In Exchange Server, each mailbox has the normal container for the user folders, containing Inbox, Sent Items, Calendar, etc. In each mailbox, there is a system folder, which is called non-IPM (Interpersonal Messaging). It contains folders and items which are not visible to the user and used by the Exchange Server.
The Recoverable Items folder in the mailbox is the third line of recovery of an email item. In Outlook, when an email is deleted, it goes to the Deleted Items folder.
If the Deleted Items folder is emptied, the items go to the system folder, called Recoverable Items folder. It is like a second Recycle Bin for the mailbox. From here, the user can recover items which were deleted from the Deleted Items folder.
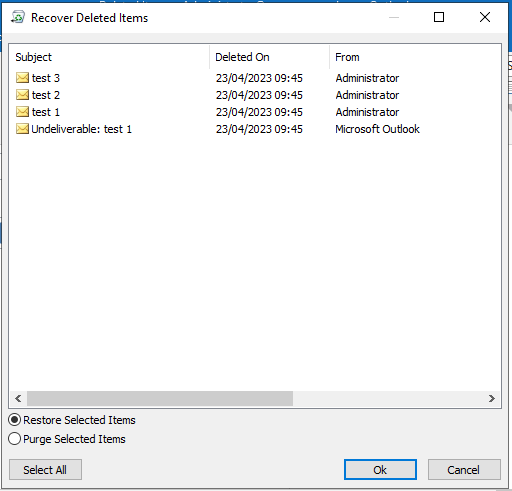
If the user uses the Shift + Delete keys to delete an email, it will bypass the Deleted Items folder and go straight to the Recoverable Items folder.
What happens when a user purges data from the Recoverable Items folder?
In a normal scenario, if an email is deleted or purged from the Recoverable Items folder, it will be permanently deleted. In Exchange Server, there is a feature called LitigationHold. The LitigationHold holds a copy of the items either indefinitely or for a specified number of days by the business. The Litigation Hold is enabled either via the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or the Exchange Management Shell (EMS). After it is enabled, it will take approximately 60 minutes to be activated.
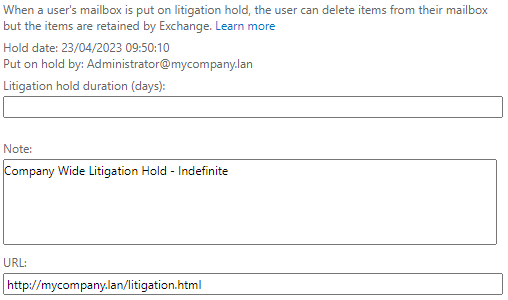
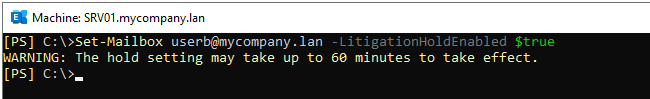
To enable this feature, you can use the below command in PowerShell.
Set-Mailbox \user address="" -LitigationHoldEnabled $true /user
When emails are purged from the RecoverableItems folder, these emails would still be recovered through eDiscovery by the Exchange Server admins, if LitigationHold is enabled.
What does the Recoverable Items folder hold?
Apart from the deleted items, the RecoverableItems folder holds the following items.
- If an In-Place Hold or LitigationHold is enabled, the folder will hold Versioning of the items, containing the original and modified copies of the deleted items. Let’s say, a user deletes an email, moves it to the RecoverableItems folder, recovers it, changes it, and puts it back in the folder. Then, the folder will keep all the versions, but keep them hidden from the user.
- When the RecoverableItems folder is purged, the items will still be kept if a Litigation Hold is enabled, while keeping them hidden from the user.
- If the Mailbox Audit Logging is enabled for the mailbox, the audit subfolder is kept with all the audit log entries of the mailbox.
- Discovery Holds folder will keep all the items which hold query parameters and hard deletions. This is not visible to the user. It is only created when an In-Place Hold is enabled.
How long does it hold the items?
Emails or items, which are deleted, will be kept in the Deleted Items folder, until the retention period of 14 days is passed. This is a default item retention period, which can be increased to 30 days. The permanent deletion of items from the Recoverable Items folder is subject to the company and is based on size (for example 20 GB).
There is also an option that keeps the deleted items until a full backup is done. If not enabled and the retention period is reached, the item will be permanently removed.
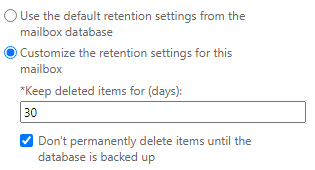
If the option “Don't permanently delete items until the database is backed up” is enabled, although the retention period is reached, the email will be kept until the Exchange Server is fully backed up. After the backup is complete, the items will be removed.
What are the benefits of this feature?
Here are some benefits of the RecoverableItems folder:
- It offers another chance to the user to recover a hard deleted email (in case of mistake), without the administrator’s intervention.
- The RecoverableItems folder has its own storage quota.
- It helps in tracking of changes of items.
- With the LitigationHold enabled, it will hold items indefinitely.
- When a mailbox is moved to another mailbox database, the RecoverableItems folder is moved as well and nothing is lost.
Is there an easy way to recover data after an Exchange Server crash?
In case of a crash, malicious attack, or a hardware/software failure, you need to rebuild the Exchange Server. But if the databases are corrupted, there isn’t much to do apart from recovering from a previous backup. However, this will result in data loss.
In such cases, you can use a specialized and renowned Exchange Server Recovery application, named Stellar Repair for Exchange. With this application, you can easily open multiple EDB files (healthy or corrupted), from any Exchange Server with no size limit. You can browse through the normal folders of the users in their structure. You will also be able to view the hidden system folders, including the Recoverable Items folder and its subfolders. You can granularly export the data to PST or other file formats. You can also export directly to another live Exchange Server database of any version or even to an Office 365 tenant.














 5 min read
5 min read