Often such notifications as the “Operation can’t be completed because the disk is full” contain troubleshooting tips in the error notification itself. The error message tells you that Mac can’t complete the process because there isn’t enough space on your drive to create, save, or edit new files.
Basically, the only solution to this problem is to create more disk space. We have listed several ways to do this here.
What Causes the “Operation Can’t Be Completed Because the Disk Is Full” Issue on Your Mac
You may encounter the error message “The operation can’t be completed because the disk is full” on your Mac for several reasons. Here are the most common causes:
- Large files: Having files that take up much space on your Mac leaves less for other files.
- Too many files: If you have a lot of files on your computer, they can also take up a lot of space. Some of them may even be useless for you.
- Temporary files: Those files are created by various applications and programs on your Mac. These files are supposed to be deleted automatically, but sometimes they are not, causing them to take up space on your hard drive.
- System files are essential for your Mac to function correctly. However, these files can also take up a lot of space on your Mac.
- HD errors: If your hard disk includes errors, it can cause it to fill up quickly, leading to the error message.
How to Deal with the “Operation Can’t Be Completed Because the Disk Is Full” Problem
We have compiled several solutions to fix the “operation cannot be completed because the disk is full” error on your Mac. You can try each one one at a time and see if the problem persists.
I. Delete Large Files
Files of a considerable size buried deep within your hard drive consume a significant amount of space on your Mac. Let’s see how to find and delete files that take the most of your space on Mac. You can free some space by deleting them and fix the “Operation can’t be completed because the disk is full” problem.
macOS Ventura includes a feature that enables effortless management of large files in your storage. It is called Storage Manager. Here is how to use it to find large files:
- Go to Apple Menu > System Settings > General > Storage.
- Click the (i) icon near the Documents to see the file categories.
 Storage folder
Storage folder
- In the opened window, you will see the files grouped by size. Delete those you do not need.
 Large files
Large files b. Use Finder
Using Finder will also help you to detect and remove files that take up much space on your Mac:
- Open Finder.
- Click on the magnifying glass on the top-right corner of your Mac’s screen and type anything in the search box.
 Search box on Mac
Search box on Mac
- Then click on the + icon that appeared.
 Add filter on Search
Add filter on Search
- Sort the files by Size > select Size is greater than 1GB > delete those files you do not need.
 Create a search filter
Create a search filter II. Delete Unneeded Files
Another way to free up storage is to go through all the folders on your Mac and delete your files. This way, you will get rid of data you don’t need and fix the “Operation can’t be completed because the disk is full” issue.
There are 3 methods to move your files to Trash:
- Drag and move the unneeded files to the Trash folder.
- Right-click the folder or file you want to remove and click on Move to Bin.
- If you are using a desktop, select a file and use the keyboard shortcut Command (⌘) + Delete to move the file or folder to the Trash.
To fully delete a file, you need to empty the Trash.
III. Delete Temporary Files
Various applications and programs on your Mac create temporary files. These files are supposed to be deleted automatically, but sometimes they are not, causing them to take up space on your hard drive.
To delete temporary files on your Mac, follow these steps:
- Open Finder.
- Click on the Go menu and select Go to Folder.
- Type ~/Library/Caches in the box and click Go.
 Go to ~/Library/Caches
Go to ~/Library/Caches
- Select all the files and folders in the folder that opens.
- Right-click on the selected files and folders and select Move to Bin.
- Repeat this process for the ~/Library/Logs folder.
 Go to ~/Library/Logs
Go to ~/Library/Logs IV. Delete System Files
System files are essential for your Mac to function correctly. However, these files can also take up a lot of space on your hard drive.
To delete system files, follow these steps:
- Open Finder.
- Click on the Go menu and select Go to Folder.
- Type /Library in the box and click Go.
- Review the folders and files in the Library folder.
 Library Folder
Library Folder
- Delete any unnecessary files or folders.
Note: Be very careful when deleting system files. Make sure you do not delete any essential files.
V. Repair Disk Errors
If your hard disk has errors, it can cause it to fill up quickly, leading to the error message. To repair disk errors, follow these steps:
- Run your Mac in Recovery Mode.
- Select Disk Utility from the macOS Utilities window.
 Disk Utility
Disk Utility
- Select your Mac HD from the list on the left.
- Click on the First Aid button.
 Disk Utility > First Aid
Disk Utility > First Aid
- Wait for the disk to be scanned and repaired.
