Solid-state drives (SSDs) are a better alternative to Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) in terms of performance, power, and energy efficiency. SSDs comprise several flash memory chips integrated inside a metallic body. Unlike HDDs (which rely on mechanical components), SSDs use memory chips that allow faster read and write performance. They are comparatively expensive but reliable. Thus, many people prefer SSDs over HDDs.
Although SSDs do not contain revolving components that are more susceptible to damage, they may fail or get damaged for many reasons, resulting in data loss.
Data Loss in SSDs
One of the major reasons behind data loss from SSDs is the failure of one of the NAND flash chips. A damaged or failed NAND flash chip makes data stored in its transistors inaccessible. One NAND chip failure can also lead to the failure of other NAND flash chips, eventually failing the entire SSD. Other reasons that lead to data loss from SSDs are:
- Power failures or voltage spikes: Sudden power outages or voltage spikes can corrupt the data stored on SSDs, leading to data loss.
- Physical damage: Physical damage to an SSD can cause it to fail, resulting in data loss. This damage can be caused by dropping the drive, water or other liquids exposure, or overheating.
- Virus or malware infections: Viruses and malware can infect an SSD and cause data loss by corrupting or deleting files.
- Human error: Accidental deletion of files or formatting of the SSD can result in permanent data loss.
- Firmware bugs: Issues with the SSD firmware can cause data loss by corrupting or deleting files.
- Wear & tear: SSDs have a limited lifespan; prolonged wear & tear makes them less reliable and prone to data loss.
- Unsafe drive usage practices: SSDs may also fail due to unsafe device removal practices, such as using them during a power surge.
SSD data recovery is still possible regardless of the reasons. However, before you begin any troubleshooting, ensure that the TRIM command is disabled.
Disable TRIM Command
TRIM is an Advanced Technology Attachment (ATA) command that tells a Solid-State Drive (SSD) which data blocks it can erase when they are no longer in use. The TRIM command improves the SSD’s read/write performance and extends lifespan.
When the data deletion or loss occurs, the TRIM command tells SSDs that the area containing data is no longer in use. SSDs then erase the data upon data deletion to overwrite it permanently, making recovery impossible. So, ensure you disable it first and then move on to the recovery methods. Follow the given steps:
- Open the command prompt from Windows Search and run it as administrator.
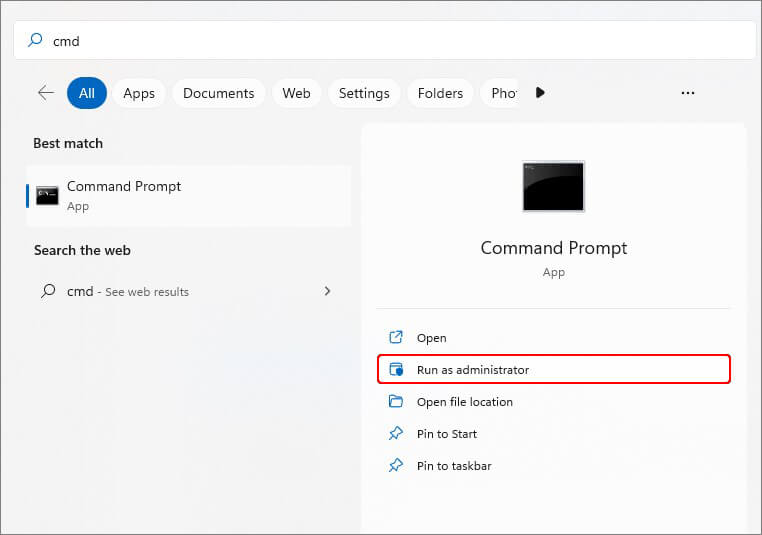
- In the elevated window, type fsutil behavior set disabledeletenotify 1 and press Enter.
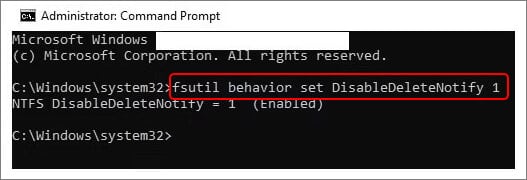
Close the window and reboot your system. The command will be disabled.
