Your Windows PC uses a hard drive to store and retrieve data. A hard drive is an electro-mechanical storage device that stores data in sectors and blocks on a rotating platter surfaced with magnetic material, and the data is retrieved randomly through a read-write magnetic head.
When you delete a file on your computer, the Windows operating system doesn't remove the file from the hard drive by writing random 0s and 1s on the storage sector or block. Instead, to speed up computing, the OS simply updates the hard drive's file system and marks the pointer to the storage area containing the file as free. Any new file can overwrite the free storage area. So, after data loss, you must stop using the drive immediately to avoid any overwriting on the deallocated storage space. You may resume hard drive usage after performing data recovery.
The following sections describe how data loss can happen on a hard drive and what all you can do to recover your lost data from the hard drive.
Common Data Loss Scenarios on Hard Drive
- Deletion is the most common scenario for data loss on a hard drive. You usually delete your file (document, photo, video, email message, audio, or archive file) by pressing the Delete key, then later empty your Recycle Bin without peeking into its stored content, or use the Shift + Delete key combination to remove a file from your PC. Later, you realize, you need those deleted files back and suffer from data loss.
- Formatting is another likely scenario for data loss on a hard drive. Usually when you format your PC at the time of installing Windows or format a non-boot volume or external hard drive, you back up its stored content beforehand. Data loss occurs when you don't have a backup and the hard drive is formatted either accidentally or purposefully.
- Corruption of a hard drive is yet another data loss scenario. When an internal hard drive gets corrupted, your PC won't boot due to damage in the master boot record or boot configuration data. For the external hard drive, corruption in the file system makes it inaccessible but is visible in Disk Management as RAW. If partition data turns corrupt, one or more drive partitions are lost. Reasons for corruption can be a power outage, virus, bad sectors, improper ejection of an external hard drive, incomplete data saving on the hard drive, etc.
- Crashing is also another common data loss scenario on a hard drive. When system software crashes, Windows throws a blue screen of death (BSOD) and the internal hard drive data becomes inaccessible. Also, when any application software freezes or stops responding, ending the task by using Task Manager won't save the app's unsaved data, resulting in data loss.
- Hardware Failure is an inevitable data loss scenario on a hard drive. A hard drive fails automatically at the end of its lifespan. But it can also fail earlier due to other reasons such as mishandling, power surges, fire, or water that creates bad sectors, damages its internal components, or makes the drive dead. Data loss due to severe physical damage to a hard drive can't be avoided but the hard drive's backup can act as a savior in such a case.
Methods to Retrieve Data from Hard Drive
1. Use Recycle Bin
Recycle Bin stores the records of your deleted files temporarily. So, when you delete a file on your PC by using the Delete key, you can immediately press the Control + Z key combination to undo the operation. If you've deleted your file earlier, then you can't undo it. In such a case, open the Recycle Bin to look for deleted file/s. When you find your file/s, right-click on it, and select Restore to return the file/s to original locations.
This method won't work in case you've used the Shift + Delete key combination, emptied your Recycle Bin, or deleted a file from an external hard drive, as the file's record is not saved in the Recycle Bin and is removed immediately. Then a backup or a data recovery software can help retrieve your deleted data from a hard drive.
2. Use an App's Inbuilt Recovery Feature
Applications such as Microsoft Outlook stores deleted emails on your hard drive in the Deleted Items folder. If you've deleted an email message accidentally on Outlook, immediately press the Control + Z keys to undo the deletion. Or else, go to the Deleted Items folder from the left pane of Outlook and drag and drop the message to the Inbox folder.
If the message is also deleted from the Deleted Items folder, then open the Deleted Items folder, and in the Home tab, click Recover Deleted Items from Server. Select the required email message and click OK to get back the deleted message on the Deleted Items folder.
3. Use File History Backup Drive
When you have backed up your PC hard drive before data loss by using File History, you can use the File History backup drive to restore your deleted files. For an external hard drive, File History won't work. In such a case, a clone of the external hard drive, a backup of important files to yet another external hard drive, or a data recovery software can help retrieve your lost data from the external hard drive.
4. Use OneDrive
If you have synced your important folders on your PC hard drive to OneDrive, the proprietary cloud storage drive from Microsoft, you can use your OneDrive account to access your synced data from anywhere, anytime by using the Internet.
5. Use a Professional Windows Data Recovery Software
A professional data recovery software like Stellar Data Recovery Professional can help you retrieve data from your internal or external hard drive that is subjected to deletion, formatting, corruption, or software failure. The steps are as follows:
- Download and install Stellar Data Recovery Professional for Windows on your PC.
- Launch the software.
