In this age of high speed computing, SSDs have become a staple for consumers and enterprise needs alike. SSDs are new-age storage media that provide reliability and higher performance as compared to traditional platter-based Hard Disk drives or HDDs.
While the SSDs provide exceptional performance, they tend to have shorter life spans (SSD endurance is measured in TBW or Total Bytes Written). Not just that, due to their compact size and lack of mechanical parts, SSDs are prone to data loss in various scenarios like power outage, improper SSD removal, and more. Unexpected power outages or power cuts not only lead to data loss but could also render the drive unusable.
To minimize the chances of data loss and device malfunction in case of unexpected power loss or outage, manufacturers add a layer of Power Loss Protection or PLP mechanisms to ensure data safety and device’s integrity. Both, consumer and enterprise grade SSDs come with baked-in PLP mechanisms to function as a safety measure for safeguarding data and device’s health.
Power Loss Protection – A Closer Look at SSD Resiliency
Data loss in a storage device due to an unexpected power outage is nothing new. Same is the case with the SSDs. Consumer SSDs, especially the NVMe SSDs are compact designed for mobility. Power loss protection or PLP mechanisms are countermeasures added by the manufactures into their SSDs to provide an additional layer of security for keeping the data secure and the device’s integrity intact.
Early consumer SSDs were not equipped with any kind of PLP and thus were quite susceptible to data loss due to unexpected power outages or cuts. Newer ones have firmware-based PLP mechanisms that provide data protection during power outage.
All PLP mechanisms require technical support from the drive controller and firmware for detecting power losses and commencing data flush process. They work in tandem with capacitors present on the PCBA for providing backup power supply to the drive for safely transferring data from DRAM to NAND flash storage.
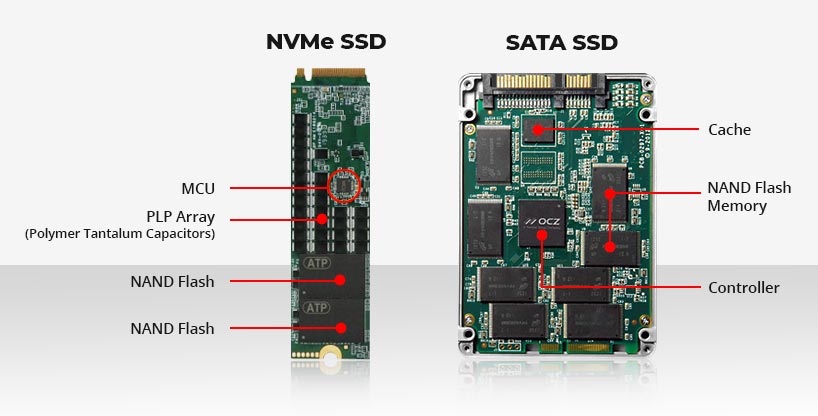
Consumer SSDs come with basic surface-based standard ceramic capacitors that work on additional code embedded into the SSDs firmware. This mechanism provides a very short duration (approx. 1ms) of backup power to the DRAM to flush the data into the NAND flash.
Enterprise SSDs, on the other hand, are used in medium and large scale organizations, military and other important places and hence they are embedded with tantalum capacitors, a.k.a. super capacitors that are efficient and can work at high temperatures. These capacitors ensure device’s integrity and safeguard data during an unexpected power loss.
Unexpected power outages are one of the biggest reasons for severe data loss and device corruption. Though regular backups ensure data recovery in case of data loss. They too fail at times like these. Power outages could lead to severe data loss causing massive downtimes, ultimately impacting businesses and consumers, altogether.
