Summary: Digital forensics professionals use hashing algorithms, such as MD5 and SHA1, to generate hash values of the original files they use in an investigation. This ensures that the information isn’t altered during the investigation since various tools and techniques are involved in data analysis and evidence collection that can affect the data’s integrity. Another reason why hash values are important is that electronic documents are shared with legal professionals and other parties during the investigation. Therefore, ensuring that everyone has identical copies of the files is crucial. Stellar Email forensic is state-of-the-art software that automatically calculates hash values corresponding to emails in the mailbox data.
What is Hashing?
Hashing is a programming technique in which a string of characters (a text message, for instance) is converted into a smaller, fix-sized value, also known as a hash value. This hash value is always unique and has a fixed length, representing the original string. However, the hash value can’t be used to recover the original message. This ensures privacy and security while sharing the message.
Hashing is generally used to index and access items in a database since finding a shorter hash value of the item is faster than finding the original data directly. In digital forensics, however, hash values are calculated with the help of a hashing algorithm to ensure eDiscovery integrity.

What is a Hashing Algorithm?
An algorithm used in hashing is called the hash function. The value returned by this function is called a hash value. Hash values are a fast, robust, and computationally efficient way to compare the contents of files under forensic investigation. Each hashing algorithm uses a specific number of digits to store a unique “thumbprint” or a “digital fingerprint” of the file contents. Just as fingerprints are considered a unique biometric modality, the hash value generated by a hash function provides a unique characteristic of contents under forensic investigation. The unique hash value can be extracted for a single file, a group of files, or even entire disk space. This is a crucial process for deduplication and empirical evidence verification in ediscovery and forensic investigation. The following are some characteristics of hash functions:
- Hash functions are complex one-way functions, meaning you cannot reverse a hashing process to extract original data from a hash value. Reverse engineering is not possible, given a hash value.
- The hash value size is permanently fixed, and it’s independent of the input data size.
- Two different input files cannot produce the same hash value.
- Hash values don’t depend on the name of the file. Even if the file names are different and their contents are identical, it will produce the same hash values corresponding to these files.
- Different hash functions will produce different hash values corresponding to the same contents in the respective files.
- Some hash functions are more secure than others. For example, the MD5 hashing algorithm can be cracked with a fair amount of computational power. Hence, two different files having different contents can be created to produce the same MD5 hash value. This scenario is called a hash collision.
 Figure 1: Working of a Hashing Algorithm
Figure 1: Working of a Hashing AlgorithmMathematically, a hash function T also called the transformation function, takes a variable-sized input x and returns a fixed-size string, called a hash value y . Here, y=T(x)
The fundamental features of a hash function are as follows:
- The input string x can be of any length.
- Output string y has a fixed length.
- For any given x, T(x) is easy to compute, given the mathematical steps.
- T(x) is a one-way function and is collision-free.
Collision-free hash functions can be classified into two categories: strong collision-free hash functions and weak collision-free hash functions.
A strong collision-free hash function T is the one, in which, it is computationally infeasible to find two messages a and b, where T(a)=T(b). Given a weak collision-free hash function, it is computationally difficult to find a message a not equal to b, such that T(a)= T(b).
MD5 and SHA1 Hashing Algorithms
MD5 and SHA1 are the two most popular hashing algorithms used by digital forensics professionals today.
MD5: MD5 or Message-Digest algorithm 5 is a hashing algorithm that was created by Ron Rivest to replace the previous hashing algorithm MD4. MD5 is the fifth and latest version of the original hashing algorithm MD and it creates hash values of 128 bits.
SHA1: SHA1 or Secure Hash Algorithm 1 is another popular hashing algorithm that is modeled after MD5. It is more powerful than MD5 and produces hash values of 160 bits.
The following are the main differences between MD5 and SHA1 hashing algorithms:
| Differentiating Factor | MD5 | SHA1 |
| Length of hash value | 128 bits | 160 bits |
| Security level | Moderate | High |
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Algorithm complexity | Simple | Complex |
Let us take a sample string which we enter in an MD5 hashing algorithm and obtain its hash value:
String Input: Sam is eating apple
Hash Value: 387f51d0ccbab6be677275c9933c250e
Now, let’s modify the string by just one character:
String Input: Sam is eating apples
Hash Value: c77426fb082c588cfe5583f7eee73309
You can see that appending just one character to the input string changes the entire hash value. This demonstrates the security quotient of hash functions.
The use of MD5 and SHA1 hashing algorithms is a standard practice in digital forensics. These algorithms allow forensic investigators to preserve digital evidence from the moment they acquire it, till the time it’s produced in court. There are many email forensics and eDiscovery software available. Stellar Email Forensic is one such software, that allows extensive and hassle-free case management during criminal investigations. One of the advanced features of this software is deleted email recovery.
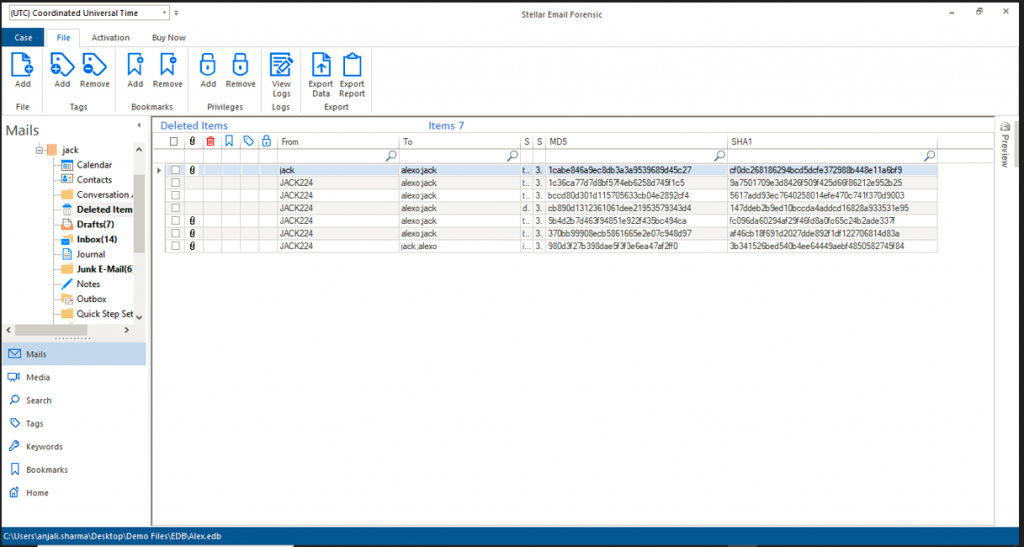 Figure 2: MD5 and SHA1 hash values corresponding to emails.
Figure 2: MD5 and SHA1 hash values corresponding to emails.Stellar Email forensic is state-of-the-art software that allows forensic analysis of emails effectively and efficiently. Stellar Email forensic automatically calculates hash values corresponding to individual emails in the entire mailbox data under consideration.
Need a fast and accurate digital forensic software for emails that also offers support for MD5 and SHA1 algorithms? Check out Stellar Email Forensic! It’s a reliable and comprehensive email forensic solution that provides hash values of emails on the fly. It also comes packed with other essential features like support for more than 25 popular email file formats, deleted email recovery, case management facility, and more! Download it today.