In Excel, Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is used to automate tasks. Sometimes, while working with VBA codes, you may encounter several errors. One such error is the runtime error 400. It usually occurs when your Excel fails to find the VBA code or you try to use an object in VBA code that has been deleted or inaccessible. It can also occur if you mistakenly put the code in the wrong module in your VBA project or the macro you are running is corrupt.
Causes of VBA Runtime Error 400 in Excel
There are a variety of reasons that can lead to the VBA error 400. Some of them are cited below:
- Incorrect registry entries.
- There is an issue with the module in which you are running the macro.
- The macros you are trying to run contain an incorrect parameter or argument.
- Macros in the Excel file are corrupt.
- Accessing an object in workbook that does not exist.
- Incorrect installation of Microsoft Excel.
- Important Excel-related files are corrupted.
- Outdated Microsoft Excel version.
Methods to Fix the VBA Error 400 in MS Excel
Follow the below-mentioned solutions and workarounds to fix the runtime error 400 in Excel.
Method 1: Move the Macro to Another Module
Problematic modules can trigger the runtime error 400 in Excel. For example, you have inserted a code in the wrong module in the VBA project. If you receive the error, then there is an issue with the module. In such a case, you can move your macros to another module. Here are the steps:
- Open your Microsoft Excel application.
- Create a new module using the below steps:
- Go to the Developer tab from the Ribbon menu.
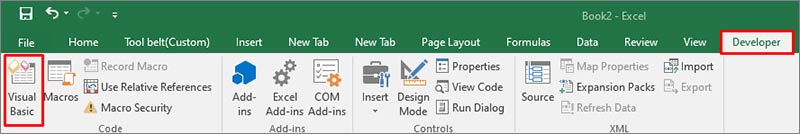
- The Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications wizard is displayed.
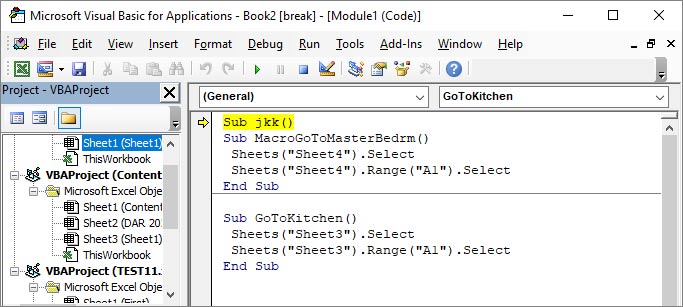
- In the VBA wizard, click Insert > Module.
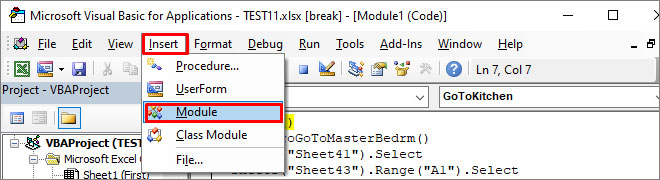
- Now, copy the code from the old module and paste it into the newly created module.
- Go to the File and click Save to save the code in the new module.
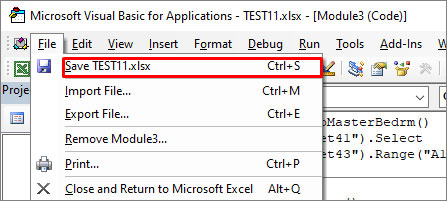
- Go to the old module, right-click on it, and click Remove Module to delete it.
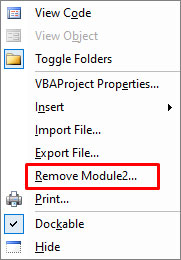
- Now try to run the code to check whether the error is fixed or not.
The Excel error 400 may occur when you try to run a macro that contains an incorrect or invalid input, such as an argument or parameter. You can check your VBA code for any incorrect arguments and their specifications using Error handling. In Excel VBA, error handling is used to handle runtime errors that appear while running the program. Also, it is used to check for invalid arguments in VBA code.
Method 3: Update your Excel Application
Runtime errors, including error 400, can occur if your Microsoft Excel is not updated. So, consider updating and upgrading your Excel to the latest version. Following are the steps to update your Excel:
- Open your Excel application.
- Go to the File menu on the top-left corner of the window.
- Select Account and click on Update Options under Product information.
- Click Update Now.
Excel will check for the latest updates and download them if available.
Method 4: Check for Deleted Objects in the Code
Sometimes, the runtime error 400 can occur if an object you are calling in a code is not available, deleted, or inaccessible. You can check your VBA code for any deleted or missing objects in the macro. You can use the debug command to check for errors in the code. Debugging in Excel can help you quickly identify and fix the errors in the VBA code.
Method 5: Enable Trusted Access to VBA
You can enable the trusted access to VBA option to provide complete access to the code to run. Here are the steps to enable trusted access to VBA:
- Go to the Developer tab.
- Click Macro Security.
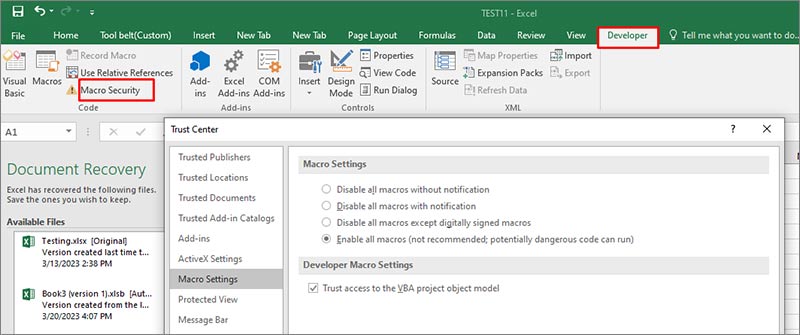
- In Trust Center window, select the option “Trust Access to the VBA Project object model” under the Developer Macro Settings section.
- Click OK.
Method 6: Fix the Corrupted Excel File
The runtime errors in Excel may occur if your file gets corrupted or damaged. To fix the error, you can try repairing the file using the built-in “Open and Repair” tool. Follow these steps:
- Open Excel and click on the File menu.
- Choose Open and select the corrupted Excel file.
- Click on the arrow next to the Open button and click on “Open and Repair”.
- Select the repair option that you want to use.
- Click OK.
The “Open and Repair” tool may not be able to repair the Excel file if it is severely corrupted or the extent of the damage is too high. In such a case, you can try a third-party Excel repair tool, such as Stellar Repair for Excel. It is a powerful tool that uses advanced algorithms to repair the corrupted Excel file, even if the damage is too extensive. It recovers all the objects from the Excel file with complete integrity.
Conclusion
The VBA error 400 in Excel can occur due to various reasons, such as invalid parameters in macros, deleted objects, or corruption in Excel file. By following the solutions outlined in this post, you can resolve the VBA runtime error 400 in MS Excel. If the error persists, then you can try a reliable third-party Excel repair software, such as Stellar Repair for Excel. It can effectively repair corrupted macros in Excel by scanning the Excel file and help you resolve the issue. The tool is compatible with all Excel versions.
Was this article helpful?