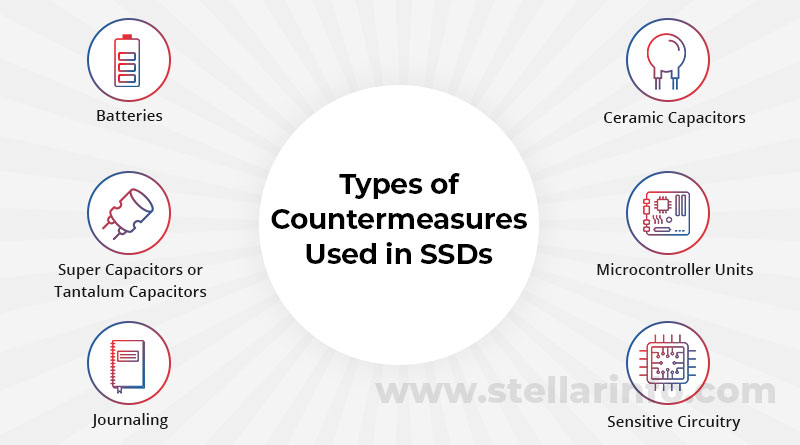
Types of Countermeasures Used in SSDs
SSD manufacturers use various types of power loss protection mechanisms or countermeasures like –
- Batteries
- Ceramic capacitors
- Super capacitors or tantalum capacitors
- Microcontroller units
- Journaling
- Sensitive circuitry
During shutdown or an expected power outage, battery or capacitors used in the SSDs provide additional power backup for a very short period of time for flushing the data from volatile DRAM to non-volatile NAND flash.
Microcontroller Unit (MCU) is a chip-based PLP mechanism that monitors fluctuations in input power and informs the drive controller to start flushing the data if it detects any loss in power. MCU works with the power capacitors to provide additional power to the drive for transferring the data from DRAM onto the NAND flash.
While the consumer SSDs are designed to be economical and thus are offered with firmware-based PLP mechanism, enterprise SSDs are designed for longevity and to maximize data security. Hence, they come with durable tantalum capacitors to provide backup power in case of sudden power loss.
How PLP Works?
A PLP countermeasure works during both normal shutdown and unexpected power loss scenarios. Basically, when the drive controller detects a drop in the input power below the threshold, it informs the host to stop sending the data and start flushing the data in-flight and the data present in the DRAM quickly to the NAND flash.
DRAM is volatile in nature and requires an external source of power to transfer the data stored into it to the NAND flash. This is where power capacitors come into the picture. They provide additional power supply to the DRAM to transfer the data and fill the mapping tables.
Doing so ensures that the data is safely stored onto the non-volatile NAND flash storage and all the mapping tables are filled with address pointing out to the stored data location.
How Sudden Power Outage Affects an SSD?
Now that we know how PLP works, let’s look at how an SSD works in different two situations – normal shutdown and unexpected power loss.
During normal shutdown, the computer informs the drive host about system shutdown. The host, then alerts the SSD about it by sending the Standby Immediate Command to prepare for data transfer and safe removal. SSD prepares for the same and starts flushing the data from the volatile DRAM to the non-volatile NAND flash storage. It also updates all the mapping tables during this process. Once done, the drive signals the host that it is ready for power removal.
This process ensures that the data present inside the DRAM along with the data in-flight has safely transitioned onto the NAND flash. It also makes sure that all the mapping tables are updated as they play a vital role in locating the data on the drive. They keep a track of logical block addresses in relation to physical flash pages and point the drive to the exact location of where the data is stored.
