The Get-MailboxServer is a PowerShell cmdlet that you can run in the Command Prompt or the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) to retrieve the information about the mailbox servers. You can run the cmdlet in Exchange Server 2010 SP1 and later versions.
In this article, you will learn how to use the Get-MailboxServer cmdlet with or without various parameters and switches in an on-premises Exchange Server 2010, 2013, 2016, and 2019.
Using Get-MailboxServer Cmdlet in Exchange Server
Before using the Get-MailboxServer cmdlet, you must assign the following roles and permissions to the user account responsible for the task.
- Database Copies
- Databases
- Exchange Servers
- View-Only Configuration
To assign the roles and permissions, open the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) and run the New-ManagementRoleAssignment cmdlet.
New-ManagementRoleAssignment –Role "Organization Management" –User Administrator
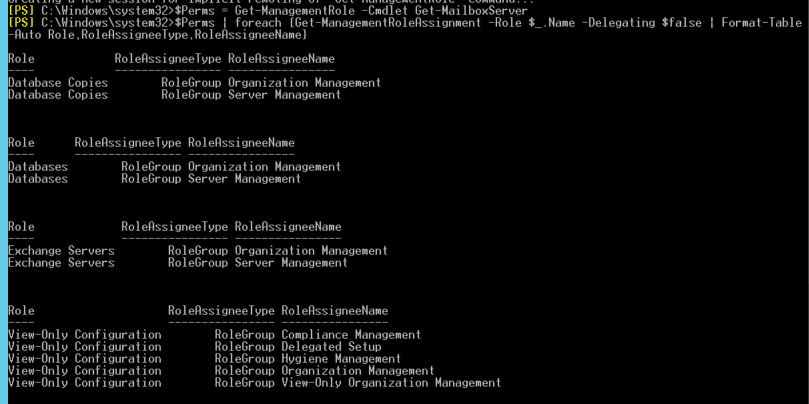
You may also use the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) to assign the required roles and permissions.
Once the roles and permissions are assigned, you can run the Get-MailboxServer cmdlet in the Exchange Management Shell.
Get-MailboxServer Cmdlet Parameters and Switches
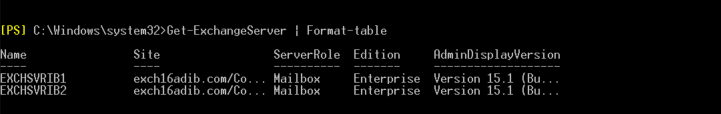
You may run the Get-MailboxServer cmdlet with or without additional parameters or switches. Based on the command, the Exchange Management Shell (EMS) displays the information about the servers in your Exchange organization. For instance,
Get-MailboxServer | ft
