While managing the Exchange database or mailboxes, if you have accidentally deleted, removed, or disconnected a mailbox from the mailbox database (.edb), you can recover and restore the Exchange 2013 deleted mailbox using PowerShell cmdlets unless the retention period is over.
Unfortunately, the Exchange Server permanently purges a deleted mailbox after the retention period, making it quite difficult to recover a deleted, removed, or disconnected mailbox.
What Happens When You Delete An Exchange Mailbox?
When an administrator deletes a mailbox from the Exchange Server via Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or PowerShell cmdlets, it’s not physically or permanently deleted.
Exchange Server puts such mailboxes in the disconnected mailbox location. Think of it like the Recycle Bin for your deleted Exchange Server mailboxes. The only difference is that any deleted or removed mailbox in the disconnected mailbox section which is older than 30 days will be automatically and permanently deleted from the Exchange Server database.
This retention period can be quickly changed by editing the mailbox database policy. For this,
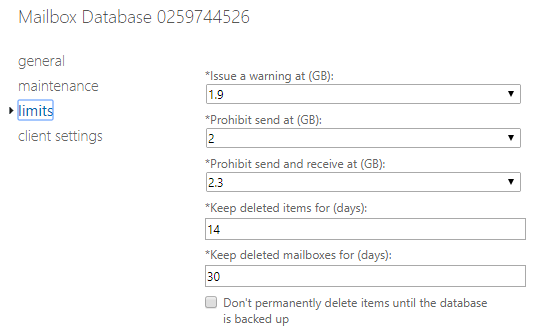
- Go to servers > databases and double-click on the mailbox database to open the properties.
- On the limits tab, change the “Keep Deleted Mailboxes for (days):” value with the number of desired days. The value is 30 days by default, as shown in the screenshot below.
Steps to Restore Exchange 2013 Deleted Mailbox
Below we have discussed two ways to restore or connect a deleted or disconnected Exchange 2013 mailbox.
- Restore deleted mailbox using Exchange Admin Center (EAC)
- Restore deleted mailbox using PowerShell cmdlets in Exchange Management Shell (EMS)
Though we recommend the PowerShell cmdlets to restore or reconnect a deleted or disconnected Exchange 2013 mailbox, you may follow any. You may also follow these instructions to restore Exchange Server 2016 or Exchange Server 2019 deleted mailbox.
Restore Exchange 2013 Deleted Mailbox via PowerShell Cmdlets (EMS)
To restore a deleted or disconnected Exchange 2013 or later mailbox via PowerShell, you can use the Connect-Mailbox PowerShell cmdlet.
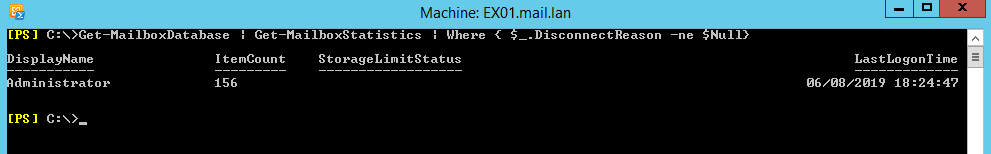
But before you can use the Connect-Mailbox cmdlet, you must know the deleted mailbox names. For this, open the Exchange Management Shell and use the Get-Mailboxdatabase combined with Get-MailboxStatistics PowerShell cmdlets to get a list of all the disconnected mailboxes in your Exchange Server environment.
Get-MailboxDatabase | Get-MailboxStatistics | Where { $_.DisconnectReason -ne $Null}
The result should be something like this.
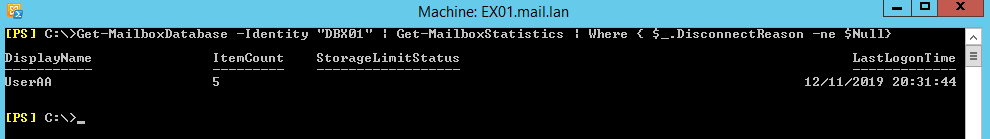
If you would like to get the disconnected mailbox for a specific Mailbox Database, you would need to update the command below to specify the name of the database.