Methods to Recover Data from Failed or Damaged SSD
The following techniques can help you recover data from a failed or damaged SSD. Try the one most relatable to your situation.
Scenario A: Use Data Recovery Software in Case of Logical Damage
Logical damage refers to the drive formatting, corruption, or bad sectors. All such reasons may cause the SSD to fail or fail to function promptly. Due to this, you may not be able to access your data. In such a scenario, you can recover your data from the SSD with the help of dedicated professional data recovery software, such as Stellar Data Recovery Professional. The software can easily retrieve data from formatted, corrupted, or crashed SSDs. Follow the given steps to recover data from a failed SSD using Stellar Data Recovery Professional:
- Download, install, and run Stellar Data Recovery Professional on your PC.
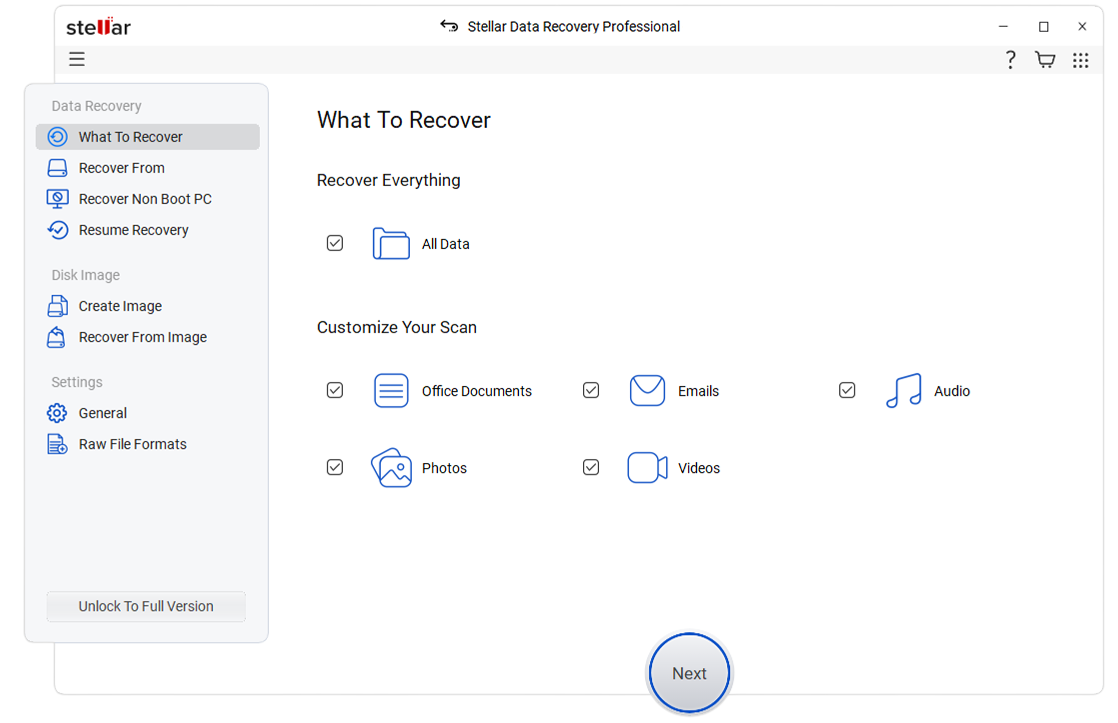
- Launch the software, select ‘All Data,’ and click ‘Next.
- There is a chance that your failed SSD may not appear on the Connected Drives list. If so, select the Can’t Find Drive option and click Scan.
