It won’t be an overstatement if we say that in today’s digital era, data is the real treasure. Organizations and users strive hard to protect and retain their valuable data. However, just like any other thing of value, data too needs space to be stored. In other words, you need digital real estate to store, access, and share your data.
What is Data Storage?
The storage space in terms of RAM, ROM and internal storage, is sometimes not sufficient to deal with the daily inflow of voluminous data. Moreover, if the internal storage is occupied in excess, it may cause slowdown of PC and lead to other problems due to lack of memory. In case of data loss and absence of a backup on data storage system, you might not be able to get back your data without a data recovery software. The only solution to counter all these drawbacks is getting a data storage option.
Data storage essentially refers to saving files, folders or other data digitally on a storage medium or system, in a ready to access format for future applications. The storage system can be based on electromagnetic, optical or other medium depending on its type. The most prominent methods of storing data include physical storage devices like tape drives, hard disk drives, solid state drives, USB, CD/DVD and virtual storage medium like cloud. The data is stored exactly in the same manner as it is on the internal storage of your computer.
Methods of Data Storage
Any data storage device uses the methods depicted in the image below. Most of the modern data storage devices are categorized into these four categories. Although you might find some minor methods but they form the sub-category of these major methods. Let us learn what the features of these data storage methods are.
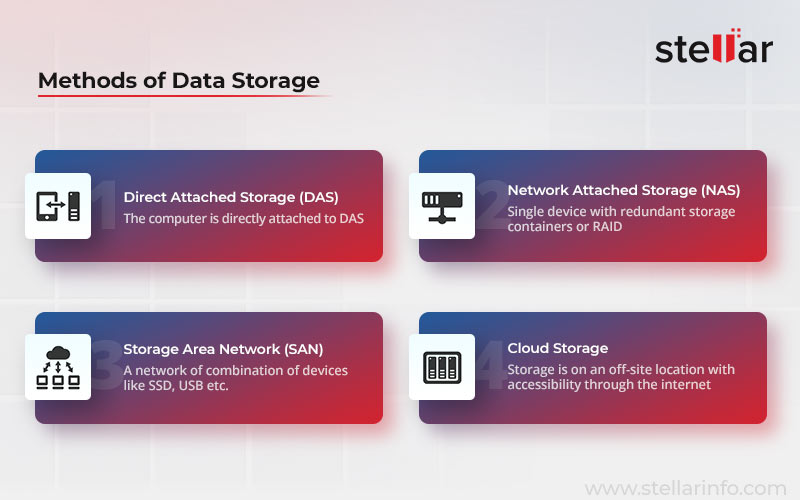
Direct Area or Direct Attached Storage (DAS)
As the name suggests, the direct-attached storage system is the one that is attached to your computer and stores any data you transfer from your system to this storage device. Mostly, the system is attached to a DAS device and it provides the backup facility for the PC. Such devices remain in close vicinity of the owner machine with limited sharing access for other systems or devices. The data storage devices under this category include:
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
- SSD (Solid State Drive)
- USB Flash Drives
- CD/DVD
- Floppy Disk
- Tape Drive and more
Network Based Storage (NBS)
As NBS is a network-based storage system, multiple systems can access it at the same time. If you need better data sharing option or if you want to collaborate with others, NBS is the best method to opt for. There are two common NBS setups viz. Network Attached Storage (NAS) and Storage Area Network (SAN).
NAS is a single device comprising a Redundant Storage Containers or RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) and is based on file storage system. On the contrary, SAN could be a network of a combination of devices like SSD, USB flash storage, hybrid storage, cloud storage and more. Furthermore, it is based on block storage system. Some other differences between NAS and SAN are:
- While NAS uses TCP/IP Ethernet network, SAN works with Fiber Channel Network.
- NAS is confined to limited number of users while SAN can be used by multiple users simultaneously.
- SAN is much faster in performance as compared to NAS.
- NAS has limited expansion options while there is no such limitation on SAN setup.