You can use the -identity parameter with Get-MailboxServer to specify the mailbox server name and check the information about a specific Exchange Server. For instance,
Get-MailboxServer –Identity EXCHSRVIB1 | format-table

To get all the details of mailbox servers in your Exchange organization, you can use the pipe (|) and fl switch with the command.
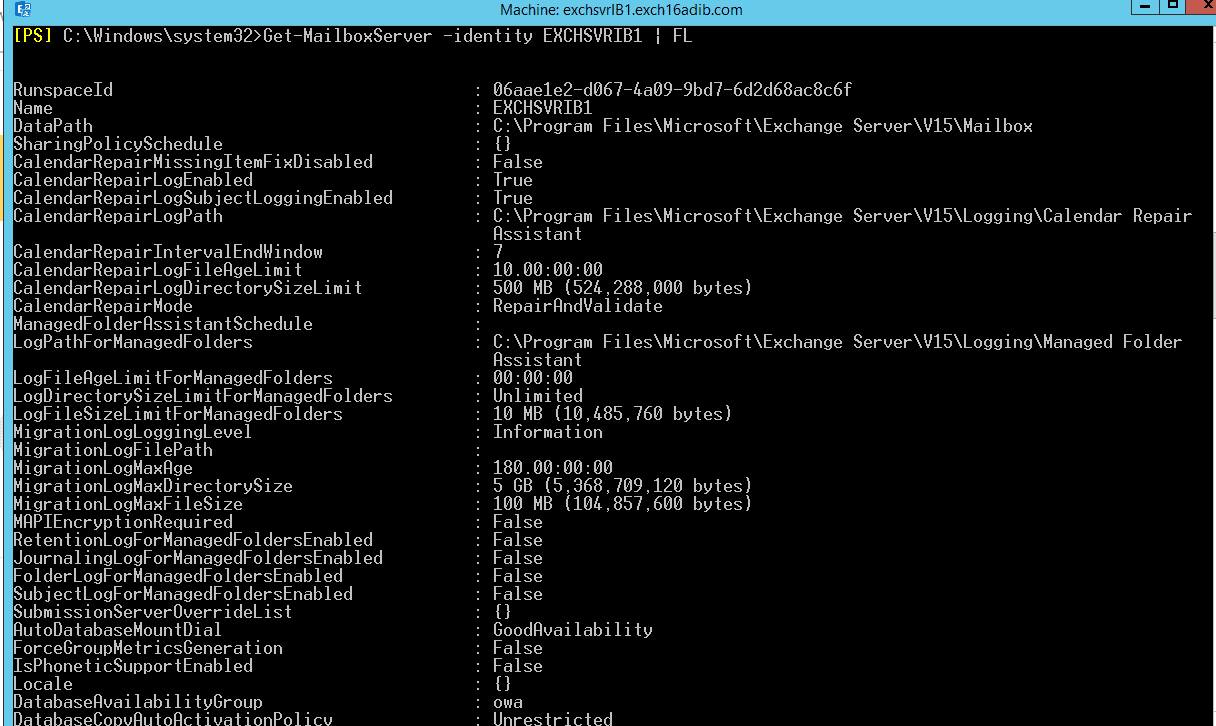
Get-MailboxServer –Identity EXCHSVRIB1 | fl
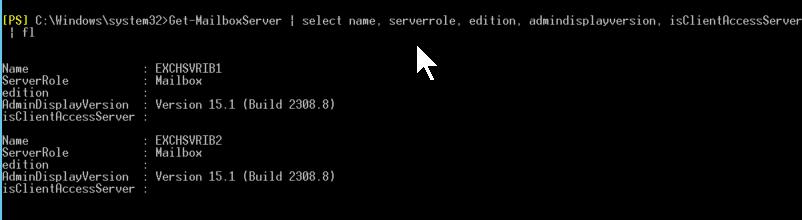
To get specific information about all the servers, such as their roles, editions, versions, etc., run the following command in the EMS.
Get-MailboxServer | select name, serverrole, edition, admindisplayversion, isClientAccessServer | fl
You can run these commands in your organization with Exchange 2010 SP1, 2013, 2016, and 2019, including mixed environments.
To retrieve the server attributes in Exchange Server 2007 and 2010, you can run the following command:
Get-MailboxServer | select name, serverrole, edition | fl
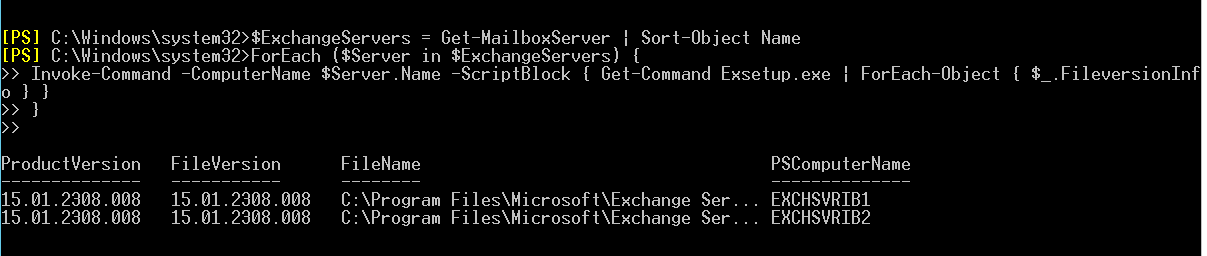
Additionally, you can run the below script with the Get-MailboxServer cmdlet to view the latest Security Updates installed on the server. For instance,
$ExchangeServers = Get-MailboxServer | Sort-Object Name
ForEach ($Server in $ExchangeServers) {
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $Server.Name -ScriptBlock { Get-Command Exsetup.exe | ForEach-Object { $_.FileversionInfo } }
}
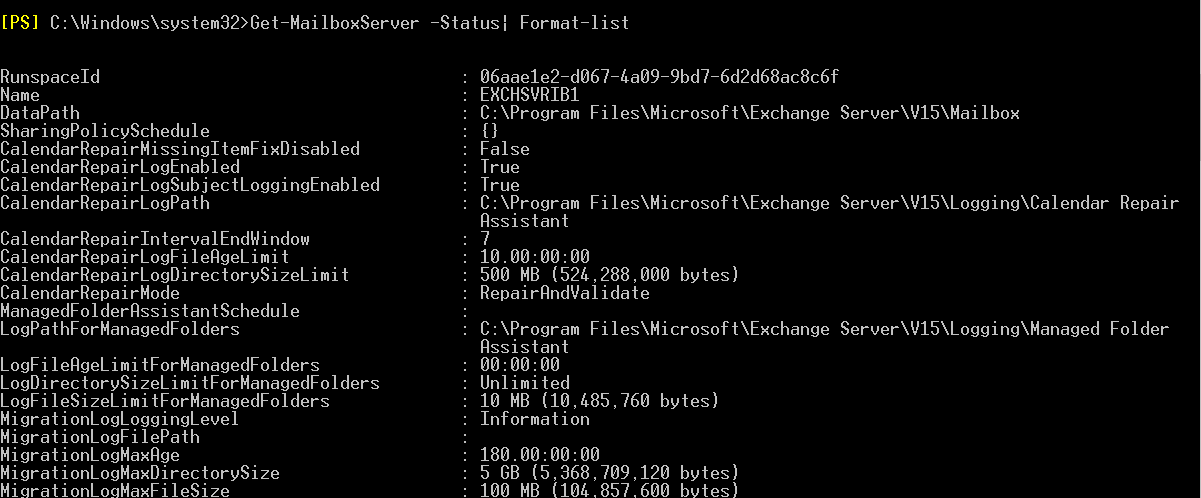
Using the -Status switch, you can gather all or specific information related to the Exchange Server, including available free space, backup progress, database mount status, online maintenance progress, etc.