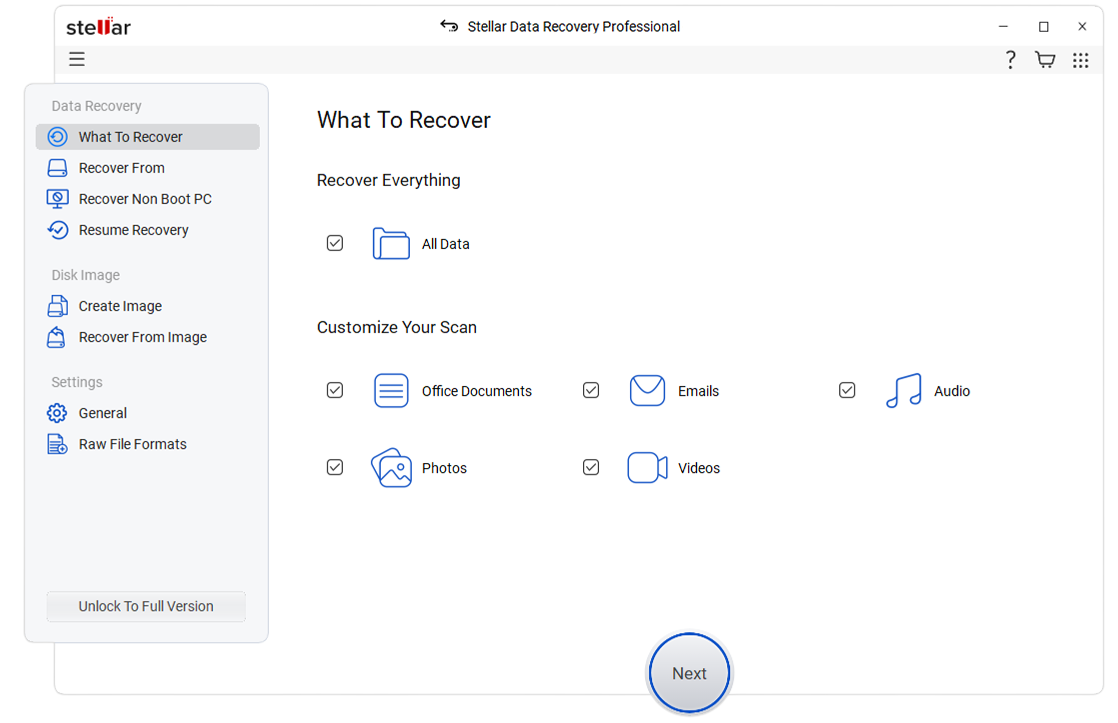
- On the 'Select What To Recover' screen, choose the required types of data and click Next.
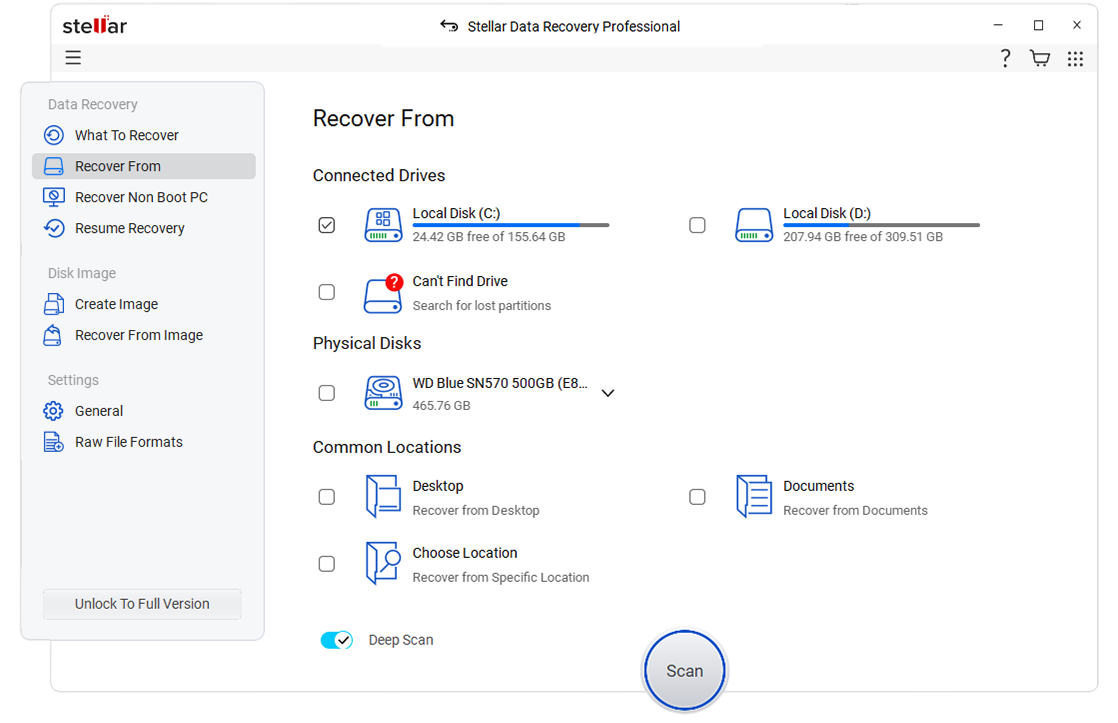
- On the 'Recover From' screen, select the hard drive, toggle on Deep Scan, and then click Scan.