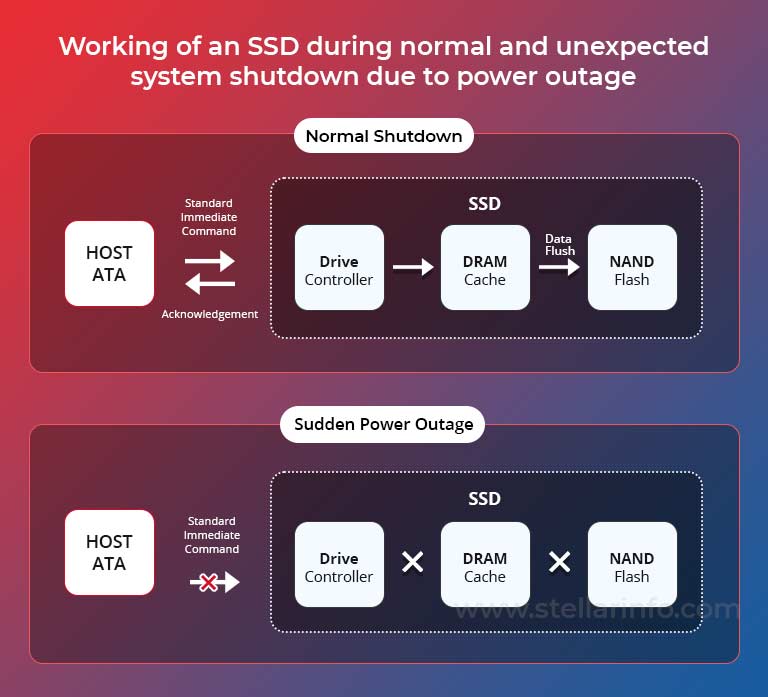
In the case of unsafe shutdown due to unexpected power outage, the host doesn’t get much time to relay the power loss message to the SSD. This prevents the data in-flight and in the DRAM from being moved onto the NAND flash. This failure in data transition causes data loss or severe corruption and in extreme cases, renders the storage device unusable.
Because SSDs are compact, they lack mechanical components and thus increases their chances of data loss in such scenarios. That is why countermeasures as discussed earlier are used to safeguard the data and also the health of the drive.
Pay Heed to Warning Signs That an SSD is Failing
While there are manufacturer-included PLP countermeasures to keep the data secured during a power outage, one should also keep a tab on the health of various storage devices in use. Let’s look at some warning signs that shows if an SSD is going bad, and prevent data loss from happening.
- Fails to save, move, or read files
- PC crashes on boot up
- S.M.A.R.T. errors
Recover Your Lost Data, in Just a Few Clicks
Power Loss Protection mechanisms provide an additional layer of security and safeguards the data present in them in cases like unexpected power outages. However, in certain extreme conditions, the extent of data loss is severe that requires a professional data care tool’s help. Stellar Data Recovery Professional is a professional data recovery software that can help recover data in such scenarios.
Stellar Data Recovery Professional is a robust and intuitive software that brings advanced data recovery algorithms and a clean UI on the table. This software also comes baked-in with a Drive Monitor tool, which monitors various metrics like health, temperature, etc. of a storage drive and graphically displays them. Any user can easily use it to recover their precious data from any storage media like HDD, SSD, NVMe SSDs etc., which got lost due to reasons like a sudden power cut.
This software has an easy-to-navigate UI and makes data recovery a breeze. Follow these simple steps to recover data lost from your SSD due to a power outage –
- Download and install Stellar Data Recovery Professional from its official website.
- Launch it. Once you are in, select the type of data you wish to recover.
