Windows Defender is a vital system application that keeps the computer safe from unwanted and malicious pieces of code. The Antimalware Service Executable or MsMpEng.exe is one such process that is responsible for real-time scanning in Windows 11/10/8.
However, the Antimalware Service Executable has been showing high CPU or memory usage in the Task Manager. This is causing lowered performance and even the computer to crash. Let’s look at this issue in detail and understand the reasons causing it to consume an absurd amount of system resources.
What is Antimalware Service Executable or MsMpEng.exe?
Antimalware Service Executable or MsMpEng.exe is an integral process of Windows Defender. It is available on Windows 11/10 and 8. This process runs in the background without affecting other activities and scans for any malicious code, virus, etc. It checks files for malware and installs various antivirus updates.
Lately, some Windows 10 users have reported seeing this process consuming a lot of system resources and take CPU or disk usage to as high as 90%. Let’s look into the details to find out why this is happening.
Why is the Antimalware Service Executable or MsMpEng.exe Showing High Disk Usage?
The MsMpEng.exe process is a CPU-intensive process. Ideally, it should run normally without increasing the disk usage. However, this error message popping up on the screen indicates a problem with the process. The Antimalware Service Executable error results in an increase in CPU usage and drains computer resources, which negatively impacts performance.
Another reason why this could be happening is because it is always running in the background and regularly scans the C:\Program Files\Windows Defender folder. Listed below are some reasons causing this issue to occur on Windows 10 PCs –
- Corruption in Windows Defender files
- MsMpEng.exe task frequency too high
- Windows Defender overlapping with another antivirus instance
- Malware attack
- Bad Windows update
Methods to Fix the Antimalware Service Executable High CPU Usage Issue
Method 1: Scan for Malware
This is the most basic and easiest way to fix the issue causing the Antimalware Service Executable process to show high memory usage. Virus-infected files in a computer could cause programs to malfunction. If you have a reliable antivirus installed on your computer or use Windows Defender, then use either of them to perform a complete scan of your computer. This should bring the malware out and eliminate it from the system.
Method 2: Exclude Antimalware Service Executable
If you are encountering that the Antimalware Service Executable is consuming high memory, you can add it to the exclusion list and fix the issue. To do this –
- Press WINDOWS + I to open Settings.
- Click on Update & Security.
- Click on Windows Defender in the left pane.
- Navigate to the Exclusions section and click on Add an exclusion.
- Click on the Exclude a.exe, .com, or .scr process option under the Processes section.
- Type MsMpEng.exe in the blue box and click on OK.
Method 3: Prevent MsMpEng.exe from Scanning its own Folder
As mentioned earlier, the Antimalware Service Executable regularly scans its own folder – ‘C:\Program Files\Windows Defender’. This causes it to consume resources in an abnormal way, thus taking the usage percentage as high as 80-90%. You can stop this process from scanning its folder, thereby reducing the CPU usage. Here are the steps to do this –
- Press WINDOWS + I to open Settings.
- Click on Update & Security.
- Click on Windows Security in the left pane and then click on Virus & threat protection.
- In the Virus & threat protection window, locate Manage settings. Click on it.
- Scroll down to Exclusions and click on Add exclusions.
- In the next window, click on Add an exclusion and then select Folder from the list.
- Paste the following address – C:\Program Files\Windows Defender and click on the Select Folder button.
- Click on Yes on the pop-up.
Method 4: Disable Real-time Protection and Reschedule Scans
You can easily disable real-time protection and reschedule scans to keep the Antimalware Service Executable high CPU and memory utilization at usual levels. Here is how to do this –
- Press WINDOWS + R and type taskschd.msc. Press Enter.
- On the left-hand side, expand Task Scheduler Library, then Microsoft, and then Windows.
- Locate Windows Defender in the list and double-click on it.