Get-MailboxDatabase –Identity “DBX01”| Get-MailboxStatistics | Where { $_.DisconnectReason -ne $Null}
An issue you might encounter is that although there are disconnected mailboxes, running the command will return no mailboxes. PowerShell will not return mailboxes if you have configured an unmounted recovery mailbox database. The problem is that if you run it, no issues occur. The recovery database must be removed before checking this. When the recovery database is removed, the mailboxes will show.
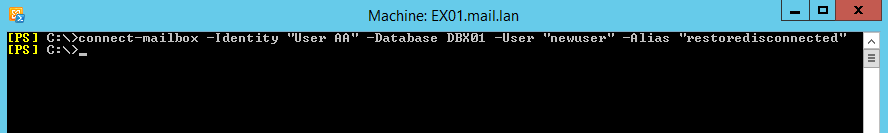
To connect a disconnected mailbox that was deleted or disabled, you would need to use the PowerShell cmdlet Connect-Mailbox. This can reconnect a user’s mailbox, link, room, or equipment.
Below is an example of the command
Connect-Mailbox –Identity "UserAA" –Database DBX01 –User "UserAA" –Alias "User.AA"
The –Identity is the Display Name of the disconnected mailbox, which can be retrieved from the previous command to get the disconnected mailboxes. The –Database is the database of where the mailbox resided. Finally, the –User and the –Alias are the Display Name and the Email Alias of the User in your Active Directory. The Alias parameter is not obligatory as if you leave it blank, the username is taken into account to create the email address of the reconnected mailbox.
After you have built up the command and executed it, you will get no message acknowledging the success of the process.
Then if you refresh the view in your Exchange Admin Center under the recipient’s node, you will see the newly restored mailbox attached to the Active Directory user you specified in the command
A note to consider when doing this is that the Active Directory user has been created beforehand. You will not be able to connect a mailbox without an existing user. It can be a new user who is not associated with the name, but it must exist if you run the command, it will just give you an error that the user does not exist.
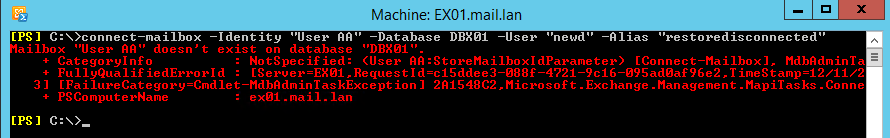
Another thing to consider is that when connecting to a disconnected mailbox user, the user cannot be disabled. Therefore, if you run the command trying to connect a mailbox and the user is not enabled, you will get an error stating that the User’s Active Directory account must be logon-enabled.
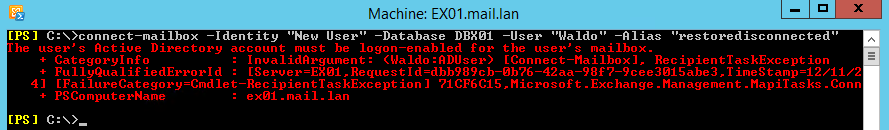
If you want to connect a linked mailbox, you need to use the same command but a little bit differently.
Connect-Mailbox -Identity "Deleted User 1" -Database DBX01 -LinkedDomainController SRV-ADC001 -LinkedMasterAccount deleteduser1@mail.lan –Alias deleteduser1
In the example below, the LinkedDomainController is the computer name of the domain controller, and the LinkedMasterAccount is the user who should be given the mailbox.
To connect a Shared Mailbox, you would need to use the same command as to connect a normal mailbox but add the –Shared parameter at the end as the example below
Connect-Mailbox –Identity "UserAA" –Database DBX01 –User "UserAA" –Alias "User.AA" -Shared
Once the mailbox is connected, you can use it and export it using the New-MailboxExportRequest cmdlet. So the steps to recover a deleted mailbox are:
- Having an enabled AD user to attach it to
- Run the Connect-Mailbox command
- Export to PST using New-MailboxExportRequest
Restore Exchange 2013 Deleted Mailbox via EAC (Optional)
If you don’t want to use PowerShell commands, you can use the EAC web interface to restore or connect a deleted or disconnected Exchange 2013 mailbox. The steps are as follows:
- In EAC, go to recipients > mailboxes and click on the more (…) icon.
- Click Connect a mailbox.
- This will display all the disconnected or deleted Exchange 2013 mailboxes.