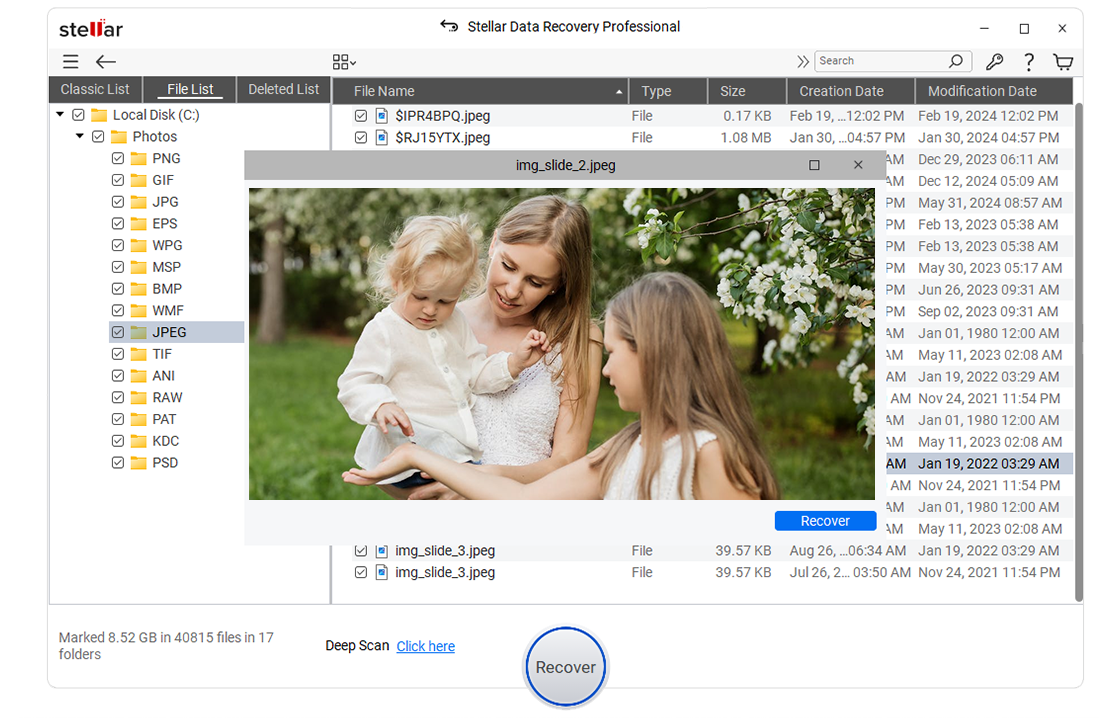
- Once the scan is over, preview the scanned files, select all those that are required, and then click Recover.
- On the dialog box, click Browse to specify a distinct save location preferably an external hard drive, then click Save.
- Once data recovery is over, verify the recovered data from the saved location.
*The demo version of Stellar Data Recovery Professional for Windows allows unlimited free drive scans and file previews. But to save your recoverable files, you need to activate the software. The best part is the software offers a 30-day money-back guarantee, so activate it with full confidence.
To recover data from the hard drive of an unbootable computer, extract the storage device and then connect it to another working computer as an external drive. If the data is accessible, copy all your files to another external storage medium. If the drive is inaccessible, use the recommended software to scan and recover your data.
6. Use Data Recovery Service
Data recovery service is useful in case of failure of a hard drive due to any physical data loss situations. If your hard drive has undergone physical damage, then don't try any unreliable data recovery method. Instead, go for the best data recovery service with the following attributes:
- Has ISO-certified service center
- Uses Class 100 clean room
- Guarantees data recovery after analysis
- Provides secure & reliable service
- Provides complete data confidentiality
- Has no recovery no charge policy
- Provides free shipping of hard drive
Conclusion
Retrieve your lost or deleted data from a hard drive (internal or external) on your Windows 10 computer by looking for your deleted files in Recycle Bin, the application's built-in recovery feature, File History backup, or OneDrive, whatever is applicable in your case.
If none of the above methods work, use Stellar Data Recovery Professional for Windows to retrieve data from your PC or external hard drive. The DIY software is compatible with Windows 10 and supports NTFS, exFAT, and FAT file systems. For physical data loss situations, use a trustworthy data recovery service.















 6 min read
6 min read





