While looking at the memory utilization on your PC, some questions are bound to cross your mind:
I have an X amount of RAM installed on my PC. Why is it not using it completely?
What is hardware reserved memory?
A PC never truly utilizes RAM to its full capacity. While most of it is used by programs, applications, background processes, and other OS features, the system allocates a small portion of RAM as Hardware Reserved Memory. In some instances, you may find the allocated hardware reserved memory too high. This causes sudden performance drops, frame drops, screen stuttering, and freezing.
What causes the hardware reserved memory to spike? Is it possible to reduce it? In this blog, we’ll uncover all the answers.
What is Hardware Reserved Memory?
As the name suggests, hardware reserved memory is a small amount of RAM allocated by the system to various hardware components, such as Bluetooth devices, sound cards, iGPU, etc. for their smooth operation.
To check the amount of hardware reserved memory allocated to a component, you can follow these quick steps –
- Press CTRL + SHIFT + ESC to open the Task Manager window.
- Click on the Performance Tab.
- Click on Memory.
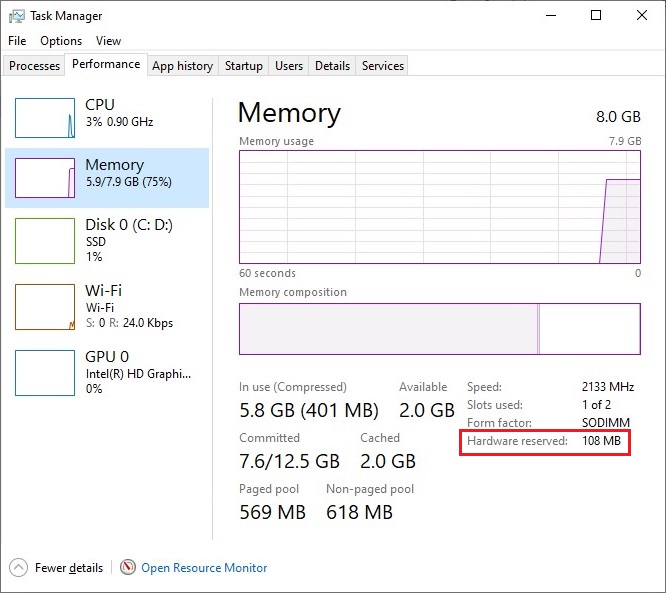
How Does the Hardware Reserved Memory Become Too High?
In some cases, low RAM on your PC can also cause the hardware reserved memory to be unusually high. Some other reasons may also contribute to this error –
- Bent CPU pins
- Non-working or dirty RAM slots
- Dust on RAM connectors
- RAM modules installed in an incorrect order
- Mismatching RAM installed
- Improper BIOS configuration
- Outdated BIOS firmware
- Improper system configurations
- Misconfigured paging file size
How to Fix Hardware Reserved Memory too High Issue?
Generally, the hardware reserved memory should range between a couple of hundred megabytes and 1-2 gigabytes. If it goes above these numbers, you might face the error for any of the reasons mentioned above.
If you find that your PC has allocated an unusual amount of RAM, the methods explained ahead can help you resolve the hardware reserved memory too high issue.
Method 1: Check the Processor for Bent Pins
This might sound strange, but bent pins in a CPU chip can cause unusually high hardware-reserved memory allocation. In most cases, users found the dual channel memory pin to be bent. In other cases, one or more pins were bent. If you come across this error and find bent pins on your CPU, straighten them to see if it resolves the error. Carefully follow this tutorial to fix bent pins on a CPU.
Method 2: Check RAM Modules & Slots
As the hardware reserved memory is a part of RAM, unusually high hardware reserved memory can be due to one or more reasons –
- Malfunctioning RAM modules
- Mismatched RAM modules
- RAM slots not working
- RAM pins are fuzzy due to dust
Here is a step-by-step guide to troubleshoot RAM-related issues –
- First, disconnect all the RAM modules from the motherboard and remove dust or debris from the RAM slots.
- Check the pins for any dust accumulation and clean them.
- Once everything is cleaned, connect just one RAM and boot the system.
- Check the hardware reserved memory by going to the Task Manager > Performance > Memory.
- If it is under control, add memory modules in the correct sequence.
Note – If you are using dual-channel memory, check your motherboard manual for the right RAM configuration. You may also refer to this public forum on how to install dual-channel RAM.
While installing RAM modules, be sure to use memory modules of the same size, speed, type, and build. If possible, purchase multiple RAM sticks, like a pack of 2 or 4. Using different types of RAM modules can lead to improper resource allocation or various performance issues, such as frame drops, freezing, stuttering, etc.
Note – In some scenarios, unexpected system crashes due to memory-related problems could result in an unbootable system. Unbootable system prevents access to the data on the disk drive. Use an advanced Windows data recovery software like Stellar Data Recovery to recover your data. Such software will retrieve your data safely on an external drive and safeguard it against unwanted data loss scenarios.
