When your Exchange Server comes to the end of life, you need to upgrade to a newer or latest Exchange version to continue receiving security updates and other support from Microsoft. In addition, you need to migrate the mailboxes and other data to the newer version. As migration sometimes can be tricky, you need to follow the best practices to ensure smooth migration process.
One of the best practices when it comes to migration is to run a test batch. You should always test migrate a few mailboxes to check the speed and performance of the destination server. This will help avoid any blockade during the migration and ensure faster migration.
While moving the mailboxes from your existing server to the destination server, you may encounter the ‘StalledDueToSource_DiskLatency’ or ‘StalledDueToTarget_DiskLatency’ error.
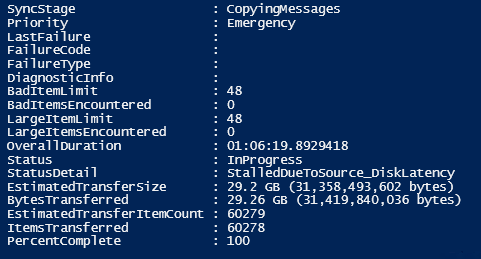
As a result, you may stuck in the export loop and fail to export or migrate the mailboxes from your existing server to the destination server. This can also inflate the destination PST file and may end up consuming all the storage on your server drive.
To fix this issue, you must be aware of the reasons that lead to the StalledDueToSource_DiskLatency or StalledDueToTarget_DiskLatency error. It is observed that the error occurs due to one or more reasons mentioned below:
- Disk performance issues either on the source disk (where database/mailbox is stored) or target disk (destination drive where PST is being saved).
- Insufficient system resources.
- Existing export requests in the queue.
- The response time from the source or target disk is very high and the migration batch or export is timed out.
However, there are a few workarounds discussed below that you may follow to overcome the error and successfully export all your mailboxes to PST and import them into your new server.
Solutions to Fix Mailbox Export Stalled Due to Source or Target Disk Latency Error
To resolve the errors StalledDueToSource_DiskLatency and StalledDueToTarget_DiskLatency, do the following:
The first thing to check is the disk performance. Check your RAID or disk management software or the data store status from your hypervisor.
Check if your server has a hard drive(s) that may soon fail. Usually, such disks are marked by the SAN or RAID manager.
Further, check if the hard drive is not performing well due to its lower RPM or data transfer speed. In such a case, consider upgrading the disks with server-grade drives or replacing them with SSD drives.
2. Verify Server Health and Available System Resources
Check the system resources using the Performance Monitor on the Windows Server hosting the source Exchange Server or mailbox database by monitoring MS Exchange Replication and MS Exchange Replication Server, along with the Average Disk Sec for Write and Read.
Similarly, check the Performance Monitor on the Windows Server hosting the target Exchange Server.
After making the required changes, run the move requests again and analyze the data storage.
3. Clear Existing or Old Export Requests
You can also check if there are any old move requests which need to be cleaned out. This is important as there could be other stuck export requests or old requests which are hindering your Exchange Server performance and PST export.
You can remove the old or existing requests using the Remove-MoveRequest PowerShell cmdlet.
Remove-MoveRequest –Identity “abc@xyz.com”
Next, add the new move request using the –Priority parameter as shown below.
New-MoveRequest –Identity “abc@xyz.com” –BatchName “TestMigration” –Priority Highest
This will execute the move request with the highest priority. With this, your export job may relinquish and start over again.
4. Suspend Move Requests
If you have a large number of move requests, you can try to first suspend the stalled mailboxes and after about 10 minutes, resume them. This can be done by using the Suspend-MoveRequest and Resume-MoveRequest PowerShell cmdlets (see the examples below).
Suspend-MoveRequest –Identity “abc@xyz.com”
Resume-Moverequest –Identity “abc@xyz.com”
Conclusion
We have shared the workarounds in this article to help you overcome the StalledDueToSource_DiskLatency and StalledDueToTarget_DiskLatency error messages. However, if they do not work or resolve the error, then you should consider using a third-party EDB to PST Converter software, such as Stellar Converter for EDB. The software can help you quickly move all mailboxes from the databases on your old or existing Exchange Server to the new Exchange Server directly in a few clicks.
The software auto-maps the source and destination mailboxes and provides an option to create a mailbox on the destination server directly from the software interface. This helps further expedite the mailbox export and helps you import all the mailboxes to user accounts on the destination server with complete integrity and original folder structure. It’s compatible with Microsoft Exchange 5.5 to the latest Exchange Server 2019. Thus, you can use it to move or export mailboxes from any Exchange Server version. In addition, it also exports the mailboxes directly to an Microsoft 365 tenant.
Was this article helpful?