For instance,
Get-MailboxServer –Status| Format-list
Get-MailboxServer –Status| ft name, server, BackupInProgress, Mounted, OnlineMaintenanceInProgress
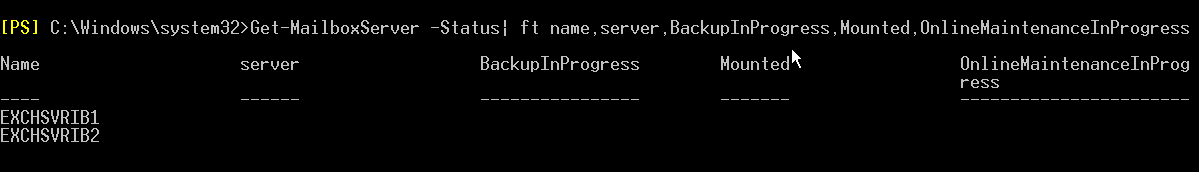
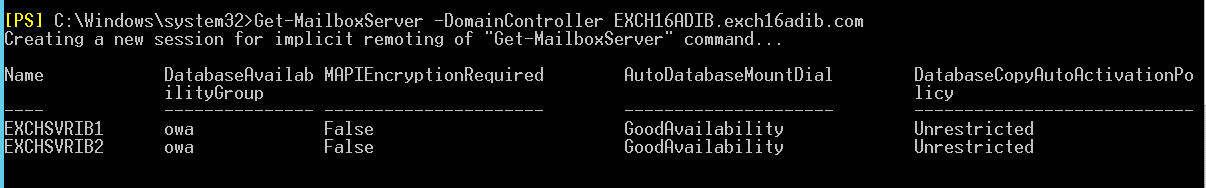
Similarly, you can use the -DomainController parameter to specify the Domain Controller (DC) and read information from Active Directory (AD). You must mention the Domain Controller using its Fully-Qualified Domain Name (FQDN). For example, dcXX.xyz.com.
Get-MailboxServer –DomainController EXCH16ADIB.exch16adib.com
The command can be used in different ways based on the information you want to retrieve to manage the Exchange Servers in a database availability group (DAG) environment. Based on the info received, you can execute other cmdlets to manage, fix, or restore the member Exchange Servers.
Conclusion
In this article, you have learned how to use the Get-MailboxServer PowerShell cmdlet. Administrators can use the cmdlet to check the server status, detect problems, take actions to fix issues if any, and ensure uninterrupted email flow. In case you detect issues with your Exchange Server or the server has failed, you can try to restore it using the recovery installation method or use an Exchange server recovery software, such as Stellar Repair for Exchange. The software can help recover all mailboxes from the database files on failed Exchange Server, including corrupt databases, and export them to a new or existing database on another live Exchange Server or Microsoft 365 tenant directly in a few clicks.














 5 min read
5 min read