- NAS has lower setup cost due to ease of setup. SAN uses complex setup and hence has a high setup cost.
Cloud-Based Storage
Cloud-based storage is a magnified form of NBS as it uses the internet instead of local area network to provide accessibility on a larger scale. It has been explained in detail in the later part of this blog.
Types of Data Storage Devices
The data storage devices have evolved quite a lot with the passage of time and demand of users. Today terabytes of data can be stored on pocket-sized SSD and the journey of compact storage devices has just begun. Here are some major types of popular data storage devices:
1. SSD and Flash Drive
The major problem with the HDD is that it has a lots of moving components and was prone to mechanical wear and tear. This issue is addressed in SSD and flash drive. There are no moving parts and data transfer speed is superior than the conventional HDDs. Flash storage uses flash memory chips to store data. Similarly, SSDs store data using flash memory. It facilitates a swift and fast data transfer between devices. The SSD and flash drives are less prone to data loss due to physical damage due to absence of moving parts.
2. Hybrid Storage
As explained above, all-flash or all-SSD storage is a quite expensive affair. To minimize the cost on storage system, organizations adopt a mixture of flash drive and conventional hard disk drives. It combines the speed of flash with storage capacity of HDD. It allows the organizations to swiftly switch from the traditional HDD storage to a high speed storage without using an all-flash or all-SSD system.
3. Cloud Storage
An on-premise storage system restricts the collaborative capabilities of a user as well as an organization. This limitation has been overcome by the advent of Cloud-based storage systems. Not only is your data secure, but also easily accessible if it’s stored on cloud storage. A cloud storage is an off-site storage system and the service provider is responsible to host, secure, and maintain the concerned servers. The host or service provider further ensures an easy access to data wherever and whenever you demand.
4. Hybrid Cloud Storage
It combines the private and public cloud storage services for storage of data. The selection of cloud system is based on the sensitivity and importance of data to be stored. If a data is related to legal compliance or organization’s sensitive information, it is stored on a private cloud storage. However, if the data is harmless to the user’s privacy and security, it can be uploaded to a public cloud. This helps in saving the cost of purchasing unnecessary cloud storage space.
5. Backup Software and devices
The backup of data is particularly useful to counter the situations of fraud, disaster or cyberattack. The Windows 11 and 10 have a dedicated application File History while Mac systems have Time Machine.Both the applications backup and store a copy of the data on your system to a secondary storage device like external HDD, SSD, Tape Drives, etc. However, the backup storage is provided as a service known as BaaS (Backup as a Service), which is a low cost alternative with remote storage location and easy accessibility.
What to do if the Data Storage Device malfunctions?
If you’re using a physical data storage device and suddenly it starts malfunctioning due to corruption or if the data gets accidentally deleted, you can still get it back. To recover data from a Windows storage device, you need to get your hands on a reliable data recovery software. One such solution is the Stellar Data Recovery Free Edition for Windows. The DIY software can easily recover up to 1 GB data free of cost from any storage device.
The Stellar Data Recovery is capable to retrieve almost any file type from HDD, SSD, USB flash drive, etc. Moreover, it allows you to preview the data before recovery. Moreover, if you want to recover data from an external hard drive that isn’t detected on a Windows PC, the Stellar Data Recovery Free for Windows comes in handy.
Note: Stellar Data Recovery Free Edition for Windows software is fully compatible with Windows 11, 10, 8 and 7 OS.
Which Data Storage Method is best for you?
The answer to this question depends solely on your requirements and affordability. Based on your needs, you can choose from the methods and devices explained above. However, it is always better to choose the cloud or hybrid cloud storage as these relieve you of the worries of security, maintenance, management and storage of valuable data at a minimal cost. Furthermore, being an off-site storage system, the cloud and hybrid cloud storage shields your data from any on-site mishap.















 3 min read
3 min read