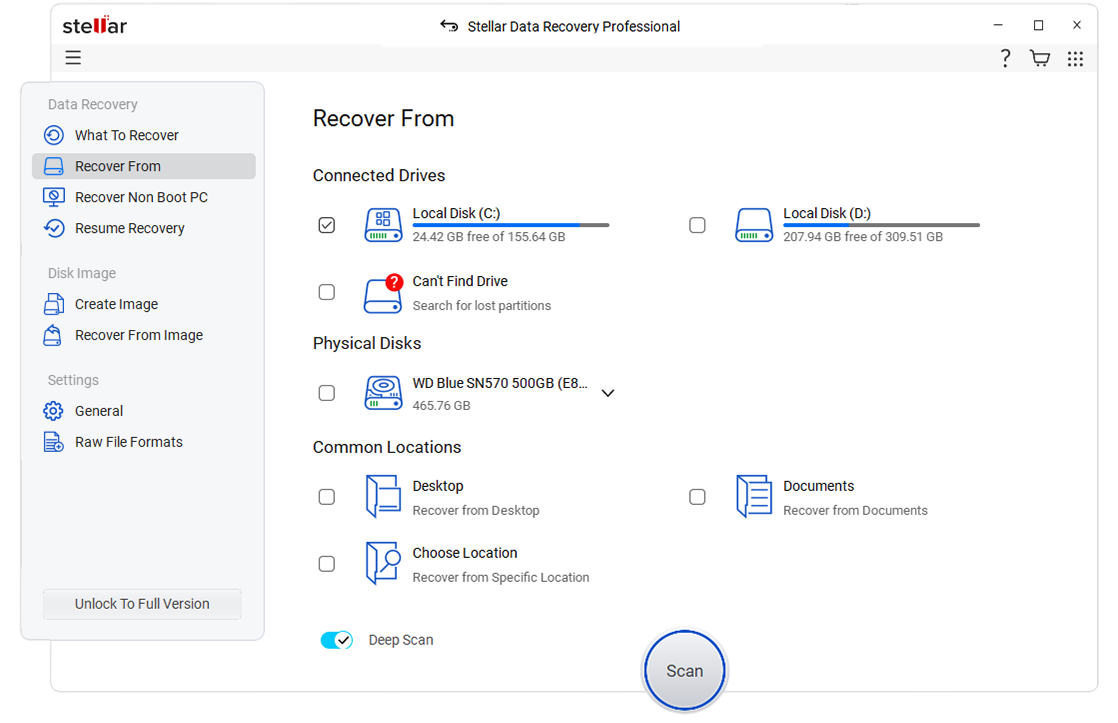
- Now, choose a hard drive with missing or deleted partition(s) in the Select Hard Drive to Search Lost Partition window and click Search.
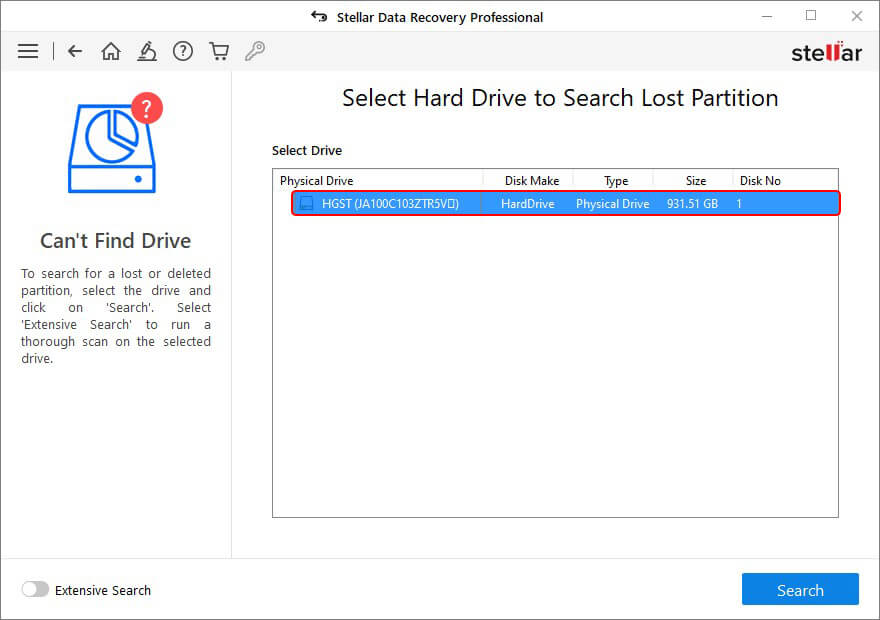
- All the partitions found will appear in the Select Partition to Recover Data window. Choose the desired partition from the list and click Scan.
