Several users have reported experiencing the runtime error 3274 in MS Access when using the TransferSpreadsheet function in a macro to import data from an Excel file into Access database. There are multiple factors that can lead to this error. Let’s discuss the reasons behind the error 3274 and the solutions to resolve it.
Causes of Runtime Error 3274 in MS Access
The Access runtime error 3274 may occur due to several reasons, such as:
- Excel file you are importing is in incorrect format.
- MS Access application is not updated.
- Database file in which you are working is corrupted.
- Cell data is above the prescribed limit.
- Macro in the Access file is corrupted.
- You are trying to access locked records.
- You do not have permission to import files.
- You’ve uploaded the wrong file to import in Access.
Fix Runtime Error 3274 in MS Access
Following are some workarounds you can try to fix the Access error 3274.
You can get the error 3274 if you import an Excel (.xls) file having cells containing data more than 8224 bytes. To fix this issue, you can do any of the following:
- Use the .xlsx format instead of .xls.
- Restrict the text fields to a length less than 8224 bytes.
2. Change the RecordLocks Property
Sometimes, the error can occur if you are trying to access locked records in MS Access. In such a case, you can use the RecordLocks property to check the locked records and change their settings. It allows you to set three options – No Locks, All Records, and Edited Records – in your form’s property sheet or a macro. To check and change the RecordLocks property, follow these steps:
- First, click on the Microsoft Office icon.
- Then, select Access Options.
- The Access Options dialog box will appear on the screen. Choose Advanced and then click on the option under Default Record locking.
- Check the default settings and make changes if required.
3. Check the Table Name in the Macro
Sometimes, the “runtime error 3274: External table is not in the expected format” can occur in Access when using the TransferSpreadsheet function in VBA code. It usually occurs if you have mistakenly entered the incorrect name of the table or worksheet. To fix this, you can check the name of the table you entered in the queries. You can run debug feature in MS Access to locate the errors. To use this feature, follow these steps:
- Open your database.
- Go to Database Tools and then click Visual Basic.
- The Visual Basic Editor is displayed. Click on the Debug button and then click Compile.
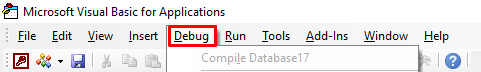
- It will highlight the line with errors.
Once you found the source of the error, do the required changes.
4. Remove Missing References
The runtime error 3274 can occur if the function in the code is a reference to a missing object library. You can delete the missing references from the VBA. To do this, follow the below steps:
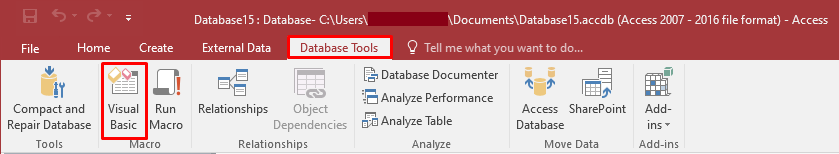
- Open the database (in which you are getting the error).
- Go to Database Tools > Visual Basic.
- On Visual Basic Editor, go to Tools and then click References.
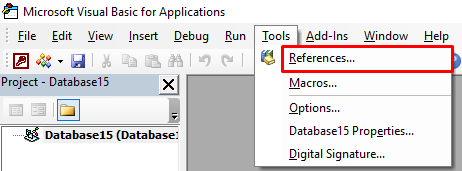
- In the References dialogbox, search for the object library or type library that you see as MISSING:<referencename>.
- If found, then clear the checkbox next to it and click OK.
5. Check the File You’re Importing
You can get the error 3274:External table is not in the expected format, if MS Access fails to recognize the Excel file you are trying to import. It can happen if the file is in an incompatible format. To fix the issue, check the file and its format before importing it into Access.
6. Repair Corrupted Database Files
The error 3274 can occur if you are working on a database file that is corrupted or contains corrupted macros or other objects. In such a case, you can run the “Compact and Repair” tool in MS Access to fix database corruption. Also, it compacts the database file by deleting unused space. To use this utility, follow the below steps:
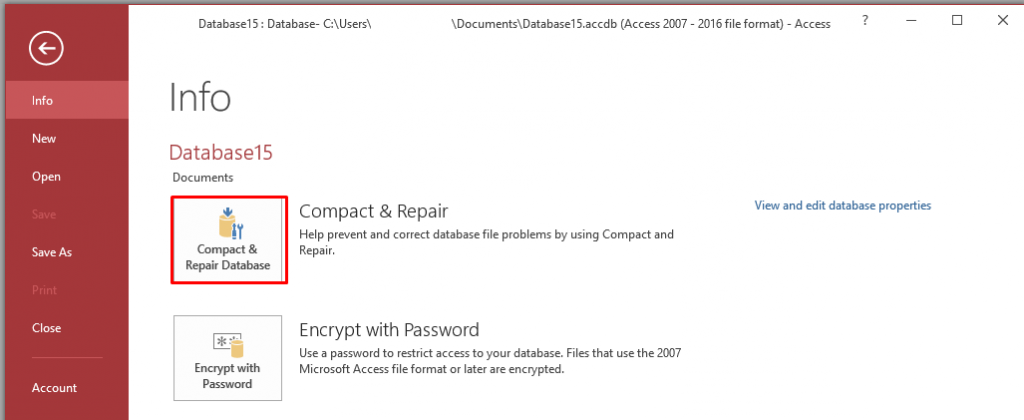
- Open your MS Access database.
- Go to File and then click Info.
- Click Compact & Repair Database, under the Info section.
A copy of the compacted and repaired database is created at the same location.
If the Compact and Repair utility fails to fix corruption issues, you can use an advanced Access repair tool, such as Stellar Repair for Access. It is an easy-to-use DIY tool that can repair severely damaged or corrupted Access database files. This tool can recover all the data from corrupt Access database files in just a few clicks. You can effortlessly use it on Windows 11/10/8/7/XP to repair a corrupted database.
Wrapping Up
In this blog, we have discussed some possible causes behind the runtime error 3274 and some workarounds to fix it. If your database file gets corrupted, you can use the built-in ‘Compact and Repair’ feature in MS Access. However, if it doesn’t work for you, use Stellar Repair for Access for repairing the corrupt database file. It can recover every single bit of data from the corrupted database file. You can download the free trial version of the software to scan and preview the database file.
Was this article helpful?