While using HDDs, we have encountered errors causing various problems, such as inaccessible data, data corruption, slow computer, and BSoDs. In such situations, CHKDSK helps fix hard drives and restore the data on them.
In short, CHKDSK or Check Disk is a built in Windows utility that is used to fix hard drive related errors, monitor a hard drive’s health and restore functionality to an error-riddled HDD. Let’s dive further in details to learn more about CHKDSK and how it aids us in correcting malfunctioning hard drives.
What is CHKDSK?
As the name suggests, CHKDSK is a disk monitoring utility that comes pre-built with every copy of Windows OS. It is a vital tool that is used to scan and repair numerous hard drive-related issues, such as –
- Corrupted data
- Corrupted file system
- Corrupted MFT or Master File Table
- Slow performance
- Bad/damaged sectors
- BSoDs or frequent crashing
- Misaligned time stamps
- Incorrect file size data and security flags
Running the CHKDSK also helps in keeping the system data organized, resulting in good computer hygiene.
How Does CHKDSK Work?
CHKDSK is a simple command that starts by scanning & checking the file system of a drive, followed by data integrity and file metadata. Alongside these checks, it also looks for logical errors, corrupted entries in MFT, misaligned time stamps, etc. and repairs them right away, without affecting the drive’s data.
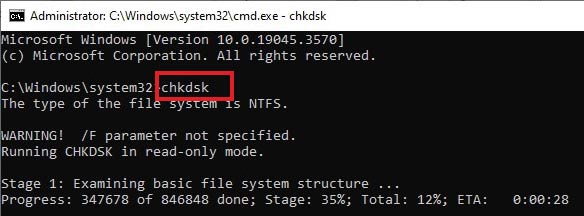
Over time, Hard drives develop two types of errors - soft errors and hard errors. Soft errors are temporary issues like bit flips, which are due to external factors like electrical or magnetic interference. Hard errors, on the other hand, are critical issues that are mostly physical in nature. Some examples of hard errors include wear & tear of platters, physical damage, or damaged circuitry due to a voltage spike.
In both scenarios, CHKDSK can be used to fix the underlying causes behind a malfunctioning HDD. CHKDSK repairs soft errors by rewriting incorrect data and hard errors by marking a section of the disk that is damaged.
How is CHKDSK Used?
There are numerous methods you can use to use the CHKDSK command. CHKDSK can be used via Windows PowerShell, or Command Prompt, or from the File Explorer. While using the CHKDSK command via PowerShell or CMD, it needs administrator-level permissions.
Using the CHKDSK is quite simple. You can deploy the CHKDSK command using either of the modes mentioned above.
However, if you use the CHKDSK via command line, you will need to follow its syntax and use the desired parameters, as per the requirement.
The Syntax is –
chkdsk [<volume>[[<path>]<filename>]] [/f] [/v] [/r] [/x] [/i] [/c] [/l[:<size>]] [/b]
Each parameter serves a different function. Here is a list of some commonly used parameters –
| Parameter | Description |
| /f | Fixes errors on the disk. The disk must be locked. If chkdsk cannot lock the drive, a message appears that asks you if you want to check the drive the next time you restart the computer. |
| /r | Locates bad sectors and recovers readable information. The disk must be locked. /r includes the functionality of /f, with the additional analysis of physical disk errors. |
| /x | Forces the volume to dismount first, if necessary. All open handles to the drive are invalidated. /x also includes the functionality of /f. |
| /c | Use with NTFS only. Does not check cycles within the folder structure, which reduces the amount of time required to run chkdsk. |
| /? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
For a complete list of parameters, you can run the CHKDSK command with ‘/?’ parameter. It will show you the complete syntax along with all the usable parameters and their descriptions. This is how it looks –
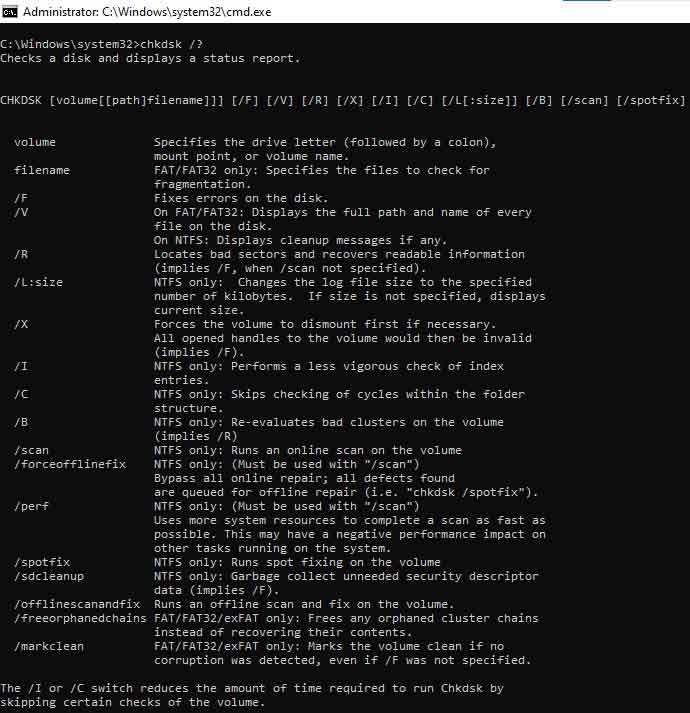
Usually, to fix a hard drive using CHKDSK, not many parameters are used.
