Standard Redundant Array of Independent Disk (RAID) drives are built by combining multiple Hard Disks Drives (HDDs) to offer redundancy, better read/write performance, and protection against data loss. These RAID drives are built on unique data storage mechanisms, including Striping, Mirroring, and Parity. Although most people are familiar with standard RAID technology, Nested RAID levels are now gaining popularity for their advantages over standard RAID arrays. But what exactly are Nested RAID drives? Read this comprehensive article to understand Nested RAID and how to recover data from these drives in the event of data loss.
Nested RAID Explained
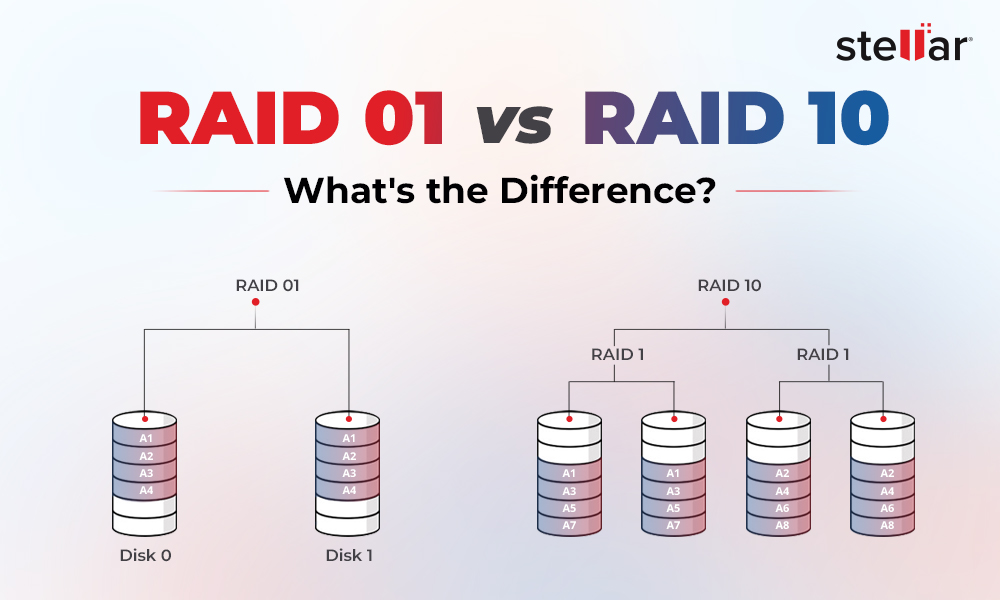
Nested RAID drives are built with two or more of the standard RAID levels, which is why they're also called hybrid RAID. Nested or hybrid RAID drives let you reap the benefits of two standard RAIDs. All hybrid RAID arrays include RAID 0 (Striping), meaning that data is split across multiple disks, thus offering quick read-and-write performance.
The standard RAID drives are numbered using a single number like RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5. On the contrary, the Nested RAID levels are numbered using a series of numbers, including RAID 01, RAID 10, RAID 50, RAID 60, and RAID 100.
Which Nested RAID is best?
When choosing the best-nested RAID, it's important to understand them well. Here, we've discussed the most popular Nested or hybrid RAID levels. You can read their differences and choose the best fit for your needs. Let's start!
RAID 10
This hybrid RAID configuration combines RAID 1 and RAID 0 based on Mirroring and Striping mechanisms, respectively, making it fast and resilient. It can also be called a "Mirrored RAID 0 level" or RAID 1+0. RAID 10 is the safest choice as mirroring duplicates all your data with the combination of striping that splits data across multiple disks. Additionally, it can survive up to 2 disks failure, one from either side. It requires a minimum of 4 disks.
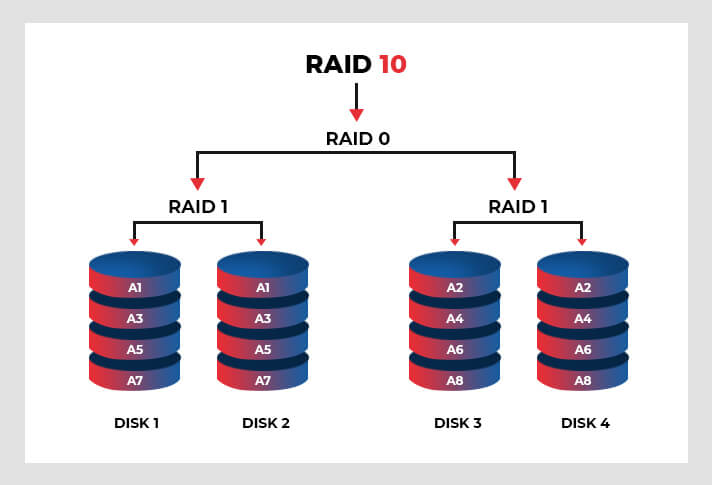
However, the total storage is halved due to mirroring, meaning that if you use 4 1 TB drives while setting up RAID 10, it will eventually offer you 2 TB usable storage. But, if you require hardware-level data protection with quicker read-write data storage performance, RAID 10 is the best option.