Method 3: Change the Amount of Allocated Boot Memory
If the amount of memory allocated by the system to boot processes is high, it can result in higher hardware-reserved memory usage. You can adjust this memory by going into the system configuration. It will help you free up memory and reduce the amount of allocated hardware reserved memory. Here’s what to do –
- Press WIN + R to launch Run.
- Type msconfig and press Enter.

- It will open the System Configuration window.
- Navigate to the Boot tab and click on Advanced options.
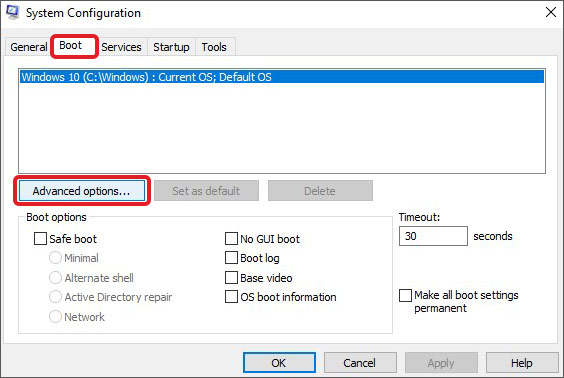
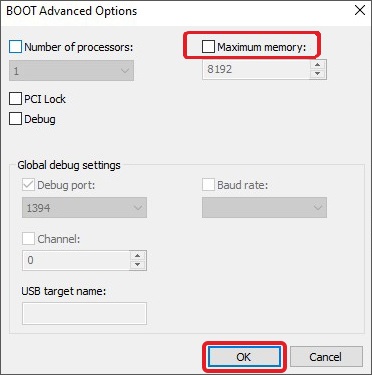
- Click OK, then Apply and OK.
- Restart your PC.
Method 4: Optimize Virtual Memory Usage
Virtual memory or paging file size allows the system to increase the memory of a PC using a small portion of the disk drive as RAM. Usually, the virtual memory settings are preconfigured when you install Windows. However, they can be customized based on user preferences.
In case they are misconfigured, they can result in problems like the hardware-reserved memory being very high. You can optimize the virtual memory usage to reduce the hardware reserved memory allocated by the system. To do this –
- Press WINDOWS + I to open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Scroll down in the left pane and click on About.
- Click on Advanced system settings.
- In the System Properties window, click on the Advanced tab.
- Go to the Performance section and click on Settings.
- It will open the Performance Options window. Click on the Advanced tab.
- Navigate to the Virtual memory section and click on Change.
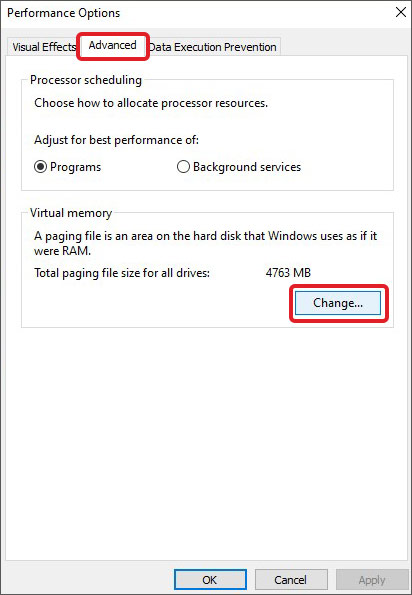
- Uncheck the Automatically manage paging file size for all drives option.
- Select the C: drive. Select the Custom size option and enter values based on the values at the bottom.
- Click on OK.
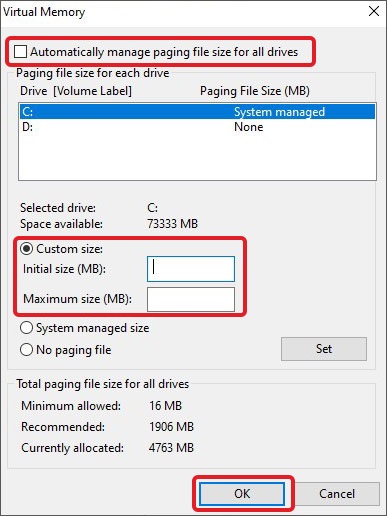
- Click on Apply and OK.
- Again, click on Apply and OK.
- Close everything and restart the PC.
Changing the paging file size should help you reduce the hardware-reserved memory allocated by the system.
Method 5: Update BIOS
Outdated BIOS or UEFI can result in unwanted problems, such as compatibility, performance & security issues. It may also lead to mismanaged system resources. Updating BIOS or UEFI enhances system compatibility, optimizes the memory management system, and resolves memory-related issues. You can refer to the motherboard’s manual or check the manufacturer’s website to install the latest firmware. You can also refer to this guide to update BIOS.
Conclusion
While hardware reserved memory is essential for hardware components, excessive allocation can result in performance drops, screen stuttering, and occasional system freezes. If the hardware reserved memory is too high, you can reduce it to improve your PC’s performance using the methods explained above.
A word of caution: Carefully update BIOS/UEFI, better with the help of an IT professional. Any wrong step can result in an unbootable system.
Was this article helpful?