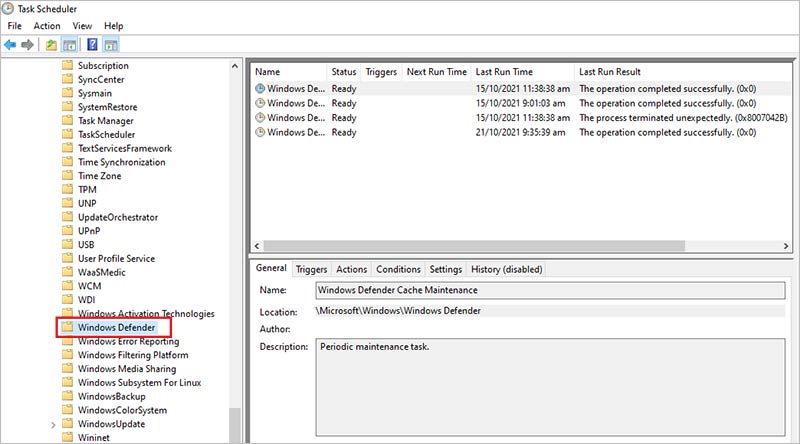
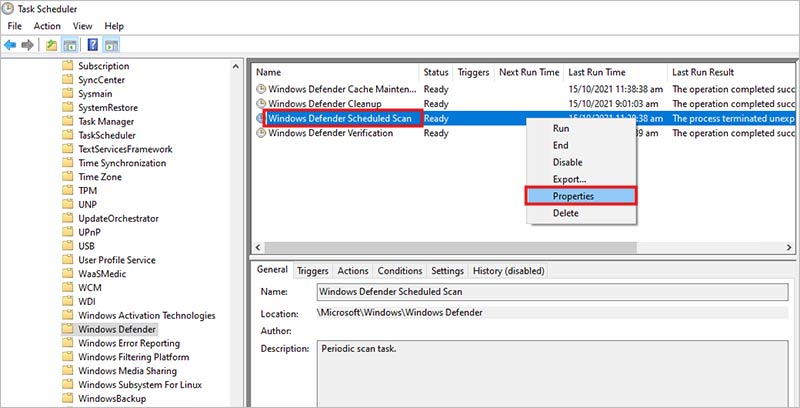
- On the right-hand side, right-click on Windows Defender Scheduled Scan and click on Properties in the context menu.
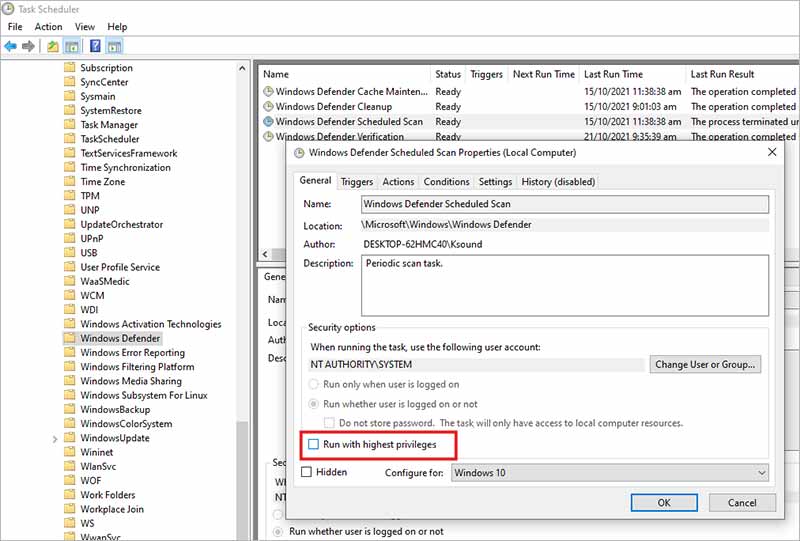
- In the Properties window, click on the General tab and uncheck the Run with highest privileges option.
