RAID, which stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drives into one or more logical units. A RAID volume provides data redundancy, performance, and data storage reliability. RAID is available in multiple levels, including RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 5, and RAID 6. Some of these offer more data redundancy than others, which comes down to the question i.e., how RAID levels store data?
Knowing the storage mechanism of every RAID level could be the first thing that may help you decide which RAID level is ideal for you. So, let's start with that.
How RAID Levels Store Data?
RAID levels are the set of RAID configurations, which uses three techniques to read and write data from the system hard drives called – Striping, Mirroring, and Parity.
Striping (RAID 0)
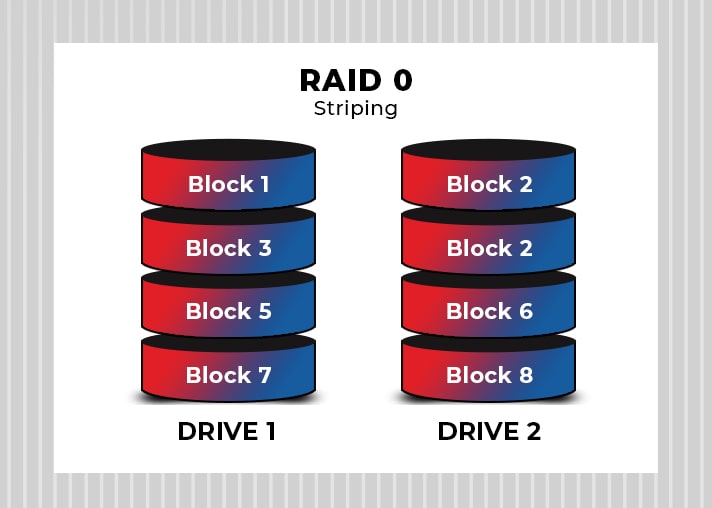
RAID 0 is based on striping configuration, which is built using several disks of different sizes. However, the main thing to focus here is that the storage space added to the disks is limited only to the smallest disk size. Multiple disks can be accessed in this configuration as the data is split into block sizes written across the disks one by one. This way, it allows quick read/write functions.
Mirroring (RAID 1)
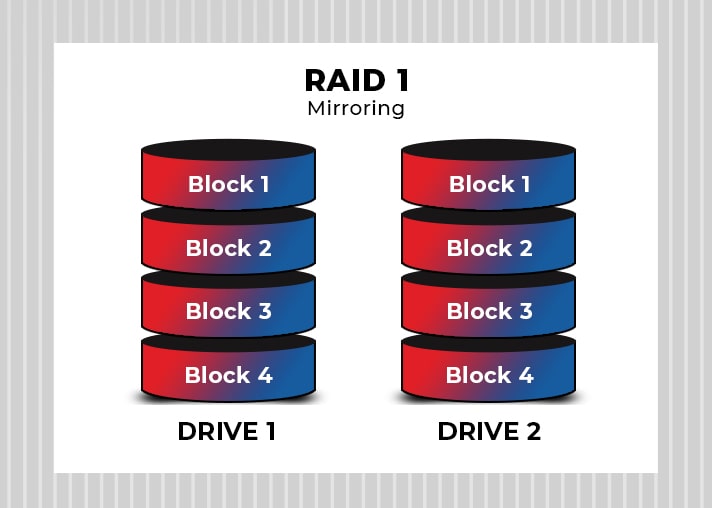
RAID 1 follows the mirroring mechanism, replicating the data to two or more disks. The data on the blocks are copied and mirrored to multiple drives, meaning it offers excellent read speed but not writing speed, as it takes time to copy the information on each drive. It also doesn't provide parity striping; hence can survive only up to one disk's failure.
Parity (RAID 5)

