The Microsoft Exchange Replication Service is one of the many Exchange Server services responsible for the mailbox import/export (.pst files) or restoring disabled or soft-deleted mailboxes. It is also used for moving mailboxes from the primary database to another targeted database within or across Exchange servers.
When you add Exchange Servers in the Database Availability Group (DAG), the Microsoft Exchange Replication Service installs the failover clustering feature and initiates the cluster creation process. Once servers are configured in DAG, you can add a mailbox database copy to the DAG using the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or the “Add-MailboxDatabaseCopy” PowerShell cmdlet in Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
But sometimes, while adding the mailbox database via EMS or EAC, you may encounter the following error message:
The seeding operation failed. Error: The Microsoft Exchange Replication service may not be running on server Server Name.contoso.com.
Error: Error 0x6d9 (There are no more endpoints available from the endpoint mapper) from cli_RpccGetDbSeedStatus [Server: ServerName.contoso.com]. However, the copy is still created.
In this article, you will learn the reasons behind the error “The Microsoft Exchange Replication service may not be running on the server” and the solutions to fix it.
Reasons for “The Microsoft Exchange Replication Service may not be Running on Server” Error
There could be several reasons that can lead to the error while adding a new mailbox database copy or moving the database from one server to another in your DAG cluster. Some of them are:
- The Microsoft Exchange Replication Service is not running on one of the member servers
- Outdated Exchange Servers
- Issues with File Share Witness (FSW)
- The mailbox database is inconsistent or damaged
- Datacenter Activation Coordination mode issues
- Firewall-related problem
- Security or permission issues
Solutions to Fix “The Microsoft Exchange Replication Service may not be Running on Server” Error
Below are a few solutions that you can apply to resolve or overcome the error message “The Microsoft Exchange Replication service may not be running on server” in Exchange Server 2010, 2013, 2016, or 2019.
Add Server to Exchange Trusted Subsystem Security Group
If the server isn’t a member of the Exchange Trusted Subsystem Security Group, you may encounter issues while adding or moving the mailbox database copy from one member server to another in a DAG. To resolve the issue, you must add the member server to the Exchange Trusted Subsystem Security Group.
The steps are as follows:
- On the domain controller, press Windows + R, type dsa.msc, and press OK or click the Enter key.
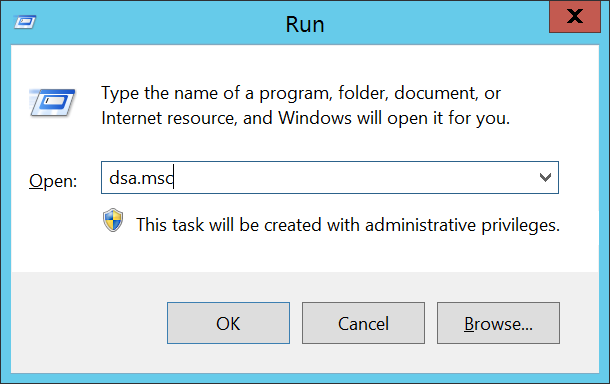
- This opens the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in. Click OK.
- Find the domain and then click the Microsoft Exchange Security Groups container.
- Double-click on the Exchange Trusted Subsystem under the details pane.
- Click on the Members tab.
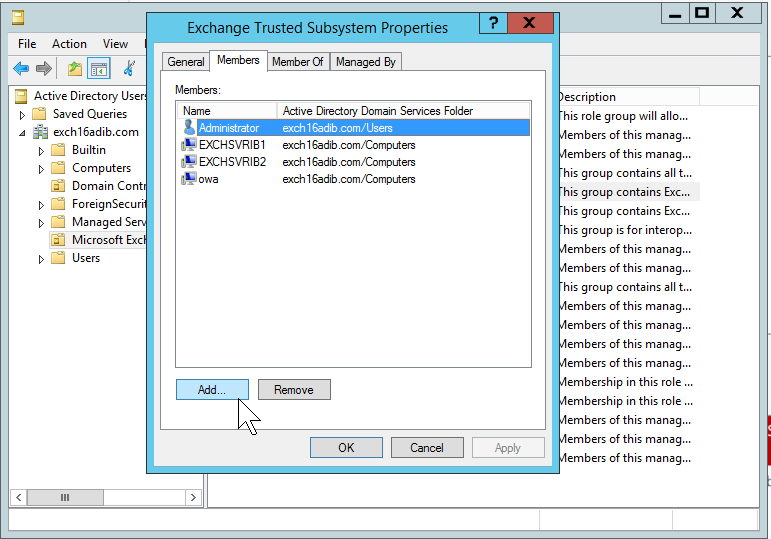
- Add the server to the Members list.