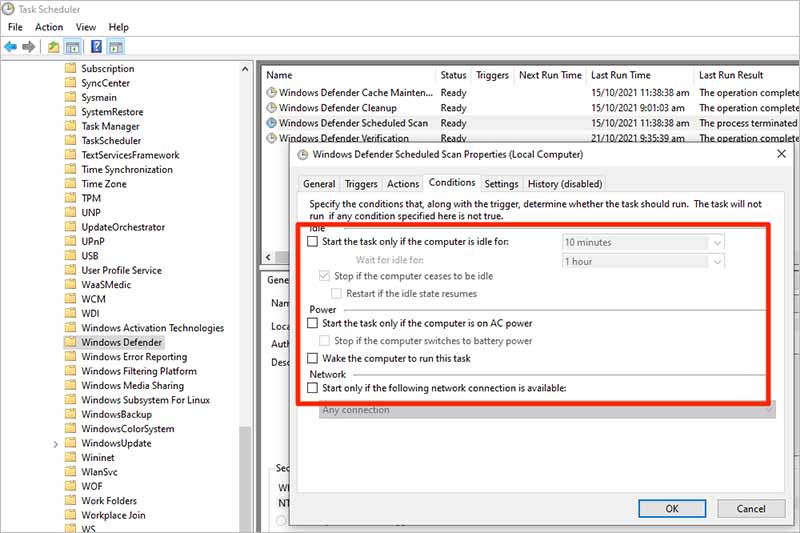
- Navigate to the Conditions tab and uncheck all the boxes there.
- Then, click on the Triggers tab and click on New…
- In the New Trigger window, you can customize the frequency, scan time, and date of the scan.
- Click on OK.
- Restart your computer.
Doing so should lower the Antimalware Service Executable high CPU or memory usage issue.
Method 5: Turn Off Windows Defender Using Local Group Policy Editor
You can turn off the Window Defender once and for all to eliminate the Antimalware Service Executable high CPU utilization issue. However, you should make sure that you have a reliable third-party antivirus software to safeguard your computer from malware. Carefully follow the steps as mentioned here –
- Press WINDOWS + R and type gpedit.msc. Press Enter.
- In the Local Group Policy Editor window, expand the following in the left pane – Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components.
- Look for Windows Defender Antivirus in the list and select it.
- In the right pane, double-click on the Turn off Windows Defender Antivirus.
- In the next Window, choose the Enabled option.
- Click on Apply and then OK.
- Restart your computer to apply the changes.

Pro Tip –
The above-mentioned methods should help you resolve the high memory utilization issue with the Antimalware Service Executable. It is a known fact that high CPU usage could lead to random system crashes, computer stuck in a boot loop, or even data loss in severe cases.
If the MsMpEng.exe issue has caused high memory and CPU usage on your computer and led to crashes causing unbootable computer, you can recover your data from it using a professional data recovery software like Stellar Data Recovery Professional.
This is a powerful tool that can easily help you retrieve your lost data in all kinds of data loss scenarios like data corruption, formatting, unbootable computer, and more. It supports recovery of almost every type of file ranging from .docx to CR2 and CR3 files. It allows affected users to use a bootable media for recovering lost files & data from a crashed or unbootable computer.
Final Thoughts
The Antimalware Service Executable or MsMpEng.exe is an important process of Windows Defender. It is a background process that keeps an eye on malicious viruses and keeps them out of your system. While it is a critical system process, it can sometimes run into problems causing issues related to high CPU and memory usage.
In this post, we discussed the Antimalware Service Executable high system resource utilization issue and explained various methods that can be employed to fix this. We also looked at a professional data recovery software and how it can help you retrieve data in case your system is rendered unbootable due to unprecedented system crashes. We hope this guide helped you resolve the pressing issue at hand and get your computer back to normal usage patterns.
FAQs
What is MsMpEng.exe?
MsMpEng.exe is a background process of Windows Defender that looks for malware and viruses in the files and quarantines them.
Was this article helpful?