Although RAID drives are popular for offering high storage capacity, fault tolerance, and redundancy, they are still not entirely immune to data loss scenarios, such as multiple drive failure, controller failure/malfunctioning, human errors, or software corruption. All these scenarios lead to RAID failure and permanent data loss. Hence, you must implement a data backup strategy to protect critical data stored on a RAID system. This article discusses the best options to back up RAID levels and provides tips to prevent data loss from RAID. Let's begin!
Best Ways to Back Up RAID Drive
Below are the most recommended methods for RAID backup. You can create backup copies of your RAID drive in any way, be it cloud, local, or server backup. Create at least three copies of your RAID backup to ensure multi-level protection against data loss.
#1 RAID Backup on Synology NAS

Synology NAS provides two primary backup and data protection solutions: Snapshot Replication and Hyper Backup. These solutions let you create RAID data backups to protect your data from hardware failure, software corruption, ransomware attacks, or even simple data deletion scenarios. Backup your RAID data using the following steps:
- Log into your Synology NAS and go to Control Panel.
- There, select Backup & Replication.
- Next, click Backup Task.
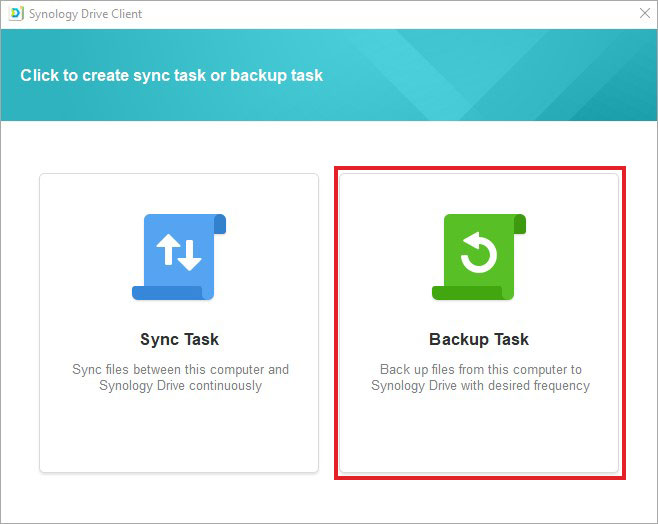
- Now, select the backup source (RAID array) to backup and choose a desired location for storing the backup. The destination for backup storage could be an external drive connected to the NAS, another Synology NAS, or a cloud storage service.
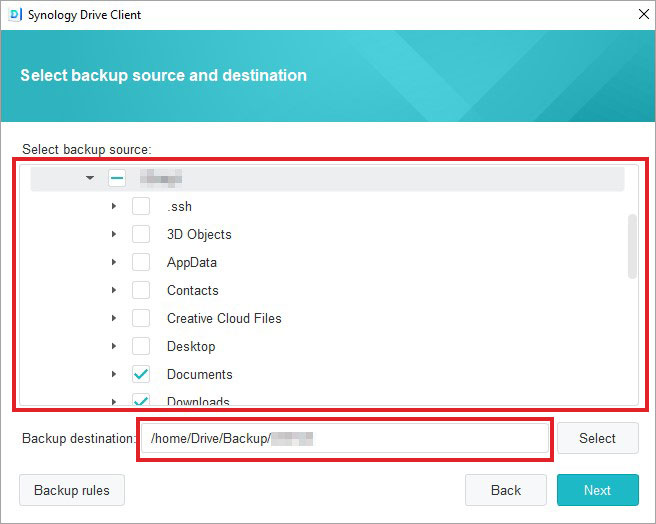
- Now, move to the Backup Mode tab and configure the backup settings, including Manual Backup, Schedule Backup, frequency, end time, and more.
- After that, continue with uncompleted backup tasks (if any).
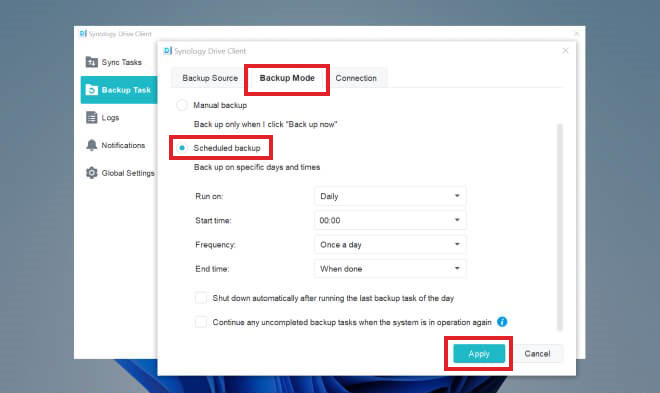
- Apply all the changes, and you will be able to successfully create backup tasks for RAID backup.
- If you select Manual backup in Backup Mode, click Backup in the backup task list to restore your RAID drive data.
#2 Backup your RAID on DAS (Direct- Attached Storage)
.jpg)
Direct-attached storage, or DAS, is a storage system directly connected to a server or workstation without going through a network. The DAS (enclosing HDD, SSD, RAID, or optical storage media) is used for local storage purposes and is typically connected through a cable or connection type, such as SAS, SATA, or USB.
You can set up DAS easily to store and back up local or offline data. DAS also provides higher performance for a large amount of data when connected to a database server, reducing latency and improving data accessibility. So, if you want to take a local or offline backup of your RAID drive, DAS is a good option. To backup RAID on DAS, follow the given steps:
- Identify your RAID configuration
Determine your RAID configuration and level to understand how the data is distributed and how to back it up effectively. Once noted, connect the RAID to your system.