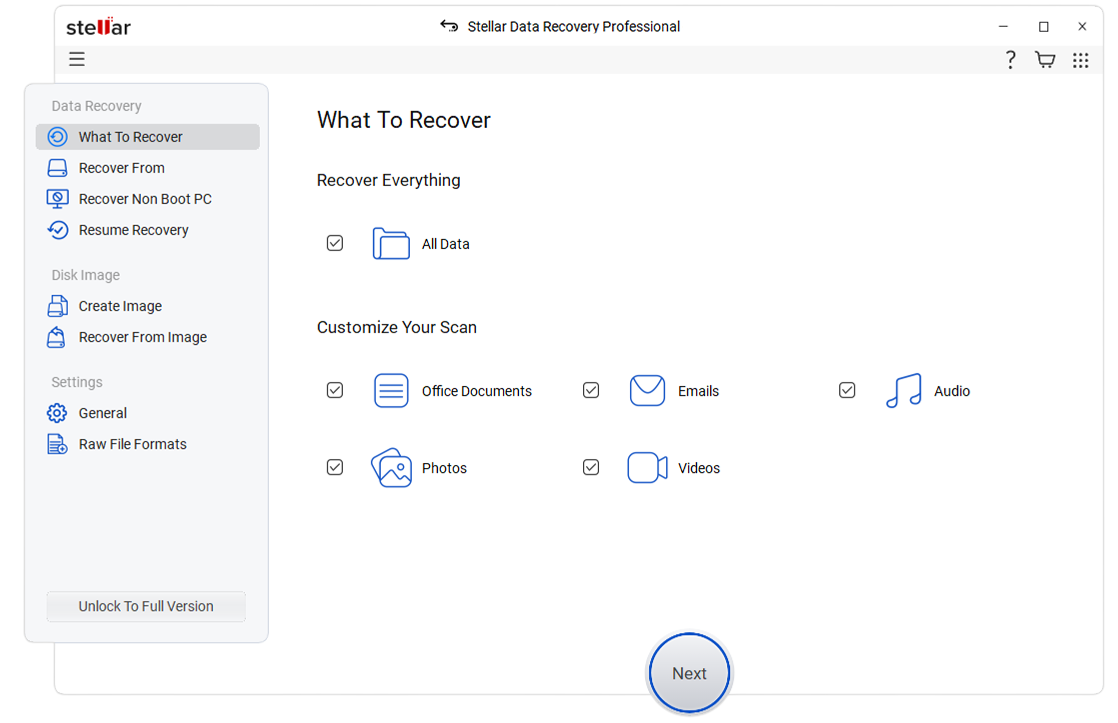
- Select the storage media from where you wish to recover and click on Scan.
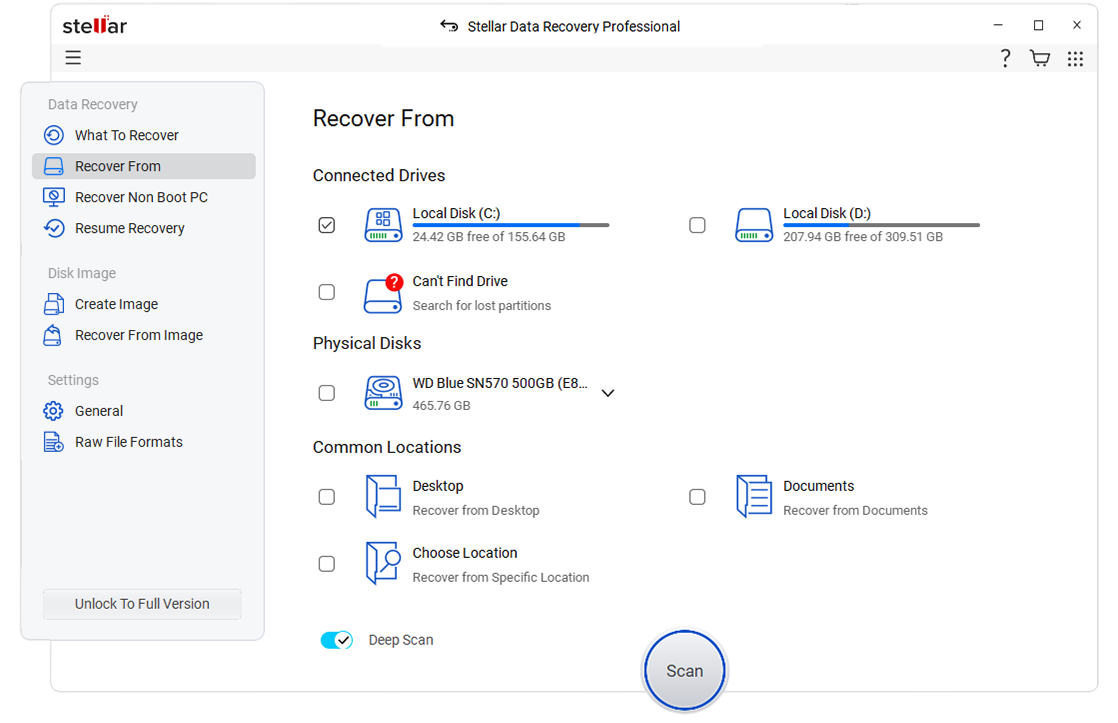
- Once the scanning is complete, you can preview the recovered files by clicking on the Preview
- If you are satisfied with the results, click Recover and recover the files onto your desired external drive.