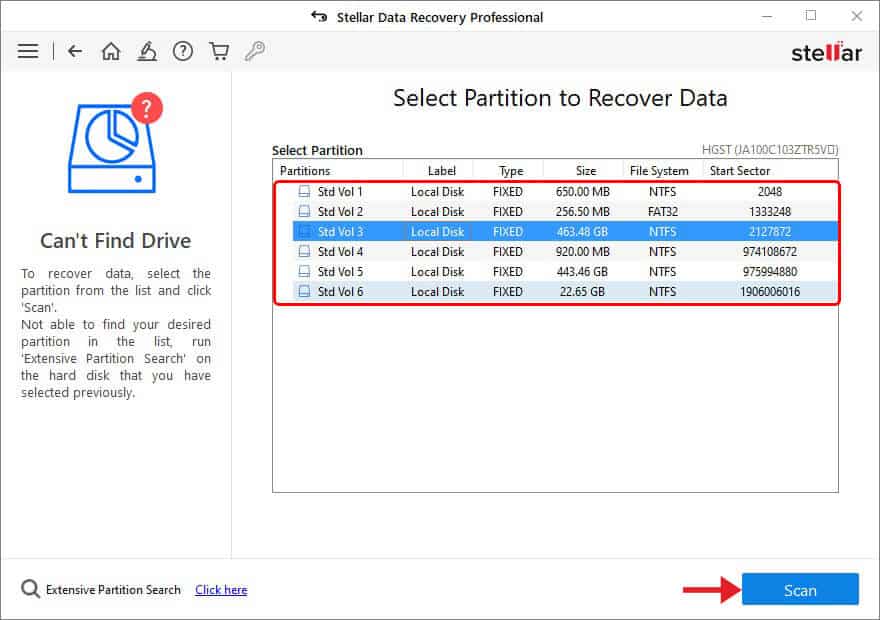
- Once the scanning is done, the files will show on the screen. Select the files you need and click Recover.
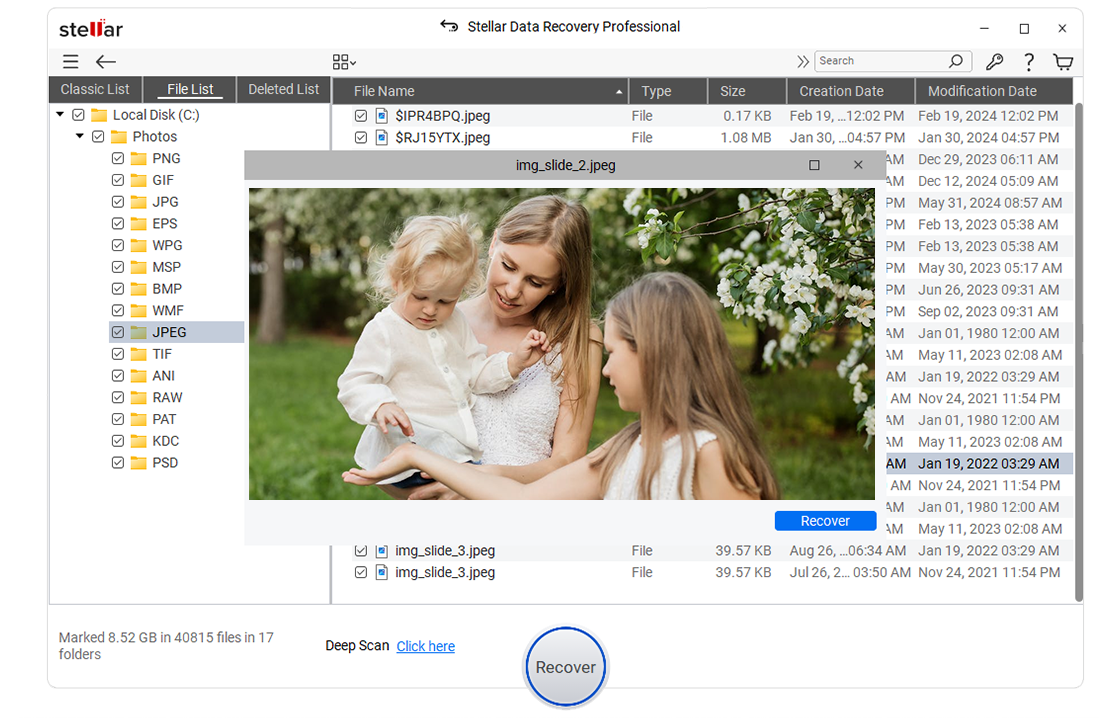
- Next, click Browse to choose the desired location (an external drive or another system partition) to save the recovered files, and finally, click Start-Saving to complete the process.