Notes –
- You should not interrupt the CHKDSK process.
- CHKDSK can only be used for local drives. It will not work on drives mapped or connected over a network.
- CHKDSK locks the drive to bring accurate results. If the CHKDSK command is used without any parameters, it will work on read-only mode, which can affect the results.
- CHKDSK will not work if a disk is in use. You should close all the running applications and then use the CHKDSK command.
Caution – While using the CHKDSK command on FAT file systems, error fixing leads to changes in the file allocation table. This might cause data loss. Hence, you should take a backup of your files before running the CHKDSK command. However, if you find that you have lost files after running the CHKDSK command, you can easily recover them using a powerful data recovery software.
What are CHKDSK Exit Codes?
Once the CHKDSK has addressed errors with the disk, the process will end and generate an exit code. These end codes have a meaning, which can be a bit difficult for a novice user to understand. To recognize the result easily, we have compiled all the exit codes with their descriptions in the table below –
| Exit Code | Description |
| 0 | No errors were found. |
| 1 | Errors were found and fixed. |
| 2 | Performed disk cleanup (such as garbage collection) or did not perform cleanup because /f was not specified. |
| 3 | Could not check the disk, errors could not be fixed, or errors were not fixed because /f was not specified. |
How to Use the CHKDSK Command to Fix Hard Drive Errors?
There are various reasons why a hard drive shows errors or starts to malfunction, such as –
- Bad sectors
- Physical failure
- Corrupted file system
- Corrupted data
- Logical errors
- Stored data near its total storage capacity
There are three situations where a hard drive goes bad or shows signs of failure. In these situations, you can perform the CHKDSK repair.
Situation 1: Using CHKDSK on an External HDD
If you feel like your external hard drive is slowing down the computer or indicates towards a failure, you can run CHKDSK to fix it. Simply connect the drive to the computer and run the CHKDSK command either via PowerShell, CMD or File Explorer.
To use CHKDSK via PowerShell or CMD –
- Press WINDOW + R and type either CMD or PowerShell.
- Press CTRL + SHIFT + ENTER to open it with administrator privileges.
- Type CHKDSK D: /x /r. (You can replace D with the letter of the hard drive on your computer.)
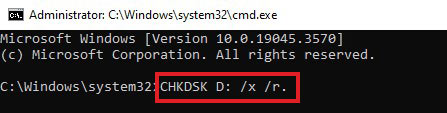
- Let it scan for the errors and repair them.
- Once the process is complete, it will end with a summary of the results.
To use Error Checking via File Explorer –
This is another form of CHKDSK repair that runs via File Explorer. To use this –
- Open File Explorer and locate the problematic hard drive.
- Right-click on it and click Properties in the context menu.