- Click on the mailbox you need to restore from the list and click the Connect icon.
If the matching user isn’t found, click. No, I want to connect to a different user account.
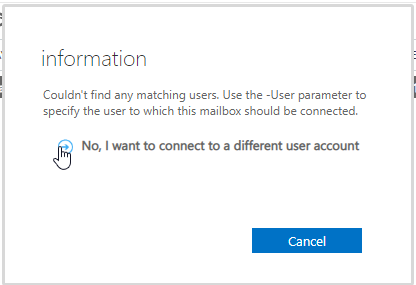
Choose User Mailbox or desired option from the list and click Next.
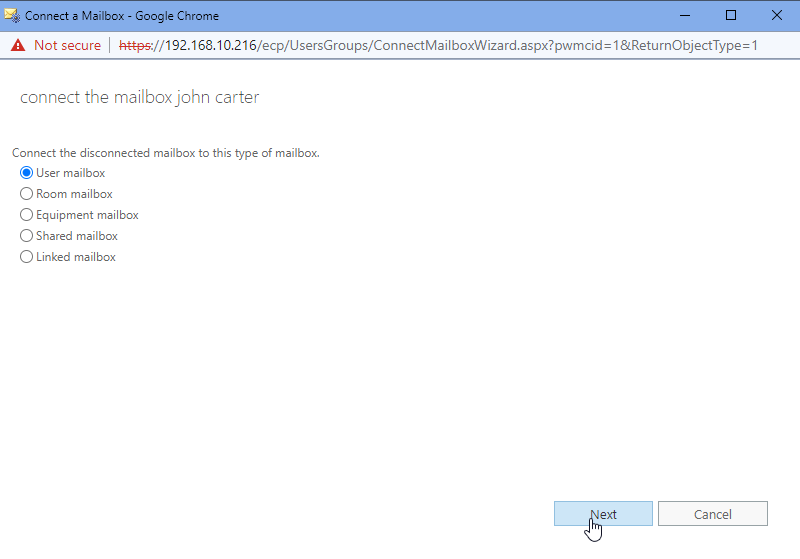
Click Browse to choose the user and click Finish. Make sure you have a user without a mailbox assigned. Create a new user account if required to connect to the mailbox.
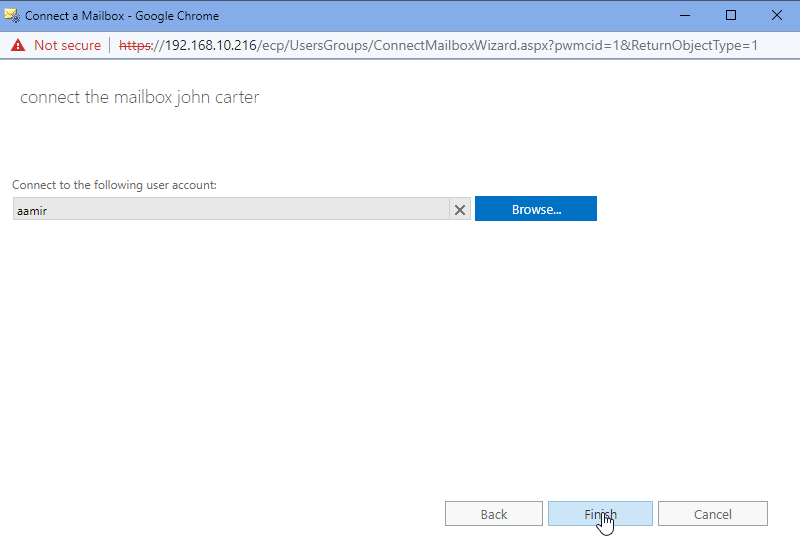
- The user to whom the mailbox is connected can now access the mailbox content.
To Conclude
If the PowerShell cmdlets do not help, you can use an application like Stellar Repair for Exchange to recover and restore deleted mailboxes from all Exchange Server versions as PST or export them to the Exchange database directly. With Stellar Repair for Exchange, you can choose the EDB file from where the mailbox was deleted and run repair to recover the deleted mailboxes and items. You can use filters or search to find a specific mailbox or mail items to export to PST and other formats. You may also export to Office 365 in just a few clicks.
Was this article helpful?