- Restart your Mac.
How to Restore Deleted Files?
Stellar Data Recovery Professional is a tool that can help you recover lost or deleted files on your Mac.
Here’s a short instruction on how to restore files using Stellar Data Recovery:
1. Download & install Stellar Data Recovery Professional for Mac on your system.
2. Select the type of data you want to recover and click Next.
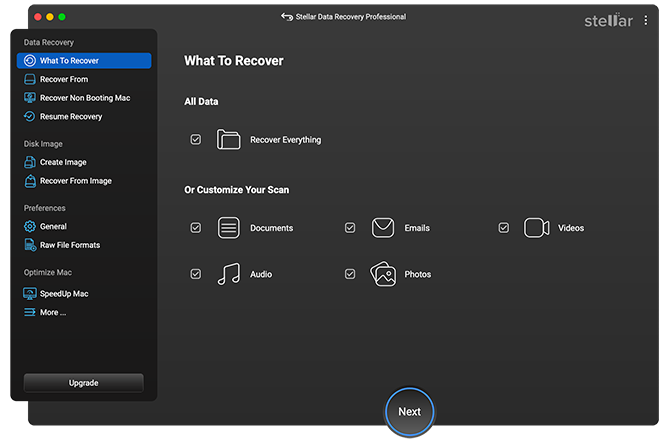 Stellar Data Recovery Professional > Select what to recover
Stellar Data Recovery Professional > Select what to recover 3. Choose the location where the files were stored before they were lost or deleted. If you’re not sure, select the Can’t Find Volume option, and click Scan.
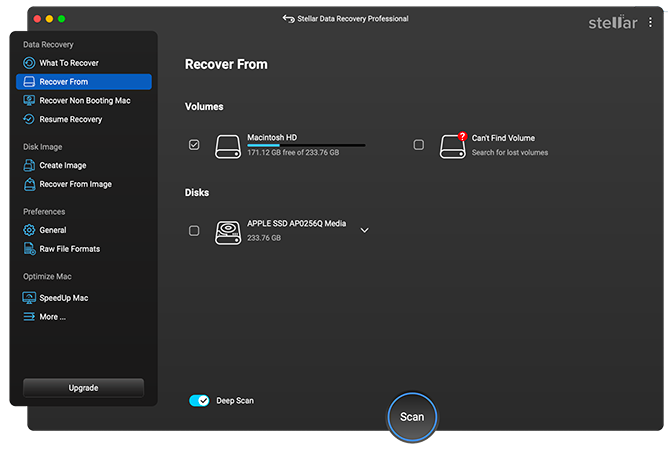 Stellar Data Recovery Professional > Recover From
Stellar Data Recovery Professional > Recover From 4. Wait for the scan to complete, once the scan is complete, you can preview the recoverable files in the scan results window.
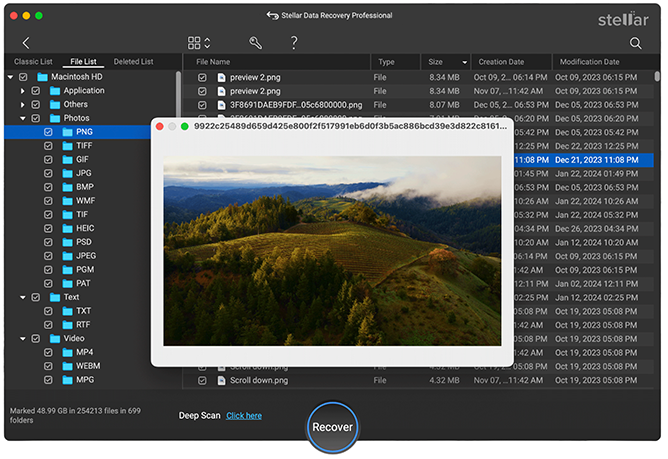 Stellar Data Recovery Professional > Preview
Stellar Data Recovery Professional > Preview 5. Select the files you want to restore and click on Recover to start the recovery process.
Wrapping Up
Following simple tips, you will clear some memory on your Mac, thus fixing the “Operation can’t be completed because the disk is full” issue.
The primary advice is to monitor if there is a free space on your Mac. Remember to clean the Trash and check your computers for unneeded downloads and duplicates once in a while.
Before you start cleaning your Mac from unneeded files, don’t forget to have a back of your important data or install apps that will help you to get your files back in case you accidentally delete important ones.
Read more:
Was this article helpful?