Basics of Exchange file types- EDB & Log
Exchange Server Databases are stored in .edb files. Another is Transaction logs that is use for Exchange database recovery.if Exchange database was not shut down properly, and some transactions might not be committed. You can use these logs to replay uncommitted transactions to a database. Apart from that, the transaction logs in the Exchange Server database folder are not just log files, these logs purpose is to act as a buffer along with the memory of the server, for data to be temporarily stored until it is committed to the database after a successful backup.
There are various ways to restore an Exchange Server database. You can use the Windows Server Backup feature to restore the Exchange database from backups stored on local, cloud, or network storage devices. One may also use third-party Exchange-Aware backup software or applications to create regular backups and restore the Exchange database when the server fails, or the database gets corrupt or damaged.
In addition, you may also try to repair or recover a corrupt or damaged Exchange database using EseUtil or an Exchange recovery software when backups are not available or fail to restore the database.
Things to Keep in Mind Before Restoring Exchange Database
- Ensure that the backup application you are using is compatible with the Exchange Server version you have installed (Exchange-aware)
- Restoring the whole virtual machine is an issue as snapshots of Exchange Server are not supported
- When restoring, you need to factor in extra resources and administrative effort required in the operation
- Using Windows Server Backup, you can restore from the last successful backup. If your server would fail in the middle of the day and backup is taken at night, restoring from backup will make you loose any data changes from when the backup was taken to the point it failed.
- It’s important that apart from having a proper backup solution, along with the advice of the vendor or supplier, one must ensure that the solution is compatible with the version of Exchange Server installed and its application aware. If the backup is not executed successfully with a VSS backup, the transaction logs will not be committed, thus the logs are not purged. This will end up with the transaction logs filling up the disk space fast.
Reasons to Restore the Exchange Database
There could be many reasons why you (as an administrator) may want to restore an Exchange Server database. Some common ones are as follows:
- Hardware failure
- Malware infection or ransomware attack
- Software issues
- Lost emails, historical data, or deleted mailboxes
- Database corruption or damage
- Server failure
You need to go for restoring an Exchange Server database when there is no way back or no way to recovering from failures or corruption of data.
Steps to Restore Exchange Database using Windows server backup
You can follow the steps below to restore an Exchange mailbox database using the Windows Server Backup service.
Step 1: Open the Windows Server Backup. After opening the Windows Server Backup, select the day to restore. Then, follow the wizard until you reach the Select Recovery Type screen. On this screen, select application.
Step 2: In the next window, you will see a list of all the applications that Windows Server Backup is aware of.
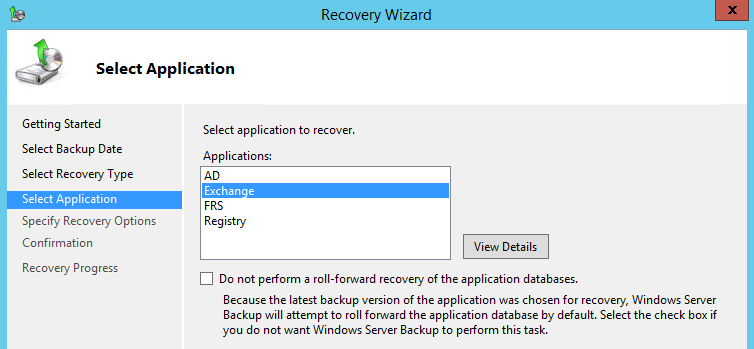
You need to make sure that the application is compatible and aware of Exchange Server. If you do not see the Exchange in the list, it means that there is misconfiguration in your backup software and you will be only able to perform a file level restore.
Note: When restoring an Exchange Server database, you need to make sure that there is ample space in your hard drive.
Step 3: In the next screen, select the Recover to another location option — if you are restoring a mailbox or mail items from the backup. If you are restoring the entire database, select the Recover to original location option.
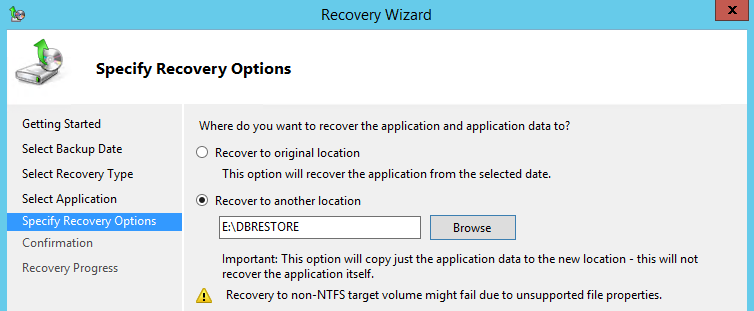
Step 4: After the Exchange restore is complete, you will notice that the destination is populated with the same folder structure.
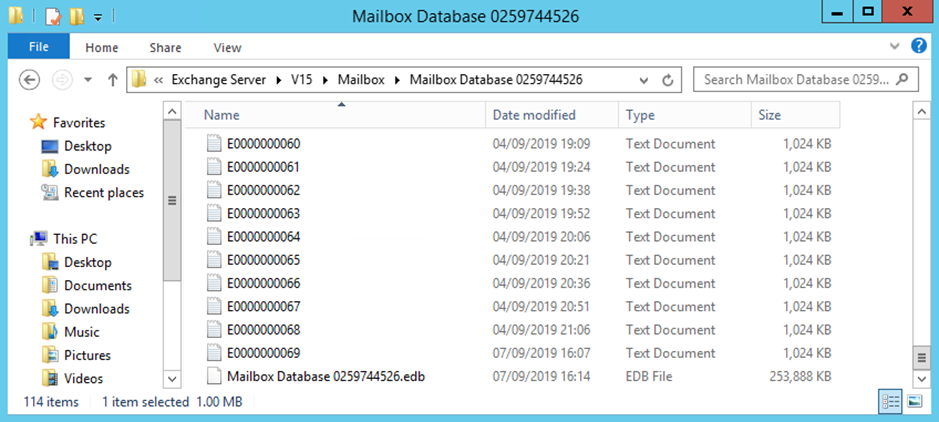
When an Exchange data recovery process is done from a server backup, one would need to check if the database restored is healthy. One cannot just mount the database and it will work. One might encounter an error during the mount of the database and apart from the database restore being corrupted, there could be possibilities that there is issue with the Exchange Server installation, logical corruption, and even physical damage on the server. After a successful recovery it is recommended to run a smooth recovery process with EseUtil to ensure that any small corruption is cleared out.
To confirm or check the Exchange database status, run EseUtil with the /mh switch. For instance,
eseutil /mh databasepath dbname.edb="" /databasepath
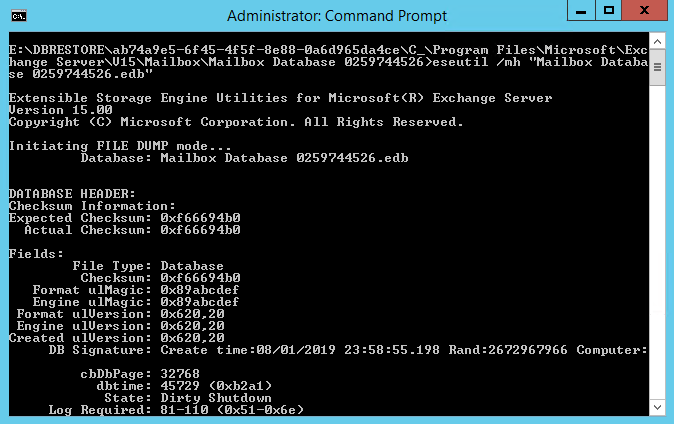
If it is showing in Dirty Shutdown state, you need to recover Exchange database using Eseutil or Third party Exchange database recovery software.
Exchange Database Recovery using Eseutil
By using EseUtil, you can recover the database to Clean Shutdown state and then use Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or Mount-Database cmdlet in Exchange Management Shell (EMS) to mount it. EseUtil has two methods of recovery – soft recovery and hard recovery.
First, you can perform the soft recovery by using the eseutil/r switch.
ESEUTIL /R E00 /d /I /L "E:\RecoverDB\MBX\LogFiles "
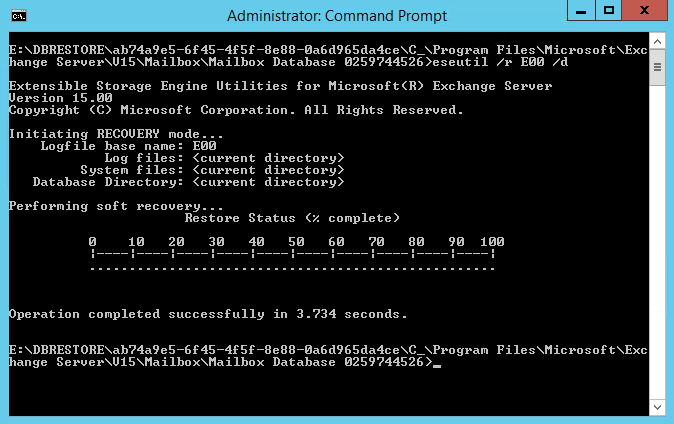
- The recovery process may take some time, depending on the size of the database. After the recovery is complete, you need to run the EseUtil with the /mh switch to confirm that the database is in Clean Shutdown. If the database is still in Dirty Shutdown, you need to run the eseutil hard recovery.
You need to know that this process will wipe any data which is deemed as corrupted and there is no guarantee that this will fix the problem. If you’ve recovered the database to its original location, you can go ahead and mount the database. The users can now access their mailbox. However, as mentioned earlier, they will lose all the data between the backup and the crash.
Restoring using the Recovery Database
If you have restored Exchange database from backup to recover an email or mailbox, you need to create a Recovery Database (RDB). Once the database is restored to another location and its state is in Clean Shutdown, run the below command in the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) to attach the database.New-MailboxDatabase –Name RecoveryDB –Server EX01 –EdbFilePath
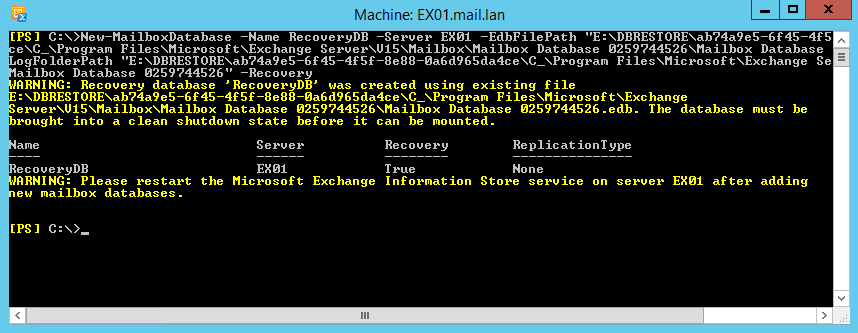
When you run the above command, you will get two warnings:
- The database must be in Clean Shutdown before use.
- Restart the Information Store for the changes to take effect.
Step 5: While running the Get-MailboxDatabase, ensure that the Exchange Recovery Database is mounted and available.
When you have restarted the Information Store Service, you will be able to export the mailboxes to PST by using the New-MailboxExportRequest PowerShell cmdlet.
Exchange database recovery using Stellar Repair for Exchange
As you can see, restoring a mailbox database could take a lot of time and resources. Sometimes, you need to go through all this trouble to restore a single mailbox. Apart from this, you need to take into consideration that the database is not portable and the Exchange Server must be online to restore a mailbox.
However, you can do this in much less time and without any hassle by using Exchange database recovery software such as Stellar Repair for Exchange. You can easily open any Exchange Database (EDB) of any Exchange Server version from 5.5 to 2019, with a few clicks. The application allows you to granularly export emails, data, public folders, and whole mailboxes to PST and other formats. You can also use the application to export directly to a live Exchange Server database or Office 365 tenant.














 5 min read
5 min read