RAID 50
RAID 50 is also called RAID 5+0. This array offers the benefits of both RAID 5 and 0 by following the Parity & Striping mechanism. It needs at least six disks to set up RAID 50 in a nested environment. It can support a maximum of 48 disks in single or multiple mirrored arrays of RAID 5. With this Nested RAID level, you can get higher read/write speed performance, faster rebuilds, and better data protection.
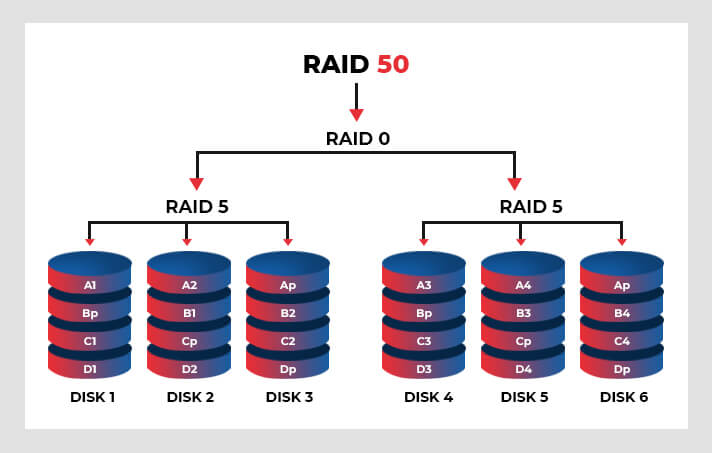
This hybrid level can withstand up to 4 disks failure as long as each failed drive occurs in a different RAID 5 array. RAID 50 is best used for handling high request rates with high data transfer and lower disk cost than a RAID 10 level. Considering that it requires 6 disks to set up, it is said to be an expensive hybrid RAID configuration.
RAID 60
RAID 60 or RAID 6+0 combines the dual parity of RAID 6 and block-level striping of RAID 0 array. This nested RAID configuration can accommodate 8 or more disks. However, it should only configure more than 16 disks. It can additionally support up to 128 disks. Although it is similar to RAID 50, it offers better redundancy by providing dual drive failure protection.
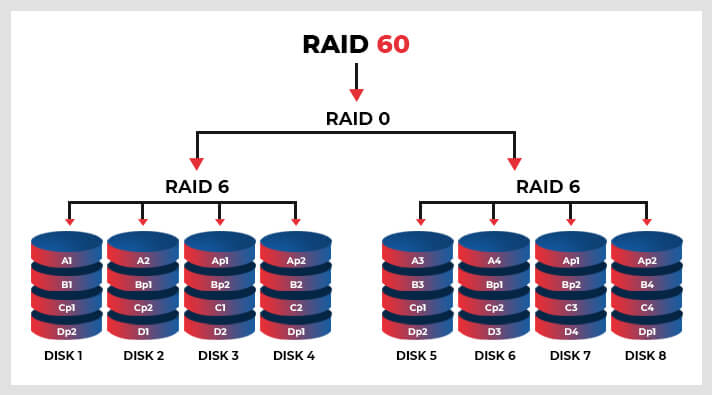
This multi-level disk set of Redundant Array of Disks renders better utilization and is best considered for large-capacity servers, archives, application servers, and backups. However, it has lower write data performance rate.
So, now you can consider all the above aspects and decide which Nested RAID level fits your needs best.
How to Recover Data from Nested RAID Drives?
To recover data from Nested or hybrid RAID drives, we'd recommend opting for reliable and powerful RAID recovery software, such as Stellar Data Recovery Technician. It is a DIY (Do-it-Yourself) software that helps you virtually rebuild and recover data from broken, damaged, corrupt, inaccessible, and failed RAID arrays in just a few clicks, be it Standard or Nested RAID. It can even build bootable USB media to recover data from unbootable or crashed PCs. The software is compatible with Windows 7, 8, 10, and 11 and can efficiently restore data from hardware and software-based RAID drives.















 5 min read
5 min read