When it comes to storing data, RAIDs (Redundant Array of Independent Drives) are considered to be safer than traditional hard drives. Additionally, RAID offers increased storage capacity, improved performance and/or fault tolerance. There are several types of RAID levels (RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, 10, 01, 50, 05, 06 and 60), having unique characteristics and offering different benefits. However, when deciding on a RAID level, you need to consider the hardware requirements and the characteristics of the RAID level, as these affect storage capacity, data redundancy, and protection against failure.
RAID 0 and RAID 1 are the most basic levels, having their own advantages and disadvantages. However, if you want to have the best of both worlds, you can use them as a nested RAID, i.e. combine RAID 0 and RAID 1. These include RAID 0+1 (RAID 01) and RAID 1+0 (RAID 10). Though both RAID configurations may sound similar, they are not the same. In this article, we will discuss both RAID 01 and RAID 10, and see if there are any differences between these RAID configurations.
What is RAID 01?
RAID 01 is a nested or hybrid RAID level built with two RAID levels—RAID 0 and RAID 1. In this, the array is created as RAID 1 whereas the elements are of RAID 0. In other words, it offers striping, which means the data is spread across the drives in the array, thus offering faster read and write performance. RAID 01 uses the mirroring mechanism that duplicates data to all the drives in the array.
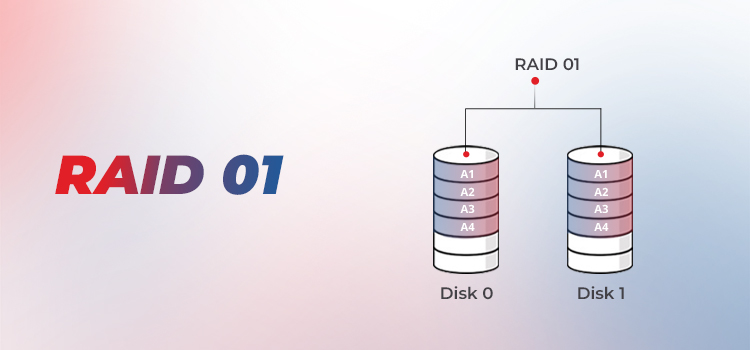
RAID 01 (RAID 0+1) is a mirrored stripe set. In this RAID level, two groups of disks act as a stripe set. A particular write operation sent to one group is also mirrored to another, creating two synchronized stripe sets. This way, this RAID level delivers the RAID 0 performance and redundancy of RAID 1. A minimum of three drives are required to set up the RAID 01. However, four drives are recommended.
What is RAID 10?
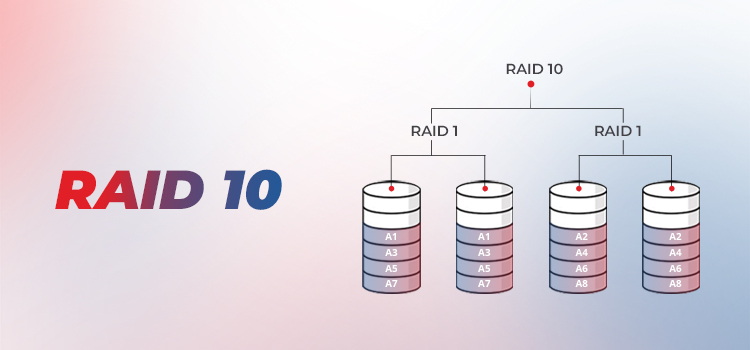
RAID 10 (RAID 1+0) is also configured by combining RAID 1 and RAID 0, which means a mix of mirroring and striping. This helps in achieving faster read and write performance as well as data security. This RAID architecture contains stripe set of mirrored pairs of disks, which means every disk is mirrored to another disk. However, this RAID array offers lower performance than RAID 01. This nested RAID level requires a minimum of four drives.
Differences between RAID 01 and RAID 10
Both RAID 01 and 10 looks almost similar when it comes to read and write speed, performance, and storage space. However, there are a few differences between RAID 01 and RAID 10. Let’s take a look at them:
Fault Tolerance
The major difference between RAID 01 and RAID 10 is that RAID 10 offers better fault tolerance than RAID 01 as RAID 10 is not limited to two groups. For example, if two simultaneous disks fail in the RAID 01 array, the entire array would fail as there are only two groups in total. On the other hand, this is not the case with RAID 10 as every disk in the array is a mirrored pair. This means if the two disks fails, the entire RAID 10 array would not fail unless the failed disks are the mirrored pairs of each other.
Configuration
RAID 01 is said to be easier to configure than RAID 10, because the mirroring of the disks happens after striping. It means that you can create a stripe set of disks first and then mirror it. On the other hand, RAID 10 array first mirrors the data on the disks and then creates a single stripe set, which is a little complex architecture.
Set Up and Architecture
RAID 10, also called Stripe of Mirrors, requires a minimum of four disks to set up. These disks are set up as pairs. This means when data is stored on one disk in the pair, it is mirrored on the other disk in the pair. In other words the data is stored on two different disks. For example, if you've 8 disks in your RAID 10, then there are 4 pairs of disks.
RAID 01, also called Mirror of Stripes, requires a minimum of 3 disks to set up. However, it is recommended to have at least 4 disks. In this array, data is striped across all the disks in the group. This means each data block is connected with a different disk.
To Conclude
As you can see, both RAID 01 (0+1) and RAID 10 (1+0) are different from each other in terms of how they store data and provide redundancy. Though they both provide redundancy, they are still prone to data loss. You can lose data from RAID 01 and 10 due to reasons, such as drive failure, bad sectors on the drives, controller malfunction, improper RAID rebuilding, etc. So, taking regular backups is always recommended. Data recovery becomes much easier if you have taken backup of your RAID data.
However, if the backup is unavailable, then the only option is to use an advanced RAID data recovery software, like Stellar Data Recovery Technician. The software helps you recover data from inaccessible, broken, or damaged RAID arrays by rebuilding them virtually. It supports recovery from RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, and nested RAID levels (RAID 01 and 10). The software can also retrieve lost or deleted RAID partitions.















 5 min read
5 min read