- Connect DAS to the system
Once you have noted the configuration, connect the external DAS (HDD, SSD, RAID, or optical media) to your system through a hot bus adapter. The DAS should have enough storage space to hold the backup.
- Use backup software
Use Windows Backup, File History, or third-party backup tools, such as Veeam Backup & Replication, Acronis Cyber Backup, etc. to back up your RAID data on DAS. You can back up the entire RAID volume or some important files and folders.
- Choose DAS as a backup destination
Initiate the backup process and choose DAS as your preferred location to back up your RAID drive. Just copy and paste the selected files into DAS. Once you’ve created the backup, confirm that all the selected files/data are backed up.
#3 RAID Backup on the Cloud
Cloud Platforms are also a good option for backing up RAID data. They provide an additional protection layer in case of hardware failure or another disaster that possibly affects the RAID drives. A cloud storage service helps you automatically back up your RAID data and restore data quickly to fight against inevitable data loss. There are several popular cloud platforms to back up RAID data, including:
Google Cloud Platform:
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers two storage solutions, Google Cloud Backup and Google Cloud Storage for backing up & archiving RAID data.
- Google Cloud Storage offers several benefits, including unlimited storage & access, no minimum object size, low latency, high durability (99.999999999% annual durability), and a uniform experience with Cloud Storage features, security, tools, and APIs.
- Google Cloud Backup allows you to protect your workloads and a large amount of data to back up RAID and ensure disaster recovery. It also allows incremental-forever backups, which helps in instant recovery and reducing space needed for storing backups.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) –
Amazon Web Services features Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS), which offers high-performing, scalable block storage resources that can be used with Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) instances. With this feature, you can create Amazon EBS volumes categorized as (I) SSD-backed storage for transactional workloads and (II) HDD-backed storage for throughput-intensive workloads. Attach these EBS volumes to an EC2 instance and use them as a local hard drive connected to your system to take RAID backups easily.
Read more. How do you create snapshots of volume in the RAID array?
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure also offers different cloud backup and recovery utilities, such as Azure Disk Backup, Blob Backup, File Share Backup, and VM Backup. All these utilities possess their own benefits and features that allow you to back up your RAID and virtual machines. These cloud backup solutions protect your RAID data on managed and unmanaged disks to ensure data protection in disaster recovery.
Read More:
Azure Blob backup using PowerShell
#4 Backup RAID Array on Tape
Tape drives are a great long-term solution for greater data storage and backup. To back up your RAID, you need compatible LTO tape drives and backup software. Some popular backup software are Symantec Backup Exec, Veeam Backup & Replication, and Acronis Backup. Tape drives allow the creation of several RAID backups on physical tape, and between each tape file is a 'tape file mark.'
However, backing up RAID data on Tape drives can be complex. However, you can complete the backup process by following general steps.
- Connect the LTO tape drive to your system and
- Install and configure the backup software that supports RAID and LTO tape drives per the vendor's instructions.
- Choose the RAID volumes or directories to back up and choose the LTO Tape drives as a backup destination.
- Configure any additional backup option, including encryption, compression, scheduling, etc.
- Next, insert a fresh or reusable LTO tape into the tape drive and start the backup process using backup software.
- Depending on the size of your RAID data and tape capacity, you may need multiple tapes for complete backup.
- Monitor the backup progress to ensure all data from RAID is copied on LTO tape drives.
|
Note: Backing up RAID arrays on Tape drives can be time-consuming, especially with slower LTO tape drives. Therefore, it is advised to use the latest LTO tape for quick backup and higher storage capacities. |
But what if RAID fails without any backup? How to recover data from a failed RAID?
Backups are always the primary way to recover your data in case of a broken, damaged, or failed RAID. However, if you don't have any backup and lost access to your RAID data for any logical reason, don't worry! You can rely on advanced RAID data recovery software like Stellar Data Recovery Technician. The software intellectually rebuilds the broken or damaged RAID sets even without parameters, block size, parity rotation, order, etc. The RAID is rebuilt virtually and helps you recover all the lost data in case of corruption, human error, controller malfunction, etc.
How to prevent data loss from RAID drives?
Even though backup helps you quickly bounce back from a RAID data loss situation, some practices must be followed to prevent such unexpected data loss altogether from RAID.
- Monitor your RAID system regularly to ensure that everything is functioning correctly. Run diagnostics to check and identify any potential issues with the drives in the RAID enclosure to prevent further damage.
- Replace the damaged or failed drives promptly to prevent data loss and continue operations.
- Prevent the RAID system from overheating, as overheating can also cause hardware failure in the RAID array, leading to severe data loss.
- Keep RAID data recovery software handy to take prompt action for data retrieval in the event of RAID failure, controller malfunctioning, software corruption, and more.
Conclusion:
People often may consider RAID as a substitute for backup, but like other storage drives, RAID is also prone to failures and errors. Therefore, it is essential to back up the RAID array. Follow all the backup methods discussed in this article to prevent your data loss from unexpected or impending drive failures or other logical issues. In the event of data loss when no backup is available, Stellar Data Recovery Technician software can help you restore RAID backup from inaccessible, broken, damaged or failed RAID 0, 5, 6, and Hybrid RAID drives.













 5 min read
5 min read