10_50.STELLAR\MSSQL\Backup\RecoverDeletedRecords.ldf',
REPLACE, NORECOVERY;
GO
--Restore Log backup with STOPBEFOREMARK option to recover exact LSN.
RESTORE LOG RecoverDeletedRecords_COPY
FROM
DISK = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10_50.STELLAR\MSSQL\Backup\RecoverDeletedRecords_tlogbackup.trn'
WITH
STOPBEFOREMARK = 'lsn:0x00000014:0000001a:0001'
Now that the data is restored, we need to check whether the deleted records have been recovered. The following query will show the first 10 rows of the table that were deleted (in Step 3).
USE RecoverDeletedRecords_COPY
GO
SELECT * from Employee
Method 2 – Use a MS SQL Database Recovery Software
If the above method fails to recover the deleted records or you don’t have backup, you can use a third-party SQL database recovery software, such as Stellar Repair for MS SQL. It is an advanced SQL repair software that can help you to quickly recover deleted records from the database file in a few clicks. The software can also recover other objects, like views, triggers, stored procedures, etc. from corrupted or damaged database files. The tool supports all Windows editions, including the latest Windows 11.
Steps to Recover Deleted Table Records using Stellar Repair for MS SQL:
- Download, install, and launch Stellar Repair for MS SQL software.
- On the software’s main interface, you’ll see a prompt to stop SQL Server database and create a copy of the database at a different location. Press OK.
- Click Browse to select the SQL database (MDF) file from where you want to recover the deleted records. If you do not know the location of MDF file, click Search to find the file.
- After selecting the database file, click the Include Deleted Records option and then click Repair.
- Select the appropriate scan mode – ‘Standard Scan’ or ‘Advanced Scan’ and then click OK.
- Click OK when the ‘Repair Complete’ message box appears.
- The software shows preview of all the recoverable items. You can look for the table records marked as deleted.
- Next, select the items (deleted records) you want to save and click Save on the File menu.
- In ‘Save Database’ dialog box, you can choose to save the recovered data in MDF, CSV, HTML, or XLS (Excel) file format. Then, click Save.
Watch the complete working process of the SQL Recovery software:
Conclusion
Above, we have discussed the methods to recover deleted records in SQL Server. If you’ve the database backup available and know the time of deletion of records, then you can use the transaction log with Log Sequence Number (LSN) to regain access to the deleted records. If this method doesn’t work or if your backup file is corrupted, then you can use Stellar Repair for MS SQL to recover the deleted data from the SQL Server database file. This tool not only helps in recovering deleted records but also restores all the data from the damaged or corrupted SQL database file.
FAQ:
Was this article helpful?