Wait for a while and then try again to add or move the mailbox database copy in your Exchange DAG.
Update the Exchange Server
The Microsoft Exchange Replication service may not be running on the server error may also occur if the Exchange Servers are outdated or lacking the latest Cumulative Updates (CU). Microsoft had confirmed the problem in the Microsoft products, specifically in Exchange Server 2019. However, the issue can be resolved by installing the CU1 or later for Exchange Server 2019.
You can refer to our previous blog to learn the steps to install the Cumulative Updates in Microsoft Exchange Server.
Repair the Mailbox Database
There could be damage or inconsistencies in the mailbox database that you are trying to add to the DAG or move to another server. Before adding the mailbox database copy to the DAG, check the database health status using the following command.
EseUtil /mh <PathToDatabase/Name.edb>
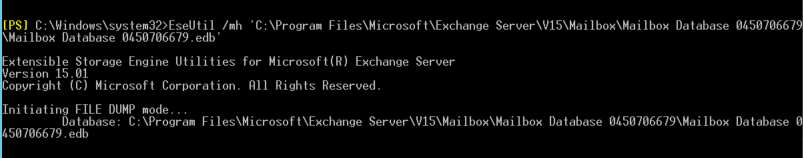
Check the State parameter. If it shows Dirty Shutdown, you must recover the database to Clean Shutdown state using the EseUtil Soft Recovery. If Soft Recovery (Eseutil /r) fails, use Hard Recovery to recover the database. However, it is advised not to go for Hard Recovery to avoid data loss.
Executing the Hard Recovery command (EseUtil /p) will purge any irrecoverable data, such as mailboxes or mail items, from the database during the recovery process. It also hard codes the database. Microsoft won’t provide any support for the hard-coded database if you require their help.
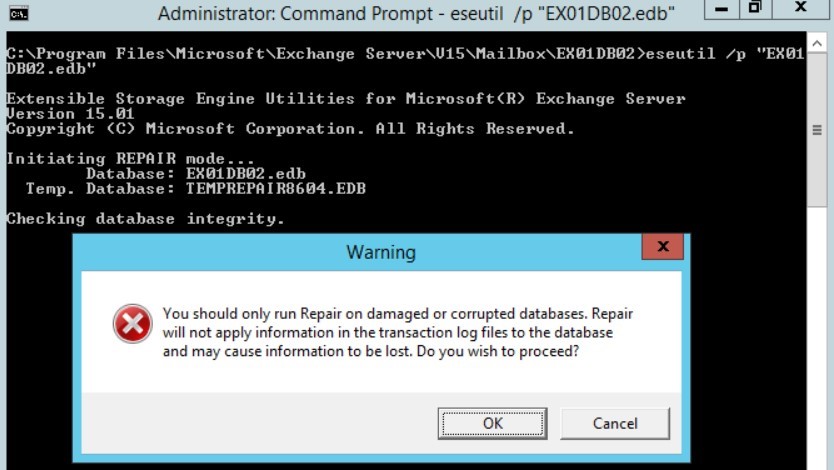
Instead, it is recommended to use an Exchange database repair tool, such as Stellar Repair for Exchange. The tool can help you fix the database and restore the mailboxes and mail items to a new healthy database on your live Exchange Server directly.
Once mailboxes are restored from the damaged database, you can add the healthy database copy to the DAG or move it to another member server using the EAC or EMS—without worrying about the error message.
Conclusion
A DAG may fail to provide High Availability (HA) and site resilience or automatic recovery if the Microsoft Replication Service is not running on the servers. It’s a critical service that also helps administrators import/export mailboxes to PST, move mailboxes to another database on the same or different Exchange Server, and restore deleted mailboxes. If you encounter the error message “The Microsoft Exchange Replication Service may not be running on the server,” follow the solutions discussed in this article to resolve it. If the issue is caused by an inconsistent, corrupt, or damaged Exchange database, try recovering it using the EseUtil Soft Recovery or an advanced Exchange database recovery tool, such as Stellar Repair for Exchange. Avoid performing hard recovery to prevent data loss.
Was this article helpful?