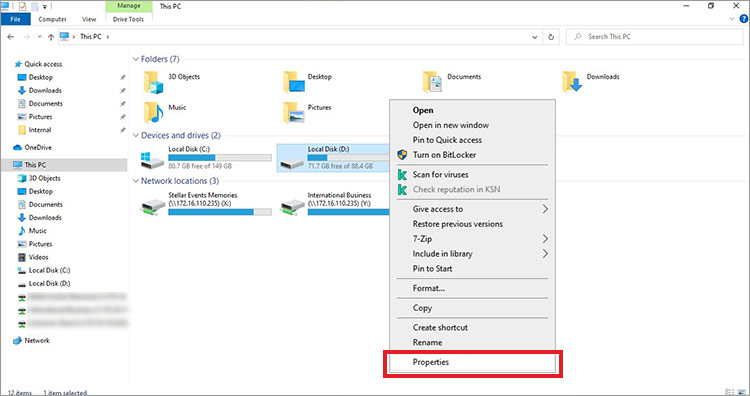
- Go to the Tools tab and navigate to the Error checking section. Click on Check.
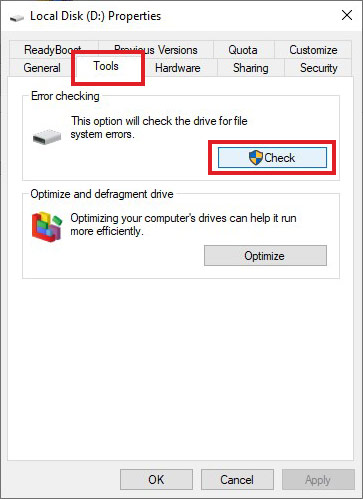
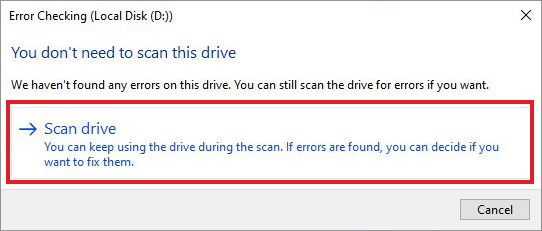
- It will show you a message along with an option to Scan drive. Select it.
- Once the CHKDSK finishes scanning and fixing hard drive errors, it will show you a dialog box. Click on Close to exit it.
Situation 2: Using CHKDSK on Boot Drive/Partition
A boot drive or partition contains installed Windows OS. While repairing the boot drive/partition, the CHKDSK locks away the drive as it is unable to scan if the drive is in use. For scanning the boot drive, the CHKDSK command requires full access to the drive. Therefore, you cannot do this while using your Windows 10 computer.
Hence, when you try to scan the boot drive, it asks you to run before the next boot. You can type ‘Y’ to give permission for this and restart the computer. It will run the CHKDSK repair on the boot drive before loading the OS.
Situation 3: On BSoD-Riddled Computers
If you have a computer that is frequently crashing, showing BSoDs or has become inaccessible, you can use Windows Installation Media to boot your computer and try to repair the boot drive using the CHKDSK command to fix the hard drive. Here’s what to do –
- Connect the Windows 10 installation media to your computer and power it ON.
- Enter BIOS by pressing the key dedicated for it.
Note – Keep pressing the assigned key to enter the BIOS. It could be F2, F8, F10, F11, ESC, DEL, or any other key designated by the computer manufacturer. Refer to your device’s manual for more info.
- Once inside the BIOS, change the boot sequence and select the Windows Installation Media in the Boot tab. It will restart the computer.
- You will see the Windows 10 Installation screen. Click on Repair your computer.
- On the next screen, click on Troubleshoot.
- It will open the Advanced Options screen. Click on Command Prompt.
- Type CHKDSK D: /r and press Enter. (Replace D with the letter of your drive.)
- It will perform the scan and repairs. Once it is over, it will bring up the results with various things like the number of errors found and corrected, total disk space, and more.
EndNote
CHKDSK or check disk is a command-line utility, which is mostly used to check and repair errors on a failing or malfunctioning HDD. In this post, we got an in-depth insight into the check disk command and how chkdsk is used to fix hard drives. If you have a hard drive that is malfunctioning or is making your computer slower than a snail, you can use the check disk repair and fix the failing hard drive.
We hope this exhaustive guide helped you understand the basics of CHKDSK and resolve hard drive-related errors.
[FIXED] – Error “Windows Cannot Run Disk Checking on This Volume Because it is Write Protected”
Microsoft’s Guide to CHKDSK
Can CHKDSK cause data loss?
Losing data due to CHKDSK depends upon the presence of bad sectors on a drive. It is also dependent on the number of errors found while scanning and repairing the drive.
Was this article helpful?