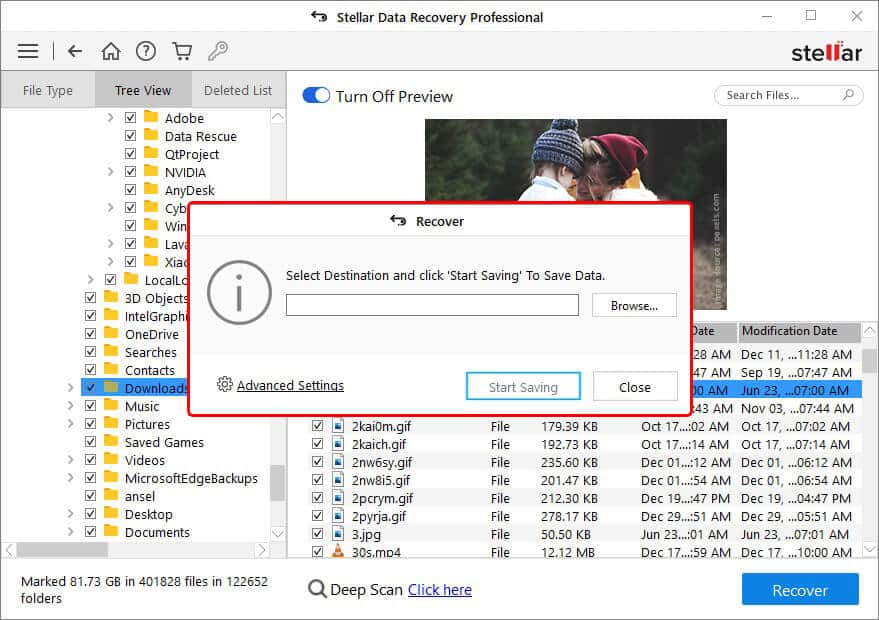
All the recovered data will be saved to the chosen location.
Scenario B: Reach Out to Data Recovery Services in Case of Physical Damage
Controller malfunction, water damage, or other factors physically harm the SSDs. In such cases, the software won’t help. Instead, you’d need to connect with a reliable data recovery services provider, such as Stellar Data Recovery Services. The data recovery experts at Stellar perform secure SSD recovery and recover up to 100% data.
How to Prevent Data Loss on SSD?
Here are some tips to help safeguard SSD files and prevent data loss:
- Create backups of your files on an external storage device.
- Regularly scan your drive with antivirus to eliminate unknown viruses or malware.
- Handle data with care.
- If you accidentally delete or lose files, use Stellar Data Recovery to restore them.
FAQ
How common is SSD failure?
Research shows that over 20% of SSDs develop errors gradually, and 30-80% develop bad blocks. Such errors make SSD failure a common occurrence.
How do I fix the SSD Not Showing up error?
SSD not showing up errors may occur for many reasons, including outdated or faulty controllers, corrupted file systems, SSD not initialized, and more. You may fix it by:
- Verifying that SSD shows in BIOS
- Updating storage controller driver
- Formatting SSD with NT File System
- Initializing SSD
- Running Windows Memory Diagnostic tool
- Assigning a drive letter to the SSD
Which is better – SSD or HDD?
Hard Disk Drives (HDD) and Solid-State Drives (SSD) are popular storage media that people commonly use. However, you should consider a few significant advantages of SSD over HDDs, such as advanced technology, superior performance, longer lifespan, and data safety.
Was this article helpful?