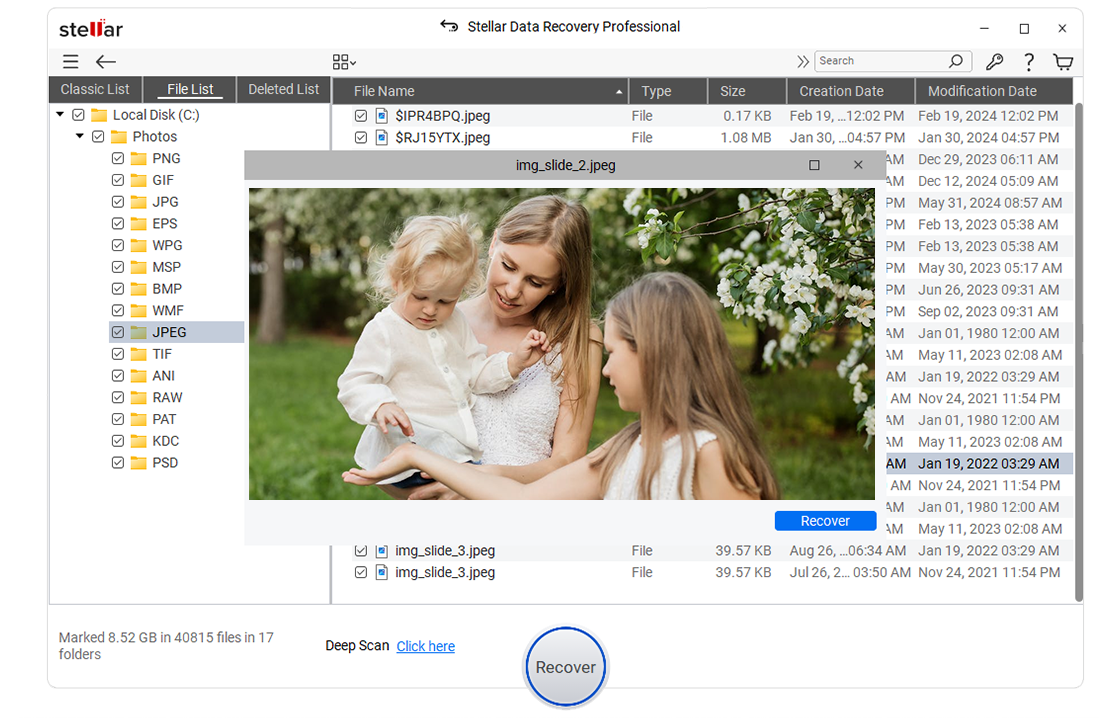
Note – If you cannot see the required files after the scan, you can perform a deep scan of the drive. During the deep scan, the software searches various drive sectors to find the missing files.
Final Words
Power outages are unexpected and annoying that affects not just our work but also the data stored on our SSDs and other storage devices. In this article, we learned about Power Loss Protection mechanisms, how they work and their requirement in general.
We also discussed about various countermeasures incorporated by manufacturers to deal with sudden power cuts that lead to data loss, and in some cases, corrupted storage drive. In the end, we also discussed about a professional tool that could help us recover our lost data from an SSD in case of various data loss scenarios. We hope you found this article insightful and learned ways to avoid data loss in case of a sudden power cut.















 3 min read
3 min read




