There’s been much talk about RAID, which stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. You must also be familiar with RAID levels based on three primary data storage mechanisms: Striping, Mirroring, and Parity. Some popular RAID levels include RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, and Nested RAID Levels – RAID 10, 50, and 60. These levels are fit to cater to unique data redundancy needs, thereby offering fault tolerance, except RAID 0, often used for speed and performance.
On the other hand, JBOD shares some similarities with RAID, but there are some crucial differences. In this guide, learn about JBOD vs. RAID, the key metrics that differentiate them, their uses, pros and cons, and more.
What is JBOD?
JBOD or Just Bunch of Disks or Drives, is a data storage architecture with multiple hard drives. It consists of multiple hard drives- Hard Disks and/or SSDs that store data through ‘Spanning.’
Spanning is a process in which when the drive in the array reaches its capacity, data starts getting stored on the next drive and so on throughout the entire unit in the array. Data doesn’t get split, mirrored, or collected as in RAID, thus storing data sequentially.
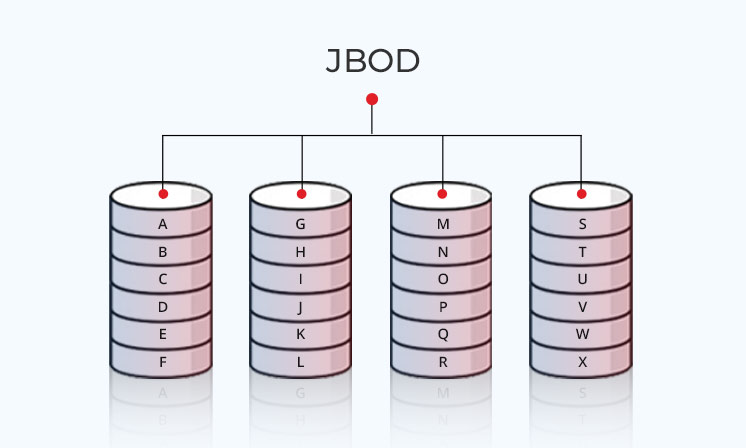
The drives in JBOD architecture can be
- Treated independently, or
- Combined in one or more logical volumes with an LVM (Logical Volume Manager) or
- Combined linearly through a “Spanning” file system like BTRFS
How is JBOD Used?
JBOD can be used in scenarios where
- Video Surveillance is needed
- Tape drives, which are typically used to cater to storage needs, are to be replaced
- Data needs to be archived and media storage is required
- Large data in the terabyte to petabyte range needs to be stored
- High availability is required (in terms of server)
- Data needs to be written quickly
The JBOD enclosure is not typically configured to act as RAID, but it can be set up in a server or RAID array with the correct host system technology.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of JBOD?
This seemingly simple configuration has some strengths and limitations.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Allows access to multiple drives by combining them through “Spanning.” | JBOD doesn’t offer data redundancy or fault tolerance. So, if a disk becomes inaccessible, data is permanently gone. |
| JBOD can store up to a petabyte of data using the 16TB enterprise capacity hard drives in 4U-JBOD. | Even though the read and write speed is quick, it still requires performance consideration because multiple drives act simultaneously. |
| It avoids wasting space and storage capacity by combining HDDs and SSDs of different sizes. | It is primarily used for storage, not data security, performance, and redundancy. |
| It offers independent and easy storage scaling, allowing up to 100 SAS/SATA drives to maximize density. |
| The data in JBOD is written sequentially, avoiding the complexity of data writing in RAID levels. |
| Easily integrates within existing or new RAID servers, supporting high online availability. |
What is RAID & How is RAID Used?
RAID is a virtualization storage technology that combines two or more hard drives in one logical unit to emphasize speed, performance, redundancy, or quick drive replacement in case of data loss from RAID.
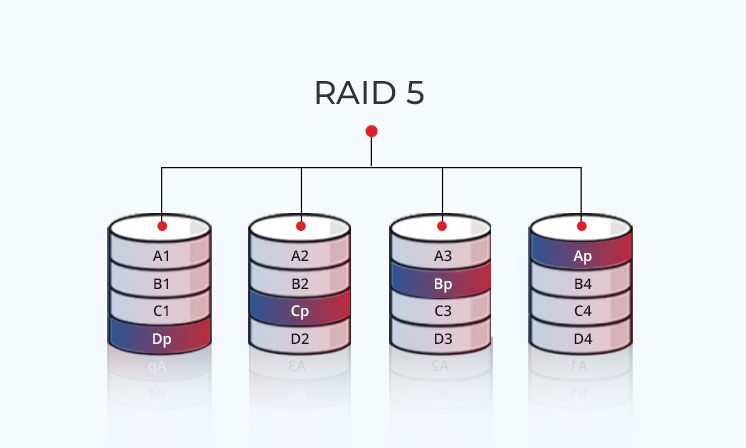
There are multiple RAID levels. However, the popular ones are RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and Nested RAID drives. All the RAID levels are based on Striping, Mirroring, and Parity mechanisms. In Striping (RAID 0), the data is split across multiple drives in the array, and Mirroring (RAID 1) replicates the data on additional disks.