RAID 5 follows the parity mechanism, a way to protect your data without having a complete duplicate of your data. There are 'parity drives in this configuration, unlike RAID 0 and RAID 1. It needs at least three disks to function. This configuration splits the data into two parts, and the third part contains the 'Parity data,' meaning the combination of the data stored on two other drives. But the parity information doesn't remain on single disks; it spreads on every disk, making every disk a parity drive. It means you can retrieve data even one of the drive fails.
Read more: How can you recover data from RAID 5 with two failed drivesOther RAID levels are available, such as RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 4, RAID 6, and RAID 10. All of them follow the above-discussed mechanisms. Below, we’re covering the features with pros and cons of the most popular RAID levels, including:
- RAID 0
- RAID 1
- RAID 5
- RAID 6 and,
- RAID 10
How to Choose the Right Level for the RAID system?
Now that you're familiar with the RAID levels, multiple other factors are essential to decide how to choose the right level for your RAID system.
Capacity Needs:
Capacity is one of the primary factors which may affect your choice of RAID level. Different RAID levels result in different amounts of net usable space that remains after accounting for RAID overhead.
RAID 0:
RAID 0 offers excellent capacity since there is no parity data and mirroring available. You can get full use of the entire disks in the array.
RAID 1:
You can take a 50% capacity hit with RAID 1 as it retains a mirrored copy of the data. It carries the most significant capacity penalty. However, sometimes it may often offset by its very own read/write performance.
RAID 5:
RAID 5 is highly popular because of its capacity overhead. It offers one disk's fault tolerance. Even if you encounter two disks failure in a RAID 5 array, you can quickly get back your access to the data stored on it using powerful data recovery software. It will allow you to lose up to 33% of the total raw capacity, depending upon the RAID volume creation.
Read more: How to recover data from RAID 5 with 2 failed drives?
RAID 6:
RAID 6 is also growing in popularity, but it contains a higher capacity than RAID 5. This RAID array needs two disks worth of space to store parity information, meaning you may take 50% capacity hit with four disks in the RAID 6 configuration.
Application Performance Needs:
Some applications are light on Input/Output (I/O) needs, and some thrash the entire day's storage system. You need to make sure that the RAID level you choose should match your workload needs.
RAID 0:
- To store and access the non-critical data
- For gaming, video, and imaging editing
RAID 1:
- For small servers
- To store critical data like accounting files
RAID 5:
- For data warehousing
- Archiving and files and application servers
RAID 6:
- For large critical databases
- Archiving and high availability solutions
RAID 10:
For application servers and quick database servers
Cost:
Achieving the necessary balance between the performance and cost is crucial. Choosing the right RAID level can be a little tricky to attain this balance.
RAID 0
If we see RAID 0 from a performance and capacity standpoint, it has the lowest price range so far. It offers maximized performance with no RAID overhead.
RAID 1
RAID 1 carries a hefty cost from a capacity perspective. But if you see it from a performance perspective, it's slightly low than RAID 0. However, you may lose 50% of your usable space under RAID 1/10. You may retain high-performance levels, making this a popular RAID configuration for various uses.
RAID 5
If you need to add RAID and don’t care much about the characteristics, RAID 5/50 could be one of the best options. As more disks are added to the array, the RAID controller's support of RAID 5 capacity overhead is also not too bad. If you see it from a performance perspective, you may find RAID 5 a bit more expensive than RAID 0, 1.
RAID 6
RAID 6 can result in capacity overhead. It is expensive in every way but offers 50% storage for use similar to RAID 1/10. But as RAID 1/10 carries a hefty write penalty, it may prove to be worse than RAID 6. It uses striping and parity to store the data and withstand two disks' failure. Thereby offering balanced read/write speeds with better redundancy. You can use RAID 6 capacity up to 88% of the combined disk storage.
>But would I be able to recover from failed RAID 6 drives and if yes, how would I do that? Don’t worry! You can get back your access to the RAID 6 data using an easy-to-use yet powerful tool, such as Stellar Data Recovery Technician. This DIY tool is efficient at recovering data of all types including files, folders, documents, photos, videos and audio files, etc. It supports recovery even from lost or formatted RAID 0, 5, and 6 drives. You can download the trial version and try recovering data.
RAID Levels: A Quick Comparison

What about RAID 50 and RAID 60?
Well, the RAID 50 and RAID 60 are nested with the configurations of RAID 5 + RAID 0 and RAID 6 + RAID 0. You will get the feature of both RAID 5 and RAID 6, as well as the high read/ write speed performance of RAID 0. RAID 50 needs at least 4 and can use up to 48 disks in a single or multiple mirrored array of RAID 5; RAID 60 requires a minimum of 8 disks configured as two mirrored RAID 6 arrays.
RAID 50 offers high read speed and medium write speed performance. Its 67-94% of storage space can be used while RAID 60 provides the same read/write speed performance, it allows 50-88% of the storage space for use. These RAID configurations can be used to store extensive databases, backups, archives, and application servers. They offer high availability and survive up to one disk's failure in every sub-array.
So, what's your take? Which RAID level are you going to choose?
We've listed all the essential things that should be in your checkbook while deciding on choosing the level for your RAID system. Every RAID configuration has its pros and cons. You can check out all the features, including Capacity, Cost, Application Performance, with the pros and cons of the RAID system. Once you have evaluated your storage and usage needs, you can choose any of them.













 5 min read
5 min read