Researchers at Kaspersky have recently identified an IIS malware called SessionManager that threat actors use as a backdoor to Microsoft Exchange Servers after they have been attacked and compromised.
Many financially motivated and state-sponsored attackers deployed web shells and dropped IIS modules, such as Owowa, as backdoors after attacking the servers with ProxyLogon vulnerabilities. These backdoors are used to maintain persistence, steal data, and use the compromised servers as malicious infrastructure to attack or compromise other servers.
Once the IIS module is deployed, they respond to specific HTTP requests sent by the attackers to collect data or emails, add more backdoors, and deploy malware.
Developed in C++, the IIS backdoor continuously processes the crafted HTTP requests sent to the compromised server like any other request. This makes the malicious software appear as a legitimate IIS module, making it difficult to detect or spot by monitoring services.
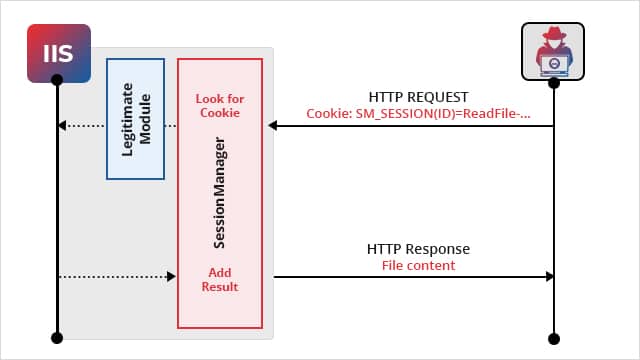
Besides, the SessionManager backdoor also provides the following capabilities to the operator or threat actors:
- Reads, writes, and deletes arbitrary files on the compromised Exchange Server.
- Executes the arbitrary code or binaries on the compromised Exchange Server (also known as Remote Command Execution or RCE).
- Establishes connections to arbitrary network endpoints.
This allows the threat actors to collect information and profile the server, gather credentials or passwords stored in memory, and deploy additional malware, exploits, tools, etc.
They are mostly targeting NGOs and government entities. However, their targets also include medical, oil companies, and transportation industries.
Steps to Protect and Safeguard Exchange Servers from SessionManager
It’s not easy to detect or disinfect Exchange Servers hit by malicious SessionManager or similar IIS modules. Antivirus or anti-malware can’t detect the malicious backdoor. Hence, you need to identify the indicators explained by Kaspersky to determine if the Exchange Server is hit or infected by the malicious IIS module.
If you find your server compromised or infected with the SessionManager or similar malicious IIS module, follow these steps:
- Take a volatile memory snapshot and get in touch with forensics experts and the incident response team, if required.
- Take your server offline or disconnect from the network and stop the IIS server.
- Take a backup of all files and logs on your IIS environment. This will help retain data for further incident response. After the backup, verify that the backups are working.
- Use IIS Manager or the appcmd command tool to remove every reference of the identified malicious IIS module from the server configuration.
- Manually review all the associated IIS XML configuration files. This will help ensure all references to the malicious modules are removed. You may also manually remove the references in XML files if found.
- Update the Exchange Server, IIS Server, and the Windows Server to patch all the vulnerabilities. You can follow this guide to install Cumulative or Security updates on Exchange Server.
- Restart the IIS server and connect the server to the network.
Conclusion
It is estimated that the SessionManager malware is still deployed and active on more than 90% of compromised targeted servers. It also highlights the need to check IIS Server modules regularly and enable the endpoint security shields.
In this blog, we have discussed the SessionManager IIS module, which attackers use as a backdoor. Although detecting and getting rid of SessionManager is complex, we did share some tips and steps that you may follow to get rid of it.
Anyways, it is highly recommended that you set up a new Exchange Server and move all mailboxes from your compromised Exchange Server. There can be other hidden backdoors, IIS modules, or web shells installed by the attackers that can be used to compromise your server or organization’s network further.
You can use the backup to restore mailboxes and data on the new server if the compromised server or database is damaged due to a malicious attack. You may also use Exchange recovery software, such as Stellar Repair for Exchange, to directly extract and move user mailboxes from compromised servers’ database files (.edb) to your new Exchange Server. This tool can help you minimize downtime and restore the mailboxes when the backup isn’t available, obsolete, or fails.
Was this article helpful?