Parity information (RAID 5 and RAID 6) collects data from all the drives in the array, offering fault tolerance. RAID allows you to choose the right level for your system, depending on your needs.
Key Differences of RAID vs. JBOD: Detailed Comparison
We’ve taken the below pointers as deciding factors for comparing RAID vs. JBOD. Read on to know more!
Data Protection
Aside from RAID 0, other RAID levels offer data protection through redundancy, meaning even if one drive fails, your data is still safe and can be recovered using powerful RAID recovery software.
On the contrary, JBOD consists of multiple drives and provides excellent storage capacity but no data protection. If any drive fails in the array, data will be lost.
Storage Capacity – Expansion
JBOD enclosure can combine HDDs and SSDs of different storage capacities and interfaces, including lightning-fast NVME SSDs, to ensure the maximum utilization of the drives’ storage space. It can add up to 100 SAS/SATA drives in the enclosure to maximize density, making it easily scalable.
While in RAID, you need to add drives or similar storage sizes to ensure less wastage of space. Additionally, RAID doesn’t cater to the significant storage requirements but speed, performance, and fault tolerance.
Speed & Performance
RAID offers performance enhancements with its data storage mechanisms, including Striping, Mirroring, and Parity. However, JBOD doesn’t provide any performance enhancement, as the drives in this configuration can be treated independently or combined in one large logical unit linearly through Spanning.
Moreover, JBOD writes and reads data on drives sequentially, especially using non-volatile memory express SSDs. Yet, RAID serves comparatively better and offers data security.
Cost
RAID controllers can be expensive due to additional hardware and storage space required for redundancy, depending on the level and hard drives included in the array.
However, SATA disks and controllers used in JBOD are comparatively cheaper since they lack data redundancy and no additional hardware requirements. Hence, making it an affordable option for storing extensive data.
Data Recovery from JBOD vs. RAID
While comparing JBOD vs. RAID in terms of data recovery, there is a fundamental difference, discussed as follows:
With JBOD, your data remains on the single stand-alone hard drive and continues to be added to additional drives in the enclosure. If one drive fails in the enclosure, the data will be lost. However, the data can still be recovered, but that depends on how the OS manages the drives. Considering this factor, JBOD recovery could be difficult.
While RAID offers data redundancy (except RAID 0) through the Mirroring and Parity mechanism, data recovery can be easily performed by hot-swapping, backup, or with the help of an advanced RAID data recovery software, such as Stellar Data Recovery Technician. The DIY software can virtually rebuild the logically damaged RAID drives and recover data quickly.
What Should I use? RAID or JBOD?
Honestly, choosing between RAID and JBOD could be easy. The decision depends on your requirements. Still, to give you a heads-up conclusively, select a RAID setup when there’s a need for speed, performance, high uptime in terms of Server, and data redundancy. The patterns of saving data on multiple drives for quick read and write and collecting data from all the disks in the array offer fault tolerance and make data recovery easier.
The JBOD should be used when there is much requirement for greater local or on-premises storage. While the former doesn’t offer much storage capacity as space is consumed in redundancy, the latter primarily caters to this need. However, JBOD can also offer speed when using non-volatile memory express SSDs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is JBOD used for?
JBOD is primarily used by organizations needing an efficient on-premises storage method. You can easily add additional storage to the system for storage expansion.
2. What are the disadvantages of JBOD?
The JBOD architecture is based on the ‘Spanning’ storage mechanism, which provides no redundancy or data protection. Additionally, there is no performance improvement since multiple hard drives are connected and working simultaneously.
3. What happens if a drive fails in JBOD?
The JBOD may continue operating generally on a single drive failure. However, the size of a failed disk will reduce the total storage capacity. In addition, if one drive fails in the array, there are chances of permanent data loss.
4. Can you use RAID with JBOD?
Yes, JBOD can be configured to act as RAID. It additionally can be used in servers for greater storage capacity.
5. Is JBOD safer than RAID 0?
When comparing JBOS vs. RAID 0, the results depend on your data amount and their storage mechanism. JBOD array might be slightly better if you’re storing smaller files than RAID 0. The RAID 0 uses a Striping mechanism (splitting data on all the drives in the array), and if a single component drive in the array goes down, the whole data will be gone. On the other hand, JBOD stores data sequentially, which might make it easy to recover data. However, it also depends on the operating system.
6. Is JBOD faster than RAID 0?
Well, it is based on your requirements. Still, RAID 0 outperforms the JBOD as it splits data between the drives in the array, increasing read and write speed, whereas JBOD adds data sequentially to all drives, giving better writing speed.
7. How much power does a JBOD draw?
A full Supermicro 24-bay JBOD enclosure can use 400 to 500 watts of power. The power can also be varied between 420 (if the array is on standby or in no activity condition) and 480W (actively continuous read/write of different-sized blocks).
8. How many drives can a JBOD hold?
JBOD is a high-capacity JBOD Storage Solution that doesn’t require a CPU or motherboard. It may support over 100 SAS/SATA drives to the maximum density.
Was this article helpful?