Exchange Server uses databases to store mailboxes, public folders, and other resources of your Exchange Server. Most of the configuration is stored in the Active Directory Schema but all the data resides in the databases.
An Exchange Server database is made up of the .EDB (Exchange Database) file and the transaction logs. It is to be noted that the transaction logs form an integral part of the Exchange Server ecosystem as these are not just normal log files that can be deleted anytime. Exchange Server uses the transaction logs to keep data in them, which are then merged into the database and purged after a successful backup.
Exchange Server Standard offers the possibility to have up to five mailbox databases running and mounted in the system. However, if your business needs more than five mailbox databases, you must opt for the Exchange Server Enterprise license.
From time-to-time, you need to either split the data into multiple databases or maybe remove some unwanted Exchange databases from your system. Removing a database from Exchange Server - be it 2010, 2013, 2016 or 2019 - is not just by using a delete button. If you just delete a database, you most probably get the below error.
This mailbox database contains one or more mailboxes, mailbox plans, archive mailboxes, public folder mailboxes or arbitration mailboxes, Audit mailboxes. To get a list of all mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database. To get a list of all mailbox plans in this database, run the command Get-MailboxPlan. To get a list of archive mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database -Archive. To get a list of all public folder mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database -PublicFolder. To get a list of all arbitration mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database -Arbitration. To get a list of all Audit mailboxes in this database, run the command Get-Mailbox -Database -AuditLog. To disable a non-arbitration mailbox so that you can delete the mailbox database, run the command Disable-Mailbox. To disable an archive mailbox so you can delete the mailbox database, run the command Disable-Mailbox -Archive. To disable a public folder mailbox so that you can delete the mailbox database, run the command Disable- Mailbox -PublicFolder. To disable a Audit mailbox so that you can delete the mailbox database, run the command Get-Mailbox -AuditLog | Disable-Mailbox. Arbitration mailboxes should be moved to another server; to do this, run the command New-MoveRequest. If this is the last server in the organization, run the command Disable-Mailbox -Arbitration -DisableLastArbitrationMailboxAllowed to disable the arbitration mailbox. Mailbox plans should be moved to another server; to do this, run the command Set-MailboxPlan -Database.
Although the error message doesn’t say much, there are some important tasks to do before you remove a mailbox database. To get started, you need to first make sure that there are no user mailboxes, shared mailboxes, public folders, or any other resource in your database. Then, there are some system mailboxes that you need to remove before you can delete the mailbox database. These system mailboxes may include:
- Arbitration mailboxes
- Monitoring system
- Audit logging
- Public Folders
- Archives
Steps to Remove Mailbox Database in Exchange Server
After making sure that all mailboxes have been moved, you need to run the below PowerShell commands in the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) to remove Exchange database.
Get-Mailbox -database "database name="""
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -archive
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -arbitration
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -publicfolder
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -monitoring
Get-Mailbox -database "database name=""" -auditlog
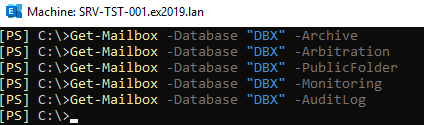
If there are still the above-mentioned mailboxes, you would need to move them to another database.
If you need these mailboxes, move them to another database by using the following command:
Get-Mailbox -Database "source database="" name="" " -AuditLog | new-moverequest –targetdatabase "destination database="" name="""

If all goes well, you should be able to remove Exchange database. If this fails, there is another option. It involves using the Active Directory Schema editor. However, it is to be noted, if you use Active Directory Schema, there is no undo button and repercussions can be catastrophic if something goes wrong.
The method involves the below steps:
- Right-click on Start.
- Click on Run and type msc.
- Open Configuration/Configuration Services.
- Open Microsoft Exchange/ "your organization"
- Open Administrative Groups and Exchange Administrative Groups.
- Open Databases and delete the desired databases from the list.
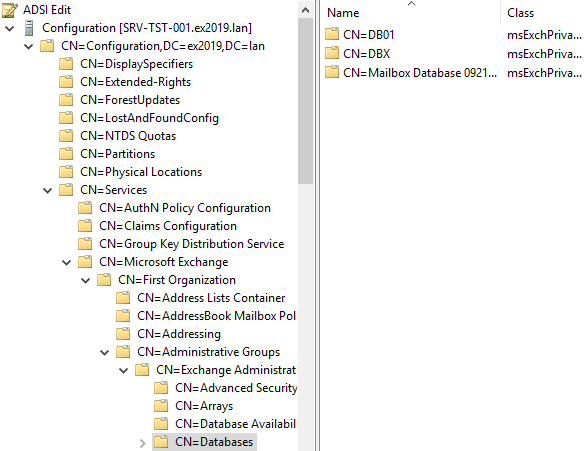
This will remove all the mailbox and public folder databases from the system.
To Wrap Up
After removing the Exchange database, if there is any corrupted data or you missed some data during the move, you will not be able to retrieve any. In such a case, you can use Stellar Repair for Exchange. By using this software, you can open corrupt databases from any version of Exchange Server, without the need of an Exchange Server. You can browse the database and granularly export anything to PST and other formats. You can also export directly to a live Exchange Server database or Office 365 tenant.